Diffuse toxic goiter is an auto-aggressive disease characterized by an increased production of thyroid hormonal substances and an increase in the size of the gland as a result of rapid cell multiplication. In another way, this ailment is called hyperthyroidism, or the disease of bazedova, Graves, Perry, Flayani. Most often, this pathology is diagnosed in a female.
Etiology and pathogenesis
In the development of hyperthyroidism, a genetic predisposition plays a major role. Often the disease is transmitted through a generation. The following factors provoke the occurrence of pathology:
- stressful situations;
- chronic viral infections;
- frequent sore throats;
- other diseases of the endocrine system - hypoparathyroidism, Addison's disease, diabetes mellitus.
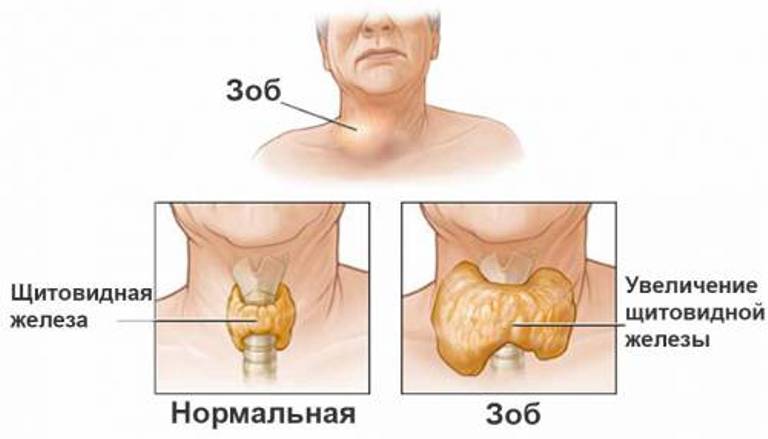
Heredity is confirmed by the fact that half of the relatives of the patient have antithyroid antibodies in their blood, and 15% have this pathology identified and confirmed. It is important that the disease itself is not genetically transmitted, but only a predisposition to it. Thus, the leading role in the pathogenesis of diffuse toxic goiter is assigned to a genetic predisposition, as well as to provoking factors, due to which the information inherent in the genes is developed. Due to the malfunctioning of the immune system, a mutation occurs in T-lymphocytes, and they, acting on the gland tissue, perceive its antigens as foreign. In addition, T-killers are able to independently damage the organ, having a toxic effect on the thyroid gland. T-lymphocytes are able to exert an indirect effect on glandular tissue through B-cells, which synthesize antithyroid antibodies. The latter stimulate the body as a result of the binding of thyroid stimulating hormone receptors to thyrocytes, i.e., thyroid cells. With the development of diffuse toxic goiter, the function of the central regulators of the immune response (T-lymphocytes) is impaired.
Various classifications
The doctor determines the size of the thyroid gland using palpation and a visual examination of the patient. According to the WHO classification since 1994, the following degrees are distinguished:
- 0 - goiter is not visible visually, and it is impossible to palpate;
- 1 - the goiter is palpated, but visually, when the neck is in its natural position, it is not visible;
- 2 - visually and palpation goiter can be easily detected.
According to another classification (according to Nikolaev), such degrees of diffuse toxic goiter are distinguished:
- 0 - iron is not palpable and not determined;
- I - on palpation, the isthmus of the thyroid gland can be determined, it is visually visible;
- II - the lateral lobes can be detected by palpation, while swallowing it is visually easy to see the goiter;
- III - a thick neck is visually visible;
- IV - the gland is enlarged, as a result of which a deformation of the shape of the neck is noticeable;
- V - thyroid gland reaches a particularly large size.
In addition, according to the severity of the disease, several degrees can be distinguished:
- Easy. Signs of pathology are manifested by increased nervous excitability, distraction, insomnia, and tearfulness. Quite often there is a low working capacity. First of all, the cardiovascular system suffers. The number of heart contractions per minute increases to one hundred. The individual begins to lose weight.
- Medium. Symptoms of diffuse toxic goiter, described with a mild degree, are aggravated. Tremor joins existing disorders. Weight loss continues, despite excellent appetite. The individual experiences severe sweating, weakness. The stool is broken, pain in the abdomen appears, which does not have a clear localization.
- Heavy. The operation of vital systems and organs is failing. Psychoses are possible. The patient has complete depletion of the body.
Another classification is known, according to which the course of the disease is distinguished:
- Subclinical - the symptoms are erased, the diagnosis is made on the basis of the results of a blood test for hormonal substances.
- The manifest - has a pronounced clinic. Thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood is not determined, the concentration of thyroid hormonal substances is overestimated.
