Intestinal pathologies are found in many people. A particularly dangerous disease of this organ is malignant degeneration of the epithelium. Colorectal cancer is one of the leading places in the oncological structure of pathologies. This disease often leads to death of patients. Therefore, it is important to timely detect those conditions that precede malignant cell growth. One of these pathologies is tubular adenoma (polyp). Despite the fact that it consists of normal epithelial cells, it can degenerate into a tumor. Therefore, upon detection of intestinal adenoma, a consultation with an oncologist is always required. In most cases, the formation should be removed by surgery.
What is tubular adenoma of the colon?
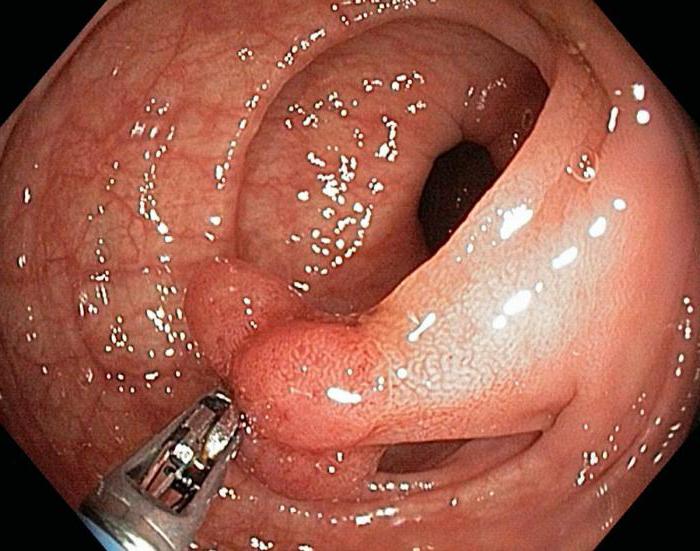
Benign neoplasms of the intestine are common. In rare cases, they bring inconvenience and make themselves felt. More often their presence is determined by chance, during a routine examination or during treatment of other gastrointestinal pathologies. One of these neoplasms is tubular adenoma of the intestine. Outwardly, it is a small growth on the inner surface of the epithelium. If you take a small piece of adenoma tissue (biopsy) and examine it under a microscope, you can see mature intestinal cells. As with all benign neoplasms, the histological structure of this outgrowth completely repeats the structure of the epithelium. Nevertheless, tubular adenoma is a disease against which colorectal cancer often develops . Therefore, it poses a danger to the health of the patient. Another name for this benign neoplasm of the intestine is polypoid adenoma. It occurs in approximately 5% of the population. In this case, the incidence of adenoma does not depend on the age and gender of the person. In some cases, multiple polyps occur. It is believed that in the presence of a single small tubular adenoma, the risk of malignancy is low. Nevertheless, this education is the reason for registration in the cancer clinic for continuous monitoring.
Causes of adenomas in the intestines
Scientists have not yet figured out the exact etiological factor contributing to the development of intestinal adenomas. There are several theories of the occurrence of benign neoplasms. Most doctors believe that a combination of several factors plays a leading role in the occurrence of this disease. Based on this, several causes of the appearance of tubular adenoma are distinguished:
- Genetic predisposition. Heredity in the occurrence of intestinal polyps is of great importance. In some cases, tubular adenomas are detected in several family members.
- The nature of nutrition. It is believed that people who have a large amount of animal fats in their diets are prone to the appearance of both benign tumors and gastrointestinal cancer. In turn, the risk of developing these pathologies decreases with the use of vegetables, herbs, foods rich in fiber.
- Bad habits.
- The impact on the body of various chemical agents, ionizing radiation.
- Stressful situations.
Most often, tubular adenoma occurs in the elderly. Due to the fact that this group of people has an increased risk of developing intestinal cancer, polyps are subject to mandatory removal.
