Infectious diseases are a group of pathological conditions that are highly contagious. Similar diseases cause certain bacteria and viruses. All infections have common characteristics. These include: epidemiology, transmission routes and clinical manifestations. One of the infectious diseases is tick-borne rickettsiosis. There are several varieties of this pathology. All rickettsioses combine such signs as fever, intoxication syndrome, primary cutaneous affect and vascular damage. The main route of transmission of these diseases is vector-borne. That is, through the bites of insects, common in specific climatic conditions.
Description of tick-borne rickettsiosis
Tick-borne rickettsiosis is an infectious pathology characterized by skin manifestations, common vasculitis and intoxication syndrome. The disease is transmissible by transmission. Mites and lice carry the infection . There are several options for the course of rickettsioses. The main difference between these pathologies is the type of pathogen. Some rickettsioses are common in steppe and desert regions, others in tropical climates. Nevertheless, all these pathologies have a similar clinical picture. The disease can be suspected by characteristic symptoms, as well as due to epidemiological characteristics. The main diagnostic method is a serological study, which allows you to accurately determine the type of pathogen.
What are rickettsioses?
As you know, rickettsioses are a large group of diseases. They are distributed around the world. The following species are considered the most common:
- Rickettsia prowazekii - this pathogen causes typhus. This disease is transmitted by a vector-borne route (via lice bites).
- Rickettsia typhi is a causative agent of endemic typhus. It is transmitted by the bites of rodents and fleas.
- Rickettsia sibirica. This pathogen causes the disease of North Asian tick-borne rickettsiosis.
- Rickettsia burneti. With the penetration of this pathogen into the human body, Q fever develops. The disease is transmitted in a transmissible way - through the bites of ixodid ticks.
- Rickettsia orientalis. Like previous varieties of rickettsioses, this pathology is transmitted by tick bites.
In addition to these diseases, there are many more infections caused by various strains of this pathogen.
Epidemiological characteristics of rickettsioses
Rickettsioses differ among themselves not only by the type of pathogen, but also by the epidemiological characteristics. Despite the widespread prevalence throughout the world, each disease is common in a particular area. For example, epidemic typhus is also called prison or ship fever, since this pathology is transmitted through the bites of lice, which were widespread among prisoners and seafarers. A similar disease, but caused by the pathogen Rickettsia typhi, is more often recorded in regions with a warm climate. It is especially common in rural areas in the summer.
Tick-borne rickettsiosis is common in the habitats of these insects. This group of infectious pathologies is found in North Asia, Japan, Australia, and mountainous regions. Most rickettsioses are zoonotic diseases. An intermediate reservoir of infection are wild and domestic animals, rodents. The carriers of rickettsiosis are various types of ticks. Since these insects breed in the summer (May-September), during this period, the incidence increases sharply. Most often, the infection affects people working on the street (cottages, gardens, pastures) and in contact with animals.
The cause of rickettsiosis
The etiological factor in the occurrence of the disease is a microorganism - rickettsia. This infectious agent can be attributed to bacteria or viruses. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that, despite the structure of the microorganism (rods or cocci), rickettsia has the ability to intracellular parasitism. The causative agent is unstable in the environment. Rickettsia die when exposed to high temperatures or disinfectants. Nevertheless, they can remain viable for a long time in a cold and arid climate. In addition to the transmissible transmission route, rickettsia can enter the body during blood transfusion, from the mother during childbirth. For some diseases of this group, other ways of infection are also characteristic. Among them - alimentary and airborne infection. Factors that provoke tick-borne rickettsiosis include:
- Contact with rural pets, dogs.
- Non-observance of personal hygiene.
- Contact with infected people and carriers of pathology.
