Tuberous sclerosis (or Bourneville disease) is a rare genetic disease. An illness manifests itself in the form of benign tumors in many tissues and organs. Translated from Latin tuber means "growth, tumor." For the first time in the mid-19th century, the French neuropathologist Bourneville was given a clinical picture of this anomaly, which is why it got his name. With the disease, the brain, heart, kidneys, lungs, fundus are affected, specific neoplasms appear on the skin. With timely diagnosis, symptomatic treatment immediately begins , which prevents the development of complications.
Disease Description
The disease affects both the male half of the population and the female, with the same frequency. With hereditary transmission, it is not detected immediately, but during the year or in adolescence. Only a third of tuberous sclerosis is caused by a hereditary factor; in other cases, the disease appears as a result of spontaneous unpredictable genetic mutations. Lesions of the nervous system are predominant in the disease. The most characteristic manifestations are convulsions, mental retardation, deviations from the norm of behavior, and a decrease in intelligence.

Tumors of the retina and optic nerve are observed, which leads to decreased vision. There are changes in the cardiovascular system with the formation of tumors located in the thickness of the muscle. The disease is always accompanied by changes in the skin. Pigment spots appear on the face and back, areas of a rough dermis are distinguished, periungual fibromas and plaques form. White areas appear on the eyelashes, eyebrows and locks of hair. If you suspect a disease, you should immediately consult a doctor and be examined comprehensively to reduce the risk of various complications.
The causes of the disease
The main cause of tuberous sclerosis is a gene mutation of the ninth and sixteenth chromosomes without any apparent background. As a result of this, there is a violation of the formation of proteins: hamartin and tuberin, which are responsible for cell division and growth. This leads to pathological changes in nerve cells and inferior development of certain parts of the brain.
The development of pathology is affected by a hereditary factor. If there is a disease, one of the parents has a high risk of transmitting it to the child. Another form is known (sporadic), which occurs without any apparent reasons and premises, spontaneously at different periods of life and any age, and the disease is difficult. The course of a family or genetic form is characterized by a mild severity.
Symptoms of the disease
With tuberous sclerosis, various tissues, organs and systems are affected, therefore, the signs of the disease will differ. Most often, the nervous system suffers. This manifests itself:
- Moderate dementia - oligophrenia, occurs in half of patients.
- Convulsive syndrome - the development of the disease begins with convulsions in babies in their first year of life. With age, this syndrome becomes epileptic seizures. They lead to impaired intelligence and become the main cause of disability.
The defeat of the skin is characterized by:
- The formation of age spots. For some, they appear from birth, for others, from the age of two. With the growth of the child, their number increases, they are located asymmetrically on the buttocks, trunk and limbs.
- In children, symptoms of tuberous sclerosis (photo below) appear on the dermis of the face and body with multiple small nodules of yellowish and pink color. Most often, these symptoms occur in adolescents.
- The emergence of "shagreen derma" - coarsened skin on the back and buttocks.
- Fibrous plaques, which are located near the nail plates of the hands, and after puberty, and near the nails of the lower extremities.
Ophthalmic changes:
- neoplasms on the retina and optic nerve have a smooth or nodular surface;
- decrease in severity and narrowing of the field of view;
- swelling of the optic nerve;
- violation of pigmentation of the iris;
- cataract;
- strabismus.
Symptoms of tuberous sclerosis with damage to internal organs:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- cancerous tumors;
- cystic formations on the kidneys and lungs;
- impaired lung function;
- rectal polyposis;
- neoplasms in the oral cavity;
- erasing tooth enamel;
- fetal death.
Internal organs often have multiple lesions that can occur throughout life.
In addition to the listed symptoms, there are the following characteristic symptoms of tuberous sclerosis in children:
- loss of interest in everything new;
- increased moodiness;
- difficulty switching attention;
- delayed reaction;
- sleep disturbances and wakefulness.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make a diagnosis, you must do:
- Interrogation of the patient. The doctor finds out the complaints, the time of the manifestation of the disease, whether there were similar cases in other relatives.
- Visual inspection. The skin is examined for the presence of rashes and areas of bleached dermis.
