A complication of osteochondrosis with significant pain syndromes causing a limitation of human mobility is called deforming spondylosis. The most common such pathology in relation to the lumbar. In this case, damage to the joints of this zone with the formation of osteophytes is noted, which narrows the spinal canal and leads to irritation of the longitudinal anterior ligament.
The concept
Osteochondrosis leads to dynamics in the structure of structures that make up the spine. The intervertebral disc begins to thin out and lose its elasticity due to metabolic disturbances. It ceases to perform a cushioning function, and therefore bone tissue begins to grow. The vertebral bodies should not be in contact in order to prevent inflammatory processes, so they should be supported by something.
This leads to the formation of osteophytes, which serve as their support, speaking beyond their edges. With extensive overgrowth processes, osteophytes can completely coalesce, which leads to the fusion and immobilization of two vertebrae.
Bending classification
Deforming spondylosis is formed as a result of impaired dynamics of the normal position of the spine. Those bends that have a physiologically correct shape begin to shift in different directions, which leads to the progression of various complications:
- Kyphosis - manifests itself in the anteroposterior plane in the chest area in the form of a curvature of the spine. A person has a narrowing chest, shoulders drop, he stoops, which can lead to the development of humpiness.
- Lordosis is a curvature of the spine in which a bulge is formed forward, observed in the lumbar and cervical regions. It can be physiologically correct if the degree of bending is normal, with a pathological ailment, the head and shoulders extend forward, the chest puffs, and the stomach goes forward. Hyperlordosis leads to compression of the internal organs and especially the heart muscle.
- Scoliosis - the spinal column is shifted relative to the central axis.
Classification of kyphosis and scoliosis
Deforming spondylosis leads to the above complications. Kyphosis according to the angle of curvature is divided into several types:
- normal;
- straightened (angle reduced);
- reinforced (it is increased).
The biggest problems are the latter. He, in turn, distinguishes three degrees:
- Angle up to 35 degrees inclusive.
- From 35 to 60 degrees.
- Angle from 60 degrees or more.
Scoliosis is divided into:
- lumbar;
- thoracic;
- cervical;
- mixed.
Curvature arcs can appear not one at a time, but several, which leads to the formation of various forms of scoliosis: C, S, Z. Depending on the degree of deviation, 4 degrees of this disease are distinguished:
- The angle of curvature is up to 10 degrees inclusive. There is a slight violation of the level of the shoulder girdle.
- The angle is 11-25 °. Deformation is noticeable.
- The value of the angle is from 25 to 50 degrees. An inner hump forms.
- The angle exceeds 50 °. Internal organs are underdeveloped, a person does not tolerate even light physical exertion.
Causes
Deforming spondylosis of the spine is most susceptible to people whose work forces them to remain in a static position for a long time or is associated with great physical exertion.
The main causes of disease are as follows:
- concomitant pathologies;
- poor circulation;
- metabolic disorder;
- back injuries;
- elderly age;
- overweight.
Other factors influence the development of deforming spondylosis of the lumbar:
- sedentary sedentary lifestyle;
- various infections, sources of inflammation, oncology;
- genetic predisposition.
Symptomatology
Signs of deforming spondylosis are different depending on where the disease is localized.
In particular, it can be located in the cervical spine. This form is dangerous and common. The danger is that cerebral circulation may be impaired. Characteristic signs in the presence of a disease in this zone:
- dizziness with sharp turns of the head;
- a crunch when making such movements;
- poor neck mobility;
- the appearance of cervical lordosis;
- numbness of the hands;
- painful syndromes in the neck, extending to the back of the head and shoulders.
The least common is thoracic spondylosis. The following symptoms are characteristic of it:
- superficial and rapid breathing to avoid pain;
- the appearance of scoliosis;
- aching or lumbar pain.