- Complicated - mental disorders are added. The work of the cardiovascular and other important systems is impaired. An individual is diagnosed with critical body mass deficiency.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
Laboratory and instrumental methods are used to diagnose diffuse toxic goiter. A blood test to determine free T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), as well as TSH (thyrotropin) is the main test. A high concentration of the first two hormones and a low indicator of the latter are characteristic of this pathology. In addition, tests for antibodies to thyroglobulin and thyroid peroxidase are prescribed. As additional research methods carry out:
- Scintigraphy, or radioisotope examination of the thyroid gland, in which the functions and its structure are studied.
- Ultrasound, with the help of which information about the structure of the organ is obtained.
- MRI is prescribed for the diagnosis of ophthalmopathy, which is present in this disease.
In addition, when diagnosing diffuse toxic goiter (ICD-10 assigns it code E05.0), the functions of the kidneys, liver and other organs necessary to prescribe adequate therapy are determined.
Causes and signs of the disease
Hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, lactation, menstruation or menopause contributes to the development of the disease. Among the main reasons provocateurs are:
- head injuries;
- mental disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- bad ecology;
- autoimmune response of the body;
- unfavorable habitat;
- infections of a viral nature.
The main cause of diffuse toxic goiter is considered to be a malfunction of the immune system. Symptoms of a pathology or a classic clinical picture are eyeballs, goiter and palpitations. From the side of organs and systems that are important for normal functioning, the signs of pathology are manifested:
- accelerated metabolism;
- intolerance to hot weather;
- excellent appetite, but there is a sharp weight loss;
- diarrhea
- malaise;
- tremor of the body and limbs;
- fatigue;
- general weakness;
- insomnia;
- swelling of the body;
- arrhythmia;
- heart failure;
- tachycardia;
- an increase in the abdomen;
- hyperactivity of motor reflexes;
- fever;
- candidiasis in the oral cavity;
- excessive sweating;
- brittle nails.
The male has erectile dysfunction, breast enlargement. Symptoms of diffuse toxic goiter in a female are infertility, menstrual cycle failure and severe pain in the lower abdomen, fibrocystic mastopathy. From the side of the organs of vision, there is an increase in intraocular pressure, conjunctivitis, a feeling of sand in the eyes, incomplete closure of the eyelids, a rare blink, the lag of the lower eyelid from the eyeball.
Complications and their treatment
Excessive production of hormonal substances by the thyroid gland has a negative effect on all organs and systems of the individual's body. The complications of diffuse toxic goiter include:
- Thyrotoxic crisis is a particularly serious consequence of the disease, representing a real threat to life. Fortunately, today this ailment is rare due to the latest methods of examination and treatment of patients. The development of the crisis has not been fully studied, but there are several hypotheses. According to one of them, it arises due to an increase in free triiodothyronine and thyroxine. On the other - due to the increased sensitivity of the body to adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine. The provocateur of the disease is stress or an infectious process. Symptoms characteristic of thyrotoxicosis increase. The crisis develops suddenly. The individual takes a forced position, the so-called frog pose, speech is disturbed, the dermis becomes wet and hot to the touch, the heart rate increases per minute to 130 beats. Urgent therapeutic manipulations include detoxification of the body, the introduction of beta-blockers, hormones, thyreostatics. In order to reduce psychomotor agitation, drugs of the barbiturate group and opioid analgesics are used. Urgent measures should be aimed at compensating for acute insufficiency of the adrenal cortex, neutralizing thyroid hormonal substances, reducing the activity of the sympathoadrenal system, eliminating metabolic disorders.
- Endocrine ophthalmopathy. The cause of this complication with the thyroid gland is relatively related, and it lies in an autoimmune attack on the eye tissues and muscles that are behind the eyeballs. Thus, the source of the lesion is the same, as with the occurrence of diffuse toxic goiter. At the same time, the eyes protrude strongly, they are also called bulging. The clinical picture is developing in stages. Initially, changes affect only one eye, with further progression, the other is affected. After a while, exophthalmos occurs. With severe damage, the optic nerve suffers, which is a direct threat to vision. Combined therapy is indicated. With untimely or incorrect treatment, the pathological process becomes irreversible.
- Pretibial myxedema. This complication is rare. It manifests itself as itching, redness, swelling and thickening of the dermis on the anterior surface of the lower leg. As a therapy, hormonal agents for topical administration are prescribed.

In addition, the progression of hyperthyroidism can lead to the following consequences:
- atrial fibrillation;
- pulmonary edema;
- psychosis
- heart failure;
- osteoporosis;
- toxic hepatosis;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- myopathy
- diabetes mellitus;
- clotting disorder.
Alternative medicine: recipes
Treatment of diffuse toxic goiter with folk remedies is recommended at the first stage of the disease. The recipes below complement the mainstream traditional therapy:
- Ripe black chokeberry berries are mixed with honey or sugar in a ratio of 1: 1, insist in a cold place for seven days. Take 40 grams daily on an empty stomach, which is equivalent to two tablespoons without a slide.
- A compress of sea salt is applied to the thyroid gland for 55 days, of which 27 times the procedure is done daily, then every other day.