Varieties of tubular adenomas
Tubular adenoma can have a different size. It ranges from a few mm to 2-3 cm. Depending on the microscopic picture, “sitting” polyps and benign formations on the leg are distinguished. Also, tubular adenomas differ in localization. They can be located in the stomach, colon and sigmoid colon. Depending on the number of adenomas, single and multiple polyps are secreted. Of greatest importance for the choice of treatment method and prognosis of the disease is the classification, which is based on the histological structure of neoplasm tissue. Depending on this, 3 types of intestinal polyps are distinguished:
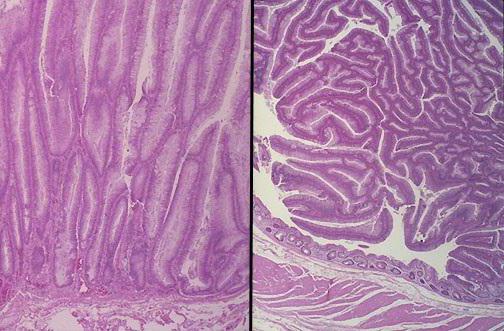
- Tubular benign adenoma. Microscopic examination reveals that polyp cells of this type are elongated or branching tubes surrounded by connective tissue.
- Tubular-villous adenoma - develops under the influence of adverse factors and in the absence of treatment. The occurrence of polyps of this type increases the risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor. Histological examination reveals both tubular cells and areas of fibrosis.
- Villous adenoma. This type of intestinal polyps is an obligate precancerous condition, that is, it always transforms into a malignant tumor. When removing such a formation, the macro similar to seaweed.
It is worth remembering that, despite the "harmlessness" of tubular adenoma, it almost always transforms into a villous polyp. On average, this occurs 4-5 years after its discovery.
The clinical picture with tubular adenoma of the intestine
With small sizes, tubular adenoma does not have any clinical manifestations. This is because the formation does not interfere with the normal functioning of the intestine and the passage of feces. If the polyp reaches several centimeters in diameter (from 2 or more), then its presence can be suspected by clinical symptoms. Among them, such changes as intestinal discomfort, pathological discharge, pain during bowel movements are distinguished. Symptoms of tubular adenoma:
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- The appearance of blood during bowel movements. This is because feces injure the wall of tubular adenoma.
- Pain during the act of defecation.
- Itching in the anus.
It should be remembered that such symptoms may indicate the occurrence of a malignant tumor of the sigmoid or rectum. Therefore, with the development of such a clinical picture, it is urgent to contact a proctologist.
Tubular adenoma of the colon with dysplasia: description
The transition of a benign tumor to cancer begins with a gradual change in the cellular composition of the adenoma - dysplasia. With a tubular polyp, this process is not observed. Often cell rearrangements take place with villous formations. Nevertheless, such a concept as tubular adenoma with dysplasia exists. The emergence of immature cells most often occurs with an increase in the polyp in size. In this case, tubular adenoma is transformed into a tubular-villous formation. Dysplasia does not always indicate a malignant process. It depends on the degree of maturity of the cells of the adenoma. Nevertheless, the appearance of undifferentiated elements, even in a minimal amount, increases the risk of developing a colon cancer.
Degrees of dysplasia in tubular adenomas
There are 3 degrees of dysplasia with tubular adenomas of the intestine. The doctor’s tactics depends on how much the polyp cells are changed. Tubular adenoma with dysplasia of 1-2 degrees has a favorable prognosis for treatment. A high probability of transformation into cancer is observed with pronounced changes in the cellular composition of the polyp. Moderate dysplasia is characterized by a thickening of the basal layer of the intestinal epithelium. The cell nucleus is hypochromic, the number of mitoses is increased. Moderate dysplasia is distinguished by the fact that the basal layer of the epithelium is blurred, pronounced proliferation is observed in the growth zone of cells. In addition, the elements themselves differ in size and shape. A pronounced degree of dysplasia is the terminal stage, followed by atypia. Cells are characterized by hyperchromism and polymorphism. The number of changed elements is from 0.5 to 1% of the epithelial tissue.
Diagnosis of tubular adenomas of the intestine
If tubular adenoma is suspected, endoscopic examinations are performed . These include colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy. The choice of method depends on the localization of the polyp in the intestine. Crucial in diagnosis is given to histological and cytological examination.
Treatment for tubular adenoma
The main treatment option is surgical removal of the polyp. In rare cases, tubular adenoma is simply observed (at small sizes). In this case, the patient must follow a diet and eliminate bad habits. Endoscopic polypectomy is often performed . With severe dysplasia, an operation is performed.
Prevention of tubular adenomas
It is impossible to predict the development of tubular adenoma. Nevertheless, preventive measures include proper nutrition (the predominance of fiber in the diet, a small amount of fat). Also, smoking and alcohol should be excluded with a burdened hereditary history. After 60 years, a diagnostic colonoscopy is recommended.