Most often, deforming spondylosis of the lumbar region is found. The following symptoms are characteristic of it:
- lumbar lordosis develops;
- muscles of the lower extremities decrease tone;
- sciatica develops;
- in the lumbar region there is a restriction of mobility;
- sharp shooting or aching pain appears;
- in some cases, lameness is observed;
- lifting up and tilting facilitate a person’s condition;
- pain syndromes are felt and at rest.
The last symptoms are characteristic for deforming spondylosis of the 2nd degree. The characteristics of the various stages of the disease are given below.
Degrees
In total, there are three degrees of this ailment.
- Initial deforming spondylosis is characterized by a first degree. At the same time, bone growths are small, not extending beyond the vertebral bodies. Symptoms are mild or absent.
- In the second degree, there is an increase in osteophytes, which begin to connect neighboring vertebrae. Spinal mobility becomes limited, periodic aching pains appear, aggravated by hypothermia and physical exertion.
- On the third degree, osteophytes fuse together, resembling a staple, which can make the spine completely motionless. The disease provokes strong muscle tension, which leads to additional pain syndromes.
Often the disease is detected upon the onset of 2 degrees.
ICD Deforming Spondylosis
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is used to bring the causes that cause them and deaths resulting from their development to a common denominator on an international scale. Spondylosis with myelopathy refers to the code M47.1, with radiculopathy - M47.2, other spondylosis - M47.8, unspecified varieties of the disease - M47.9.
Diagnostics
First of all, a complete neurological examination of the patient is carried out. After that, for an accurate diagnosis of "deforming spondylosis", relevant related studies are carried out:
- X-ray, allowing to establish the degree of damage to the vertebrae. Here osteophytes are clearly visible, having the appearance of spikes, their splicing is visible if it is present. With the help of an X-ray, it is established at what stage the disease is located, because sometimes its symptoms can be pronounced with a small size, and the opposite picture can be observed, when the symptoms are implicitly expressed, and the pathological dynamics in the spine are significant.
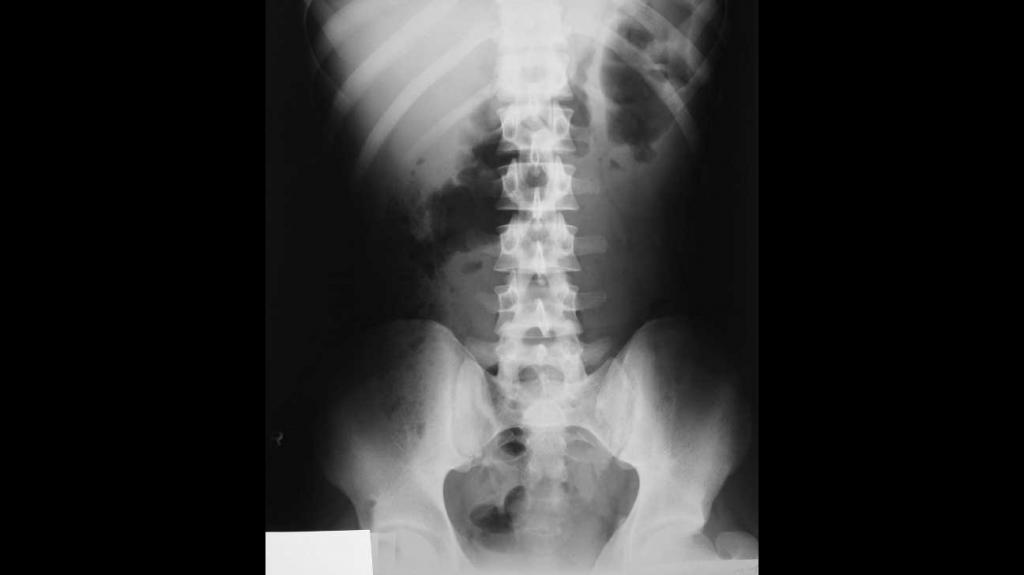
- CT and MRI are used to detect narrowing of the spinal canal and visualize the compression of nerve fibers, to view the state of nerves, ligaments and discs. Using these methods, determine the height of the intervertebral discs, the degree of damage to tissues and blood vessels.
