Adhesive disease occurs as a result of trauma to the peritoneum, which can be triggered by the presence of foreign bodies in it, pathological processes, as well as as a result of surgical intervention on the organs of the abdominal cavity. This is a rather serious disease, which is often found at a young and able-bodied age. The resulting adhesions interfere with normal intestinal motility. The consequence of this process is:
- difficulty emptying;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- constipation;
- pain in the abdomen, which increases with exertion and poor nutrition.
An increase in pain is facilitated by the tension of adhesions, in addition, they pull the intestinal loop, and the individual develops acute intestinal obstruction, or OKN.
Causes
There are a lot of factors that contribute to the progression of adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity, and all of them lead to injury to the organs and tissues of the peritoneum. Reasons that lead to the formation of adhesions:
- chemical damage;
- inflammatory process in the appendages, intestines, appendix;
- abdominal injuries.
Perforation of the stomach, rupture of the gallbladder can lead to the onset of the disease. Often the cause of disease progression in the pelvic organs is the inflammatory process in the organs of the reproductive system, which is chronic.
Signs of the disease
The volume of the adhesive process in the peritoneum can be different. In some cases, separate screeds are formed, which are fixed at two points. In others, they spread throughout the recess. Adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity happens:
- Sharp. In this case, it begins suddenly, severe pain is observed, intestinal motility increases, body temperature rises, vomiting begins. Over time, the pain intensifies. Signs of intestinal obstruction increase and are manifested by vomiting, bloating, tachycardia, increased pressure, decreased daily diuresis, decreased reflexes, increased thirst, acrocyanosis.
- Intermittent. This form is characterized by the frequency of pain attacks, which differ in intensity, there are dyspeptic disorders. In the period of increased seizures, patients are hospitalized.
- A chronic form of pathology in the peritoneum is manifested by pain in the abdomen, constant constipation and discomfort, periodic attacks of intestinal obstruction.
In addition, there are forms of peritoneal commissural disease: with pain in it and with repeated bouts of acute intestinal obstruction. The following clinical picture is present:
- cramping abdominal pain;
- bad or no exhaust gases;
- the stomach swells;
- vomiting is present.
If the individual has the above manifestations, hospitalization in the surgical department of the hospital is required. In some cases, a surgical operation is indicated, the need for it is determined by the doctor.
Conservative and surgical treatment
In most cases, this pathology is chronic. Conservative methods of treating adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity are indicated if the disease does not have a pronounced clinic. You can cope with unpleasant symptoms using folk methods and diet. To reduce pain during an attack, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed that improve the patient's condition. In addition, the pain provoked by a delay in the passage of gases is stopped by the introduction of antispasmodics, a cleansing enema, or a warm heating pad placed on the stomach. In hospital conditions, for the purpose of pain relief, an epidural blockade is performed using the drug "Trimekain". For resorption of adhesions, "Aloe extract liquid" and "Vitreous", as well as enzyme preparations, are prescribed as injections.
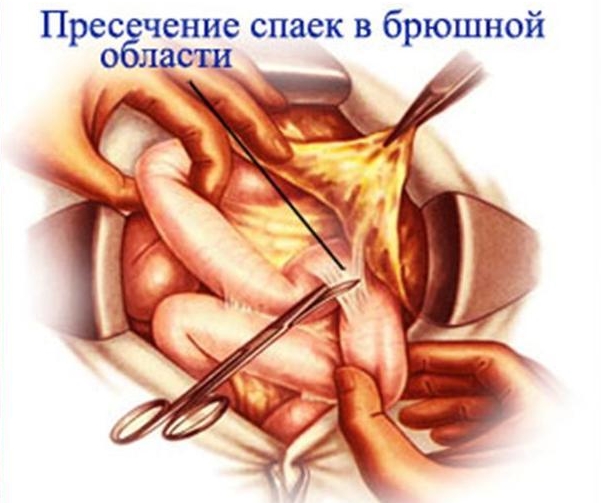
Indications for surgical therapy are determined by the doctor. Currently, they are trying to apply laser therapy, laparoscopy, electroscopy, that is, operations that have the least interference in the individual's body. However, surgical treatment for this disease does not guarantee that the adhesive process is eliminated.
Diet food
The diet for adhesive disease provides for the rejection of:
- products that increase gas formation;
- heavy for digesting food;
- grapes;
- milk;
- different seasonings;
- flour and confectionery products;
- drinks containing gases;
- legumes.
The following products are recommended:
- dietary meat;
- steamed or cooked vegetables;
- dairy drinks;
- broths without fat.
Adhesive process prevention
Preventive measures of the formation of adhesions are the timely operation in acute conditions of the abdominal organs. Of particular importance is the rehabilitation of the peritoneum, which is carried out by a gentle method, by an electric suction pump, and only in hard-to-reach areas are used for drying tampons.