- General analysis of urine and blood. The content of protein and red blood cells is monitored to determine the pathology of the kidneys.
- Analysis for tuberous sclerosis TSC1 protein hamartin and TSC2 protein tuberin is not carried out in all laboratories. Where to do this, the attending physician will tell you.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys to detect neoplasms.
- Ultrasound of the heart shows changes in the organ.
- Electroencephalography of the brain detects lesions.
- CT and MRI scans are performed to ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis.
- Consultation of a dermatologist, ophthalmologist, neurologist, nephrologist, cardiologist, genetics.
After the diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis, where all examinations, specialist consultations and test results were taken into account, a course of therapy is prescribed.
Disease treatment
It is completely impossible to cure Bourneville disease. The main goal of treatment is maintenance therapy and, if necessary, surgical intervention, so that the patient can live a normal life. Most often, complex treatment is used, in which drugs are prescribed:
- corticosteroids to reduce the frequency of epileptic seizures or to completely eliminate them;
- cardiovascular preparations for tumors in the heart muscles;
- antihypertensives to reduce pressure in kidney damage;
- hormonal, preventing further damage to the lungs.
For children, constant counseling by a psychotherapist is required to combat mental retardation. In addition, you must follow a special diet, which contains a minimum of proteins and carbohydrates and an increased amount of fat. Antidepressants and anticonvulsants along with diet can help reduce epileptic seizures and possibly completely eliminate them.
Surgical treatments for tuberous sclerosis are used to:
- removal of brain tumors causing cramps and cramps;
- destruction of polyps in the digestive tract using colonoscopy;
- annulment of neoplasms that interfere with the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- elimination of growths in the kidneys;
- cauterization of enlarged hamartas on the retina;
- elimination of significant tubercles on the surface of the skin using a laser, liquid nitrogen and high-frequency current.
Surgical treatment is carried out as a last resort: during the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant neoplasm, deformation of the internal organs and increased cranial pressure. The patient needs to stop attacks on time, follow a diet and, in extreme cases, resort to surgical intervention.
Tuberous sclerosis of the brain
With the disease, dementia occurs, epileptic seizures occur, nodular intracranial tumors form, which eventually become coated with calcium phosphate crystals. With the X-ray method of research, calcifications and improperly convoluted vessels, capillaries and small veins of the pia mater are isolated on the surface of the brain.
Impairment of mental development becomes noticeable in the first two years of life. It appears in half of patients with this ailment and is expressed in severe or moderate form. Epilepsy seizures appear from infancy, starting with infantile cramps. It is epilepsy that often becomes the cause of disability in a child. In addition, changes in behavior occur, patients suffer from autism, hyperactivity, autoaggression and aggression, which is aimed at people around.
It is noted that an early manifestation of the disease leads to serious mental retardation and impaired behavior. Patients often have problems with sleep, they suffer from insomnia, frequent awakenings and unconscious walking in a dream.
The development of the disease in young patients
Tuberous sclerosis (a photo of the symptoms is presented below) is characterized by the formation of benign tumors on the organs and skin integuments. A severe illness is not common, and one or more organs are mainly affected. According to medical statistics, it is believed that the disease is rare, although medical professionals are confident that it occurs much more often than it is diagnosed. The disease is transmitted by heredity, but completely healthy babies can be born to parents with damaged genes.
