Surgical manipulations are almost always associated with risk. In addition to the possible development of bleeding during surgery, there are more distant complications. This is especially true of extensive manipulations in which an organ or part thereof is removed. An example is the Billroth-2 operation. Its essence is to remove most of the stomach and create an anastomosis with a small intestine. After this surgery, the adherent loop syndrome often develops. A similar complication can occur both immediately after the operation, and after a few months. With the development of this condition or suspicion of it, another surgical intervention is necessary.
The concept of afferent loop syndrome
Adjacent loop syndrome after resection of the stomach occurs in approximately 13% of cases. This indicator can vary from 1 to 50%, according to doctors. Its main symptom is vomiting of bile associated with eating. Adjacent loop syndrome is a condition in which part of the intestine is “turned off” from the digestion process. As a result of this, bile accumulates in this department and, in the presence of adverse factors, spills out. Another name for this complication is duodenobiliary syndrome. This condition is a dangerous sign, therefore, requires surgical treatment.
Causes of the syndrome
The main reason for the development of afferent loop syndrome is Billroth-2 surgery. It is a massive surgical intervention and has an effect on the whole body. A similar operation is carried out with gastric cancer, with the development of complications of peptic ulcer disease, which cannot be eliminated by more gentle methods. As a result of this manipulation, the duodenum and part of the small intestine cease to be actively involved in the act of digestion. Because of this, the afferent loop syndrome develops.
Factors affecting the appearance of this complication are the following violations:
- The mechanical reason. By it is meant the ingress of food masses into the lumen of the “switched off” loop. Bile also accumulates there, which also delays the digestion process.
- Loss of muscle tone in the "off" section. This cause often causes chronic afferent loop syndrome after resection.
- Anastomosis spasm - the junction of the stump of the stomach and small intestine. Muscles can also contract in the area of the abduction loop.
- Peptic ulcer along the anastomosis. It leads to a mechanical cause of the afferent loop syndrome. It can develop both primary (after surgery) and secondary.
- Inflection of the leading loