The acute inflammatory process that occurs in the larynx is called stenosing laryngitis. Usually this pathology is observed with acute respiratory viral infections, but it can be a complication of a bacterial infection, as well as with allergies. In children, inflammation causes the lumen of the larynx to close, resulting in difficulty breathing.
Why arises
Most often, stenosing laryngitis occurs when an influenza virus, parainfluenza, rhinovirus or enterovirus enters the body. Less commonly, pathology occurs as a complication of herpes, measles, chickenpox, and some other infectious diseases.
Stenosing laryngitis in each case develops as follows: the mucous membrane becomes edematous, muscle spasm appears. Then, mucus appears in the lumen of the larynx. The body tries to remove it, reflexively increasing the spasm. As a result, hypoxia develops.
The following factors can lead to the development of laryngitis:
- Excessive vocal cord tension.
- Reception of irritating throat foods and drinks.
- Mechanical damage to the throat mucosa.
- Hypothermia.
- Decreased immunity.
- Allergic reaction.
Noisy breathing with laryngitis can be caused by the occurrence of abscesses of the pharyngeal or paratonsillar type. Also, pathology can be caused by diphtheria, epiglottitis, as a result of aspiration by a foreign body, trauma to the
larynx, burns.
In some cases, stenosing laryngitis leads to:
- laryngospasm as a result of hypocalcemia with rickets, hypothyroidism, renal failure;
- congenital stridor;
- allergic edema;
- tonsil hypertrophy;
- papillomatosis;
- cysts;
- hemangiomas of the larynx.
After establishing the cause, the doctor selects a method of treatment. He may prescribe drug therapy or recommend surgical treatment.
Development risk
Due to the structural features of the larynx, children under six years of age most often suffer from stenosis. Up to this age, the children's body is characterized by:
- thin laryngeal membrane;
- submucosal layer is loose, vascular network is strongly developed;
- epiglottis cartilage soft, elongated;
- respiratory muscles are weak.
From the beginning of the development of acute respiratory viral infections, stenosing laryngitis may appear on the second day. Most often, the infection manifests itself at night. In the development of the disease, the presence of allergies and increased sensitivity of the respiratory tract to irritants play an important role.
Clinical manifestations
Stenosing laryngitis in the early stages of development is often mistaken for acute respiratory viral infections. Intense spasms usually occur at night. A feeling of pressure appears in the larynx.
With the development of the disease, a dry, barking cough appears, during which soreness is felt in the sore throat. The nasolabial triangle acquires a bluish tint, the skin turns pale. Shortness of breath appears, the patient begins to breathe deeply, trying to grab at least a little air with his mouth or nose. As a result, the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, and nose begin to dry out. On the larynx they form crusts that block the airways.
In children, stenosing laryngitis quickly passes into suffocation due to the peculiar structure of the larynx: the narrow lumen with inflammation quickly closes, and the child begins to suffocate. To prevent this, it is necessary to be able to quickly identify a dangerous pathology and distinguish it from the flu and other infectious pathologies.
The inflammatory process in the larynx proceeds in several stages, each of which is manifested by certain symptoms.
With inflammation of the larynx, croup syndrome manifests itself. This is a clinical condition characterized by hoarseness, barking cough, stenotic breathing. In another way, croup croup is called stenosing laryngitis.
Pathology stages
Inflammation of the larynx proceeds in four stages.
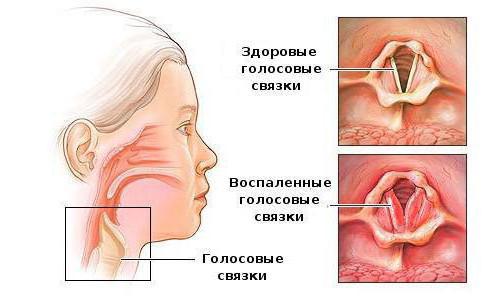
- Stage of compensated breathing. At the initial stage of the manifestation of pathology, a barking cough in a child with a temperature begins. Then the hoarseness of the voice joins, light attacks of shortness of breath may be noted.
- Subcompensation. At this stage, breathing becomes rapid, noisy. The nasolabial triangle acquires a pronounced blue tint. The general condition of the patient worsens, anxiety appears, sleep is disturbed.
- Decompensation. The whole body is covered with sticky sweat. Mixed or inspiratory dyspnea is noted. If inflammation of the larynx in children reaches the third stage, then there is a sharp excitement, weak breathing, dilated pupils. Sometimes in children confusion occurs.
- Asphyxia. Stenosing laryngitis in children rarely goes into the fourth stage. If this happens, a hypoxic coma develops with a pronounced violation of all body functions. Children become lethargic, sleepy, their breathing slows down until it stops.
In isolated cases, the fourth stage may manifest as involuntary urination and defecation, convulsions and a gray tint of the skin.
Possible complications
If stenosing laryngitis is correctly diagnosed, treatment is started on time, then the prognosis is favorable. Otherwise, the pathology leaves serious consequences. Most often, inflammation is complicated by obstructive bronchitis. Less commonly, the disease passes into the following pathologies:
- sinusitis;
- otitis;
- tonsillitis;
- meningitis;
- conjunctivitis.
The most dangerous complication is pneumonia. If she joins laryngitis, then a fatal outcome is possible.
Diagnostics
Laryngitis is suggested with the appearance of hoarseness of the voice, barking cough, shortness of breath. The doctor also takes into account the anamnesis, laboratory and instrumental examination data. They help confirm or refute the diagnosis.
In some cases, a virological study is performed with a suspicion of a viral etiology of the disease. A bacterial infection is also examined. Bacteriological diagnosis of mucus for diphtheria from the oral and nasal cavity is mandatory.
Treatment
If a barking cough appears in a child with a temperature, then you should immediately consult a doctor.
At the first stage of the disease, the doctor prescribes a plentiful drink, inhalation with medicinal herbs (sage, chamomile, etc.). The doctor selects vitamins and immune boosters. If the treatment does not give a positive result, then a novocaine blockade is performed to relieve swelling of the respiratory passages and spasm. In the first stage, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics and antiviral drugs.
In the second stage of the disease, moistened oxygen is added to the above funds, means to strengthen the cardiovascular system, diuretics.
The third stage requires special treatment. On it, hormonal drugs are included in the therapy. If the treatment does not give positive results, then the mucus is removed by a catheter, after which the mucous membrane is abundantly lubricated with oils.
With low effectiveness of therapy, the patient undergoes a tracheotomy, intubation.
First aid
Prior to the arrival of an ambulance, it is necessary to alleviate the condition of the patient who has stenosing laryngitis. First aid is as follows:
- Provide oxygen access. To do this, the upper buttons of clothing are unfastened.
- Lay the patient in bed and raise the head of the bed.
- Provide plenty of warm drink. To do this, you can use tea, warm milk.
- In winter, it is recommended to increase the humidity in the room.
- Give an antihistamine.
If no improvement is observed, then “Prednisone” should be injected intramuscularly or intravenously: 4 mg per kilogram of the child’s weight.
After examining the patient, the doctor will make an injection of an antispasmodic drug.
Prevention
The rules for the prevention of laryngitis consist of the following:
- personal hygiene;
- proper nutrition;
- restriction of contacts with sick viral and bacterial infections.
To avoid the development of the disease, you should constantly monitor your health, improve immunity, take vitamins, do exercises.