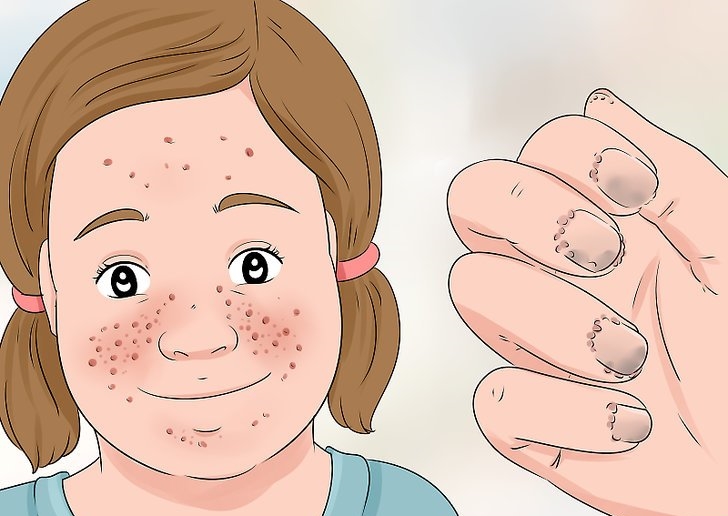
In sick children, mental retardation is observed, there are problems with learning and the norm of behavior, autism is manifested. Along with problems of mental development, speech perfection is inhibited. Kids up to a year often suffer from infantile cramps, which last a few seconds and are repeated many times a day. At the age of five, they can spontaneously stop or transform into another type of seizure. This happens due to serious brain damage and abnormal development of the nervous system. In addition, plaque formation on the retina of the eye, which the ophthalmologist reveals during the examination, is common. Almost completely in children with tuberous sclerosis, skin symptoms appear:
- The appearance in infancy and early childhood of pale spots (macula), which are asymmetrically located throughout the body, except for the hands and feet. With age, angiofibromas (benign tumors) of the face are formed.
- The formation in the womb of shagreen spots (rough areas of the dermis) on the buttocks and in the lower back.
- Fibrous plaques having a light beige hue. Localized on the forehead and head.
- Altered fibroids are located throughout the body. These are soft formations in the form of a small sac on the leg.
- Periungual fibroma appears near or under the nails. Formed in adolescence, does not occur in infancy.
With this pathology, most organs are affected, and first of all, the functions of the heart are violated, which leads to serious problems.
Treatment of the disease in children
To date, doctors have not found such a technique by which the symptoms of tuberous sclerosis can be completely cured. Only supportive treatment is carried out, which allows to alleviate the patient's condition. The following symptomatic treatment is carried out:
- For convulsions, use "Clonazepam", "Nitrazepam", "Carbamazepine", "Diacarb." The drugs stop convulsive seizures, slowing down the process of mental underdevelopment.
- Lesions of the skin are treated with a laser and dermatoabrasion (removal of the upper layer of the skin). After treatment, neoplasms may reappear.
- Hypertension. It appears due to impaired renal function. They take drugs to reduce pressure and resort to the removal of progressive tumors.
- Lag in development. Provide special training and appropriate occupational therapy.
- Heart failure. Use therapeutic agents for correction.
- Neurobehavioral problems. Prescribe drugs or apply special behavioral management techniques.
- Increased intracranial pressure. The tumors formed are removed operatively.
Treatment of tuberous sclerosis in children, started from an early age, alleviates symptoms and prolongs life.
Complications and consequences of the disease
The main complications of the disease include:
- Bouts of epilepsy. They lead to an epileptic status when seizures follow one after another for more than half an hour and the patient remains unconscious all this time.
- Kidney damage. This is expressed in chronic renal failure. In this case, the patient undergoes surgery to remove the tumor, the condition normalizes.
- Impaired vision. The characteristic formation of tumors on the retina of the eye or near the optic nerve helps to reduce vision. In addition, cataracts, strabismus occur, and the iris changes. It is treated operatively.
- Accumulation of intracranial fluid. This leads to brain dropsy. The patient complains of a headache, accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Rhabdomyomas in the heart. The resulting tumors in childhood interfere with normal blood circulation, causing arrhythmia. Subsequently, they decrease.
For all complications, symptomatic treatment is performed.
Tuberous sclerosis. Prognosis and treatment
The prognosis of Bourneville disease largely depends on the severity of the disease. The mild form provides an opportunity to lead an active lifestyle, with severe disability occurs. Most patients with proper treatment live more than a quarter of a century, in other cases - no more than five years. Severe complications of important organs require constant attention and supportive treatment. Otherwise, health problems can be fatal. To prevent the development of complications, patients should be monitored by doctors all their lives and strictly observe their prescriptions. Thanks to the development of medicine, convulsions in babies are eliminated with medication, at an older age, seizures are eliminated using chemotherapy, skin defects are removed with a laser, and intracranial pressure is normalized by shunting. All this helps to improve the quality and life expectancy of tuberous sclerosis.