- Electroneuromyography is used to detect conduction disorders of nerve fibers.
- In order to detect a tumor or area of inflammation, a radioisotope scan is used. Moreover, the highest concentration of radioisotopes will be observed in pathogenic zones.
Healing
Treatment of deforming spondylosis in most cases is conservative, although surgical intervention may be necessary. It aims to achieve the following results:
- deceleration of dystrophic dynamics;
- improvement of blood circulation and metabolic processes;
- elimination of pain syndromes;
- relieving muscle cramps.
Therapy on the spine approximately coincides. The following is an example of a treatment for lumbar spine. It should be borne in mind that the disappearance of pain does not indicate healing. The manifestations of the disease are eliminated, however, the vertebrae remain deformed.
Drug therapy
To relieve inflammation and quickly relieve pain syndromes, NSAIDs are used, which can be used in the form of intramuscular injections or tablets: Naproxen, Ibuprofen.
In addition to them, the following tools are used:
- hormonal preparations as part of intraarticular injections: hyaluronic acid, glucocorticoids;
- sedatives to normalize sleep;
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- chondroprotectors that contribute to the restoration of cartilage, providing processes that slow down its destruction and improve nutrition: Don, Elbon, Chondrolon;
- muscle relaxants - are used to partially block the signals from the brain and relieve muscle tension: “Tizanidine”, “Cyclobenzaprine”.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
It is used in conjunction with drug therapy. The following procedures are prescribed:
- massage;
- stone mineralogical treatment;
- acupuncture;
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasound treatment;
- electrotherapy.
Other conservative treatments
In addition to the above methods, they can apply:
- traction therapy, in which there is a mechanical stretching of the spine, which allows to increase the intervertebral space, reduce the compression of blood vessels and nerve roots;
- the use of a corset to fix damaged vertebrae in a physiologically correct position and relieve pain; its use is temporary, because otherwise osteophytes will grow and muscle atrophy will occur;
- lifestyle changes, consisting in the transition to a balanced diet, maintaining body weight in good condition, giving up bad habits;
- bed rest - used at the beginning of the development of the disease, duration - no more than 3 days, so as not to develop muscle atrophy.
Surgical intervention
It is carried out in 5% of cases of the development of the disease. It is required in the presence of serious irremovable pain, numbness of the extremities, impaired conduction of nerve impulses. In this case, the removal of various formations that caused pinching of the nerves occurs. The spine can be stabilized with implants.
Physiotherapy
Gymnastics with deforming spondylosis should exclude excessive load, sudden movements of damaged departments. The systematic performance of exercises improves blood circulation in them, maintains muscle tone, and maintain spinal mobility. The following is an exercise therapy course for the cervical spine. It is performed at the maximum possible unloading of the spine, lying or standing on all fours.
- Tilting the head in different directions with a hand stretched along the body.
- Starting position - hands on the back of the head, exhaling - head forward, touching the sternum with the chin, inhaling - starting position with raising the head.
- Direct standing with feet shoulder width apart, lift the last and stand for 2-5 seconds.
- Circular movements with shoulders, palms pressed along the body.
- The connection of the hands in the area of the shoulder blades is alternate.
Complications and prognosis
In general, the latter is favorable. With high-quality and timely therapy, it is possible to improve vital activity by stopping pain. Immobility can be removed or eliminated completely. If treatment is not carried out, then it is possible to limit movements, numbness of the lower extremities, which affects the ability to work. In advanced cases, pain syndromes with drug therapy do not stop.
Finally
Deforming spondylosis is a disease of the spine that develops as a complication of osteochondrosis and manifests itself in the appearance of various curvatures and osteophytes, which can grow together and immobilize certain sections of this organ. The treatment is mostly conservative, in some cases surgical. In addition to drug therapy, physiotherapeutic treatment is carried out, exercise therapy, massage are used. Timely detection of the disease is necessary, which requires urgent visits to the doctor with the slightest suspicion of the presence of this pathology.