The mechanism of the development of the disease
The disease develops a few days after the introduction of the tick into the skin. The duration of the incubation period depends on the type of pathogen and the body's immune response. When a tick bites, a local reaction occurs. The skin becomes edematous, hyperemic, pain is noted. Infiltrate occurs due to the accumulation of cells of the immune system at the site of introduction of the insect. From there, the causative agents of the disease - rickettsia - penetrate the lymphatic vessels and nodes. There they temporarily settle and breed. Given that the lymph nodes belong to the organs of the immune system, they noticeably increase. Cells are activated and proliferated to fight bacterial agents. Later, rickettsia enter the blood vessels. Bacteremia and toxinemia occur. The veins and arteries of the skin are primarily affected. An inflammatory reaction develops in the walls of the vessels, leading to destructive changes in the endothelium. In addition, rickettsia often penetrates the arteries and veins of the brain. As a result, signs of central nervous system damage, meningitis and encephalitis, possibly acute circulatory disorders develop. The mechanism of development of infection determines the clinical picture of the pathology of tick-borne rickettsiosis. ICD-10 is an international classification that includes all diseases. This infection is no exception. In addition, complications of pathology such as meningitis, encephalitis, and vascular damage are separately encoded in ICD-10. The main disease has code A77.

Tick-borne rickettsiosis: symptoms of pathology
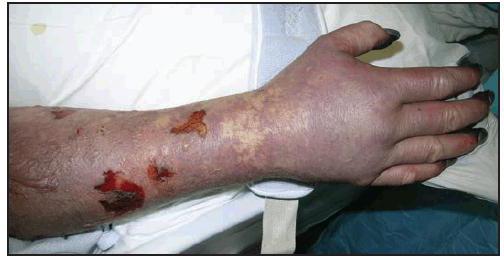
Despite the fact that tick-borne rickettsioses differ, they all have common clinical manifestations. The duration of the incubation period averages from 3 to 7 days. Often the penetration of ticks into the skin goes unnoticed at the onset of the disease. Noticeable infiltration and regional lymphadenitis are sometimes noted. Primary affect is characterized by compaction, in the center of which there is skin necrosis (brown color), and on the periphery - hyperemia (red corolla). After 2-3 days, intoxication syndrome and constant fever join. The patient complains of body aches, fever up to 39 degrees, muscle pain, general weakness. The febrile period is about 1-2 weeks. In addition to symptoms of intoxication, rashes appear at the beginning of the disease. They have a rose-papular character. First, the rash occurs on the limbs, later spreads to the body. The background of the skin does not change. Tick-borne rickettsiosis is characterized by these signs. Photos of skin manifestations can be found in the literature. Distinguishing rashes among themselves is very important for the diagnosis of infectious pathologies.
Tick-borne rickettsiosis detection
You can not rely solely on the clinical picture to detect tick-borne rickettsiosis. Diagnosis of the disease should include laboratory tests. After all, the symptoms of pathology can resemble many other infections. To make an accurate diagnosis indicating the type of pathogen, serological tests are performed . Among them - enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, complement binding reaction, hemagglutination, etc. A microscopy of blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine and detachable infiltrate is also performed.
Tick-borne rickettsiosis: treatment of infection
Since the disease refers to bacterial infections, the use of antibiotics is necessary for treatment. For this purpose, use the drugs "Tetracycline" and "Levomycetin", as well as their analogues. In severe cases of the disease, the patient should be hospitalized in an infectious diseases hospital. For the purpose of detoxification, a solution of 5% glucose with ascorbic acid is administered intravenously. With bradycardia, vasopressor drugs must be used. These include medications Atropine, Caffeine. Symptomatic therapy is also carried out - antipyretic, antihistamines. Mites are removed with tweezers. With the development of complications, specific treatment is performed.
The effects of tick-borne rickettsiosis
It is important to begin treatment of tick-borne rickettsiosis as early as possible. The consequences of infection can be severe. In case of untimely treatment, complications from the nervous, respiratory and cardiovascular systems develop. Among them - pneumonia, bronchitis, meningitis and encephalitis, myocarditis, etc. In severe cases, an infectious-toxic shock develops.
Tick-borne rickettsiosis prevention
Nonspecific prevention includes the control of insects and rodents, as well as the observance of personal hygiene rules. Vaccination is being carried out against typhus and Q fever. If a disease is detected, it is necessary to sanitize the premises, as well as to examine all persons who were in contact with the patient. If the tick has already penetrated the skin, but the symptoms of the infection have not developed, emergency medical prophylaxis is performed. Antibiotics “Doxycycline” and “Azithromycin” are used.