After surgery, patients are prescribed physiotherapy: iontophoresis, ozokerite or paraffin in the form of applications on the abdomen, mud therapy. Their action is aimed at resolving adhesions and softening scars. The sooner after surgery the individual will begin to carry out these manipulations, the higher their effectiveness. With adhesive disease, it is especially important to prevent acute intestinal obstruction and exacerbation of pain. For constipation, preventative measures are:
- eating food that enhances peristalsis;
- taking a mild laxative;
- obligatory adherence to a diet, not to allow a situation when the stomach remains empty;
- exclude foods that lead to bloating;
- avoid muscle tension and physical work, otherwise the pain syndrome will intensify;
- limit weight lifting to six kilograms.
Violation of preventive measures inevitably leads to an exacerbation of pathology. The disease reduces the working ability of citizens, and most of them are assigned the third group of disability on a special commission.
Causes and risk factors for adhesions in the pelvis
In response to a decrease in oxygen supply to the tissues or their damage, adhesions form as a protective response of the body. The propensity for this process is different for different individuals and depends on some features. The main causes of the adhesive process:
- excessive reactivity of connective tissue;
- low immune defense;
- predisposition of the abdominal cavity to such reactions.
Risk factors for adhesions:
- Internal (endogenous) are the genetic characteristics of an individual’s body. They reduce its ability to form hypoxia.
- External (exogenous). These include causes from the outside, they in their strength and power of impact on the body exceed its adaptive capabilities.
- A combination of the two previous factors. In this case, the possibility of formation and prevalence of adhesions is high.
The most common causes of adhesive pelvic disease:
- Operations. The severity of the formation of adhesions is influenced by the volume and type of surgery, the introduction of drainages into the small pelvis with the aim of outflow of fluid and blood; removal of the ovary, fallopian tube, fibroids, hysterectomy. After repeated surgical interventions in the abdomen, the likelihood of an adhesion process increases.
- Infections caused by complications during pregnancy or delivery, artificial termination of pregnancy; contraception using an intrauterine device, diagnostic curettage.
- External endometriosis of the pelvic organs.
- Pathologies of connective tissue, for example, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, scleroderma and others.
Briefly, the mechanism of development of adhesions can be described as follows: as a result of the inflammatory process, the affected tissues swell. On the peritoneum, a protein coating of fibrin is formed, which contributes to the bonding of adjacent tissues. Thus, an obstacle occurs, and further inflammation does not spread. After recovery, tissue adhesions form, they are called adhesions.
Treatment of adhesions in the pelvis
Therapy is carried out both by conservative and surgical methods. In the first case, in the treatment of adhesive pelvic disease, use:
- diet food;
- physiotherapeutic procedures: iontophoresis using enzyme preparations, magnetotherapy, ultrasound, mud therapy and others.
With a chronic form of pathology, conservative treatment is also possible. It will depend on the reason that served as the formation of adhesions. For example, with urogenital infectious processes, the therapy of the underlying disease is initially indicated, which subsequently will help to stop the formation of adhesions in the pelvic organs. Often, in the treatment of adhesions, drugs are used that promote the dissolution of fibrin - Trypsin, Longidase, Chymotrypsin. This method is especially effective in the initial stage of the disease. Conservative treatment of adhesive disease in acute and intermittent form is not recommended. In these cases, laparoscopy is indicated:
- electrosurgery - remove adhesions with an electric knife;
- laser therapy - a laser is used to eliminate adhesions;
- aquadissection - adhesions are dissected by water under pressure.
The doctor selects the specific method during the operation. Conservative treatment should begin the day after surgery.
In infertility, ovarian stimulation, artificial insemination or in vitro fertilization are used.
From traditional medicine, they use an infusion of St. John's wort herb, which is taken three times a day for a quarter cup.
Rehabilitation of adhesions in the pelvis
In order to increase the effectiveness of the treatment of adhesive disease and prevent relapse, it is recommended that within six months after surgery:
- eat food at least five times a day in small portions;
- do not lift weights;
- do not eat foods that increase gas production;
- in case of pain, take antispasmodics, such as Papaverine or Drotaverinum, and in case of severe pain, consult a doctor;
- daily exercise, do exercises aimed at increasing the muscle tone of the pelvic organs, strengthening the abdominal press;
- attend physiotherapy prescribed by a doctor.
After any type of treatment, women are recommended sexual rest for a period of three to six months and a visit to the gynecologist every six months. A favorable outcome is possible with the implementation of all recommendations.
Complications and prevention of adhesions in the pelvis
In the absence of proper treatment, the following consequences are observed:
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- menstrual irregularities;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- bend of the uterus;
- infertility;
- bowel obstruction.
Symptoms of adhesive disease that remain for life: chronic abdominal pain, constipation. Adhesions formed after resection of the cecum provoke biliary dyskinesia, dysbiosis, and constipation. Adhesive process in acute form can worsen the well-being of the individual and lead to life-threatening conditions. In adolescence, when the skeletal and tissue systems are not fully formed, the formation of adhesions provokes scantiness, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy.
