Why are the supraclavicular lymph nodes enlarged? The reasons for the development of such a pathological phenomenon will be listed below. You will also learn about what these organs are, why they are necessary for a person, and how to treat them in case of inflammation.
Basic information
Supraclavicular lymph nodes, enlarged several times, indicate serious malfunctions in the body. And before telling you what diseases provoke such a pathology, you should find out what these organs are in general.
Lymph nodes are small glands that resemble beans in their shape. As you know, they are located throughout the human body and are an integral part of the lymphatic system, promoting lymph and nutrients, as well as removing unnecessary substances into the bloodstream.
According to experts, the supraclavicular lymph node and the entire lymphatic system as a whole are an essential part of the human immune system, which protects the body from various diseases. Such glands filter lymph, capturing viruses, bacteria and other harmful elements, which are then destroyed by white blood cells, or the so-called lymphocytes.
Lymph nodes can be single or grouped. Their sizes vary from small to rather large. In the inflamed state, the supraclavicular lymph node is felt in the region of the supraclavicular fossa. Also, such glands can be noticeable in the armpit and groin area, however, they already have other names. In a healthy state, the lymph nodes do not cause pain. In addition, they are invisible to the eye and completely insensitive.
Causes of inflammation
Why are the supraclavicular lymph nodes enlarged? The reasons for the development of such a pathology can be hidden in various problems. Often, single lymph nodes hurt and swell due to various injuries, as well as tumors or infections that develop directly in them or in organs located nearby. Thus, depending on which glands are inflamed, their cause for enlargement can also be identified.
For example, the supraclavicular lymph node becomes inflamed due to a tumor or infection in the chest, lungs, abdomen, or neck. Therefore, with such a pathology, it is primarily these organs that should be examined.
Diseases causing inflammation of the lymph nodes
Why is the supraclavicular lymph node inflamed? An increase in this gland can occur in conjunction with inflammation of other glands in other areas of the body. In this case, they talk about generalized lymphadenopathy. This pathological condition is usually caused by:
- Mononucleosis, signs of which is a sore throat, fever and fatigue.
- Bacterial diseases, including acute pharyngitis (due to streptococcus bacteria).
- Lyme disease (a bacterial infection that spreads by some types of ticks).
- Viral infection - cytomegalovirus.
- Viral diseases, including rubella, measles, mumps or chickenpox.
- Cancer, including Hodgkin's disease, leukemia and lymphoma.
- Side effects from the use of the drug "Phenytoin", which is used to prevent seizures.
- Adverse reactions from vaccination against mumps-measles-rubella.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
- Sexually transmitted disease - syphilis.
Metastases to the supraclavicular lymph nodes
The following pathways for the spread of malignant tumors are known to modern medicine:
- lymphogenous;
- mixed;
- hematogenous.
Lymphogenous metastasis is characterized by the penetration of tumor cells first into the lymphatic vessel, and then into nearby or distant lymph nodes, including supraclavicular. Most often, epithelial cancer (such as melanoma) spreads in this way. Such metastasis has been well studied, therefore, it is quite easy to recognize a tumor at the stage of its nucleation.
Metastases in the lymph nodes above the clavicle very often develop in cancer of the lungs or breast, as well as in malignant neoplasms in the peritoneal region.
Causes of metastases
Metastases to an organ such as the supraclavicular lymph node most often spread due to:
- age factor (appear mainly at an older age);
- the size and localization of the initial focus of neoplasm (a large tumor increases the likelihood of developing metastases several times);
- concomitant diseases (chronic diseases that weaken the body's defenses);
- the spread of cancer cells (the growth of formations in the wall of the organ is more dangerous and most often causes metastasis than tumors that grow into the lumen of the organ).
Diagnosis of the disease
Where are the supraclavicular lymph nodes? The location of these glands in a healthy state is quite difficult to determine. If such organs are inflamed, then they are easily palpated in the supraclavicular fossa.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the lymph node should be carried out only by an experienced doctor. To do this, he explores the supraclavicular space from the sternocleidomastoid tissue to the acromioclavicular joint. In this case, the area between the legs of the sternocleidomastias is carefully checked. In this area, palpation is carried out with one middle or index finger.
With a thorough and in-depth study of the subclavian fossae, their lateral sections are felt directly at the edges of the deltoid muscles. In healthy people, supraclavicular lymph nodes are not palpable.
Other diagnostic methods
An inflamed supraclavicular lymph node on the left or right can be detected by palpation, that is, by normal palpation with the hands. Also, these glands are available for research in the following ways:
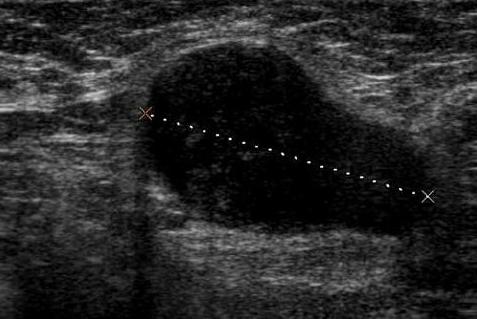
- Ultrasound Ultrasound examination of the supraclavicular lymph node is the most affordable, informative and painless way to detect its abnormal increase.
- Computed tomography is a complex method. However, it is used only to assess the condition of the lymph nodes, inaccessible to normal palpation.
- X-ray examination. This method is used very rarely. As a rule, enlarged lymph nodes are detected on the chest x-ray completely by accident.
- Mediastinoscopy, thoracoscopy and laparoscopy.
- Biopsy.
The final point in the diagnosis and search for the causes of enlarged lymph nodes is the result of a biopsy. Other research methods provide information only on the external characteristics of the inflamed gland. And only by analyzing the structure of this organ under a microscope, as well as by performing PCR analysis and bacteriological culture, we can confidently talk about the true reason for the enlargement of the lymph node.
Treatment process
How to cure an inflamed supraclavicular lymph node on the right or left? Therapy of such a gland is to directly eliminate the causes of its enlargement, soreness and swelling. In particular, a bacterial infection is treated with antibiotic drugs, and a viral infection can go away on its own without the use of drugs.
A more serious case of inflammation of the supraclavicular lymph node is a cancerous tumor. If there is even the slightest reason to suspect that the enlargement of this organ is associated with cancer, then a biopsy must be performed and, of course, a full examination by an experienced doctor.
Thus, if the enlarged supraclavicular lymph nodes did not pass in one month, while their size did not decrease, then you should immediately visit a qualified specialist. It can not be said that such glands can remain swollen for a long period after the passage of an infectious disease. This phenomenon is especially common in children.
Special information
With an increase in lymph nodes, including supraclavicular, it should be remembered that:
- the size of the lymph node in the normal state is about 1-1.5 cm;
- the main reason for the increase in this organ is a local infection;
- the greater the patient’s age, the higher the probability of the malignant nature of this pathological phenomenon;
- taking antibiotic drugs without establishing the exact cause of the development of lymphadenopathy is a false therapeutic tactic (first a diagnosis must be made, and only then appropriate treatment is prescribed);
- if the enlarged node has not decreased within a month, then its histological examination and biopsy are performed;
- enlargement of glands and spleen requires immediate verification;
- an increase in lymph nodes, along with an increase in body temperature and soreness in the area of their location indicates an infectious disease;
- a lymph node biopsy can be performed from the neck or axilla, and lymph nodes in the inguinal region are not suitable for such a diagnosis;
- aspiration of an enlarged gland with a biopsy needle does not carry diagnostically important information because it does not give any idea of structural changes.