- Young leaves of willow fill a three-liter pot, add water, put on fire and evaporate to obtain a jelly-like precipitate. The resulting mixture is lubricated with goiter for four months before bedtime.
- Every night, an iodine grid is applied to the goiter. If traces of iodine are visible in the morning, the procedure is stopped.
- A tincture is prepared from the walnut partitions, which should be drunk two hours before waking up, 15 ml for a month, then a break for 30 days. If necessary, continue the course.
Diffuse toxic goiter: clinical recommendations
This is a special document that is issued at regular intervals and is designed for practicing doctors. Clinical recommendations contain the latest information proven in practice on the following issues:
- diagnostics;
- treatment;
- rehabilitation;
- prevention.
This document defines the algorithm of action in the management of the patient. The doctor is given the right to choose the methods of diagnosis and treatment, depending on the individual characteristics of the individual, his gender, age, and also the course of the pathology. Currently, in practical medicine, the methods of therapy described in clinical guidelines are used. It is recommended to treat diffuse toxic goiter with three methods:
- conservative;
- surgical;
- radioactive iodine.
For each species, the level of evidence is given and comments are presented, which set out detailed treatment regimens and the necessary examinations. In addition, side effects and complications that occur during therapy are described. A special section is highlighted in the document, in which the requirements that are mandatory for the doctor are indicated, their implementation affects the outcome of the disease, in particular diffuse toxic goiter.
Conservative treatment
It is aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the disease. The use of tablet dosage forms allows to achieve results in a month from the start of treatment. However, after the individual stops taking them, relapses occur. In therapy, several groups of drugs are used:
- Thyrostatics - “Propitsil”, “Merkazolil”. They block the function of the gland, as a result, the synthesis of hormonal substances decreases. Treatment of diffuse toxic goiter with these agents helps to normalize the thyroid gland. Additionally prescribed drug "Eutiroks" to prevent the occurrence of drug hypothyroidism. In order to maintain the functions of the gland, monotherapy is carried out using small doses of thyreostatics.
- Beta-blockers and glucocorticoids are prescribed as symptomatic therapy in the presence of concomitant pathology (tachycardia, hypertension, palpitations, ophthalmopathy, osteoporosis), which accompanies the underlying disease.
Patients receive therapy with drugs for a year and a half.
Surgery
This method is considered highly effective, but it is fraught with various complications. The indication for this type of therapy is:
- moderate and severe form of the disease;
- lack of result from another treatment;
- thyrotoxic adenoma;
- nodal and sternal forms;
- relapses
- goiter compression of the esophagus and trachea;
- childhood;
- first and second trimester of pregnancy;
- the presence of complications in the form of atrial fibrillation.
Contraindication to surgery:
- diffuse toxic goiter complicated by mental illness;
- severe concomitant pathology of the kidneys, lungs and heart.
Before surgery, patients are prescribed the drug "Merkazolil" in order to normalize thyroid hormones, reduce toxic symptoms and prevent exacerbation of thyrotoxicosis after surgery. During the operation, the thyroid gland is removed almost completely. Only the areas where the parathyroid glands are located remain.
The use of radioactive iodine
When treating diffuse toxic goiter with this method, the isotope of radioactive iodine I-131 is introduced into the patient’s body, which affects the gland by gamma and beta rays, damaging its cells. As a result, the synthesis of hormonal substances is reduced. Treatment is carried out in an inpatient setting. During therapy, it is recommended to limit iodine-containing products.
Indications for this treatment:
- elderly age;
- severe side effects or intolerance to conservative therapy;
- patient refusal from surgery;
- the impossibility of surgery;
- development of postoperative thyrotoxicosis.
Contraindication to the use of radioactive iodine is:
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- sternal goiter;
- childhood;
- blood diseases, kidneys.
Can a diffuse toxic goiter be cured?
The prognosis in the absence of treatment is extremely unfavorable. The patient develops serious complications, the disease progresses. With normalization of the thyroid gland, the prognosis is good. In the case of surgical treatment of the disease, there is a high probability of the formation of hypothyroidism, in which the metabolic processes in the individual's body slow down. The reason for this phenomenon lies in the insufficient production of hormonal substances (triiodothyronine and thyroxine). Patients are advised to exclude foods and medicines containing a high concentration of iodine, as well as to minimize the duration of exposure to direct sunlight.
Preventive measures include:
- Maintaining and strengthening the immune system, which involves hardening, regular walking, performing gymnastic exercises.
- Compliance with diet. Include in the diet foods that contain animal and vegetable protein, vegetables and fruits in raw form.
- Exclusion of stress, since it plays a dominant role in the development of pathology. In some cases, the doctor may recommend taking sedatives of plant origin.
- Timely treatment of viral infections.
There is no specific prophylaxis for diffuse toxic goiter. To prevent pathology, a follow-up at the endocrinologist in the clinic at the place of residence is indicated.