In order to prevent, it is necessary to timely treat the pathology of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs, regularly visit a gynecologist. In some cases, to prevent the development of pathology, the doctor recommends a gynecological massage. It must be remembered that a woman's health is strengthened through natural childbirth, regular sexual activity with one partner.
Adhesions and pregnancy
There are situations when a pregnant woman finds out that she has adhesions. If pregnancy has occurred in this case, then the work of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity is not impaired. However, the adhesion process can complicate the bearing of the baby.
During this period, future mothers are recommended to eat in small portions, which will help reduce pain and not burden the intestines. Exclude gas-forming products. With an increase in the uterus, adhesions provoke severe pain in the lower abdomen. In addition, the development of an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs is possible.
Causes of adhesions in the intestines
Intestinal adhesions are a kind of formation of connective tissue between the loops of the intestine and the organs of the abdominal cavity. They lead to a fusion of the outer tissue membrane of organs between themselves. The appearance of adhesions in the intestines provokes:
- Surgery on the peritoneum.
- Injuries to the abdominal cavity and abdomen. In these cases, adhesions can be created some time after the damage.
- Inflammatory or infectious processes occurring in the peritoneum. With diffuse peritonitis, i.e., infection in the peritoneum, adhesions quite often form.
- Hereditary predisposition. Excessive production of enzymes contributes to the growth of connective tissue, so even minor damage to the peritoneal epithelial cells lead to the formation of adhesions.
- In the fair sex, they can form after surgical delivery or inflammation of the appendages.
- Radiation treatment of oncopathology. Damage to the peritoneum caused by radiation leads to the development of adhesions.
Adhesive bowel disease: symptoms, treatment
The process of adhesion formation takes a long period, and the symptoms do not immediately appear. Initially, the disease manifests itself as cramping, pulling pain, i.e., it is felt in the place where there is a commissure. After a certain period of time, the pain syndrome spreads throughout the abdomen. The nature of the pain can change to aching and increase with physical exertion, sharp turns of the body. Failure in the diet reinforces the symptoms. Gastrointestinal dysfunction develops, while the patient has bloating, constipation, vomiting, nausea, weight loss, and, as a result, irritability appears. Weight loss is present in the chronic course of the disease. In the absence of therapy, adhesive bowel disease progresses, serious complications appear:
- Acute intestinal obstruction. This condition develops in the case of squeezing the intestinal tube with adhesions. There is acute pain, vomiting, lack of bowel movement and an accumulation of gases. Cardiovascular disorders in the form of lowering blood pressure and tachycardia join these symptoms. The patient urgently needs the help of specialists.
- Necrosis of the intestine. As a result of clamping by the commissures of the arteries, the blood supply to the walls of the intestines is disturbed and their death occurs. The only way out is surgical treatment, during which the necrotic area is removed.
Therapy of adhesive bowel disease is possible with conservative, surgical, folk remedies and diet therapy. In most cases, operations are avoided. For minor functional disorders and minor pain syndrome, antispasmodics and pain medications are recommended, as well as the means by which adhesions resolve. For chronic constipation, the doctor recommends laxative medications. If pain is absent and adhesions do not manifest themselves, then treatment is not indicated. The patient is recommended dispensary observation and periodic preventive examinations.
Surgical treatment of symptoms of adhesive disease is carried out in order to restore the passage of intestinal contents. Indications for the appointment of this type of therapy is a violation of the blood supply to the intestines caused by commissures. Due to the fact that this type of treatment again causes the formation of adhesions, low-traumatic operations are practiced: laparoscopy and laparotomy. When choosing the type of surgical intervention, the doctor takes into account the patient's age, the presence of concomitant pathologies and other factors.
Dietary treatment of adhesive bowel disease
Therapy of the adhesive process involves the implementation of certain rules. To alleviate the condition of the patient and reduce the load on the digestive system, fractional nutrition in small portions is recommended, which should be eaten daily at the same time. Starvation and overeating provoke the development of complications and aggravation of the patient's condition. Food and products that promote bloating are difficult to digest, difficult to digest, rich in fiber, spicy seasonings, sodas, whole milk, strong coffee, mushroom, fish, meat broths, tea, smoked meats, marinade, canned food. Be sure to include calcium-containing foods in your diet. To reduce or relieve symptoms of adhesive bowel disease, food should be warm. Recommended Products:
- fresh kefir;
- cottage cheese;
- cheese;
- egg omelet;
- boiled chicken;
- small amount of butter;
- low-fat broths;
- boiled or steamed fish of low-fat varieties.
Treatment of adhesions by folk methods
Traditional healers recommend the treatment of commissural mild disease with herbal preparations. . :
- . 45 . , .
- . 100 , .
- , . . 100 .
- . .
If you feel worse after using medicinal plant materials, stop taking and visit a doctor.
An active lifestyle should be taken to prevent symptoms of adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity. However, heavy physical exertion is recommended to be excluded. Observe the diet, choose the optimal diet, monitor the digestive system, prevent constipation. Adhering to these simple tips, you will live a full life, and the adhesion process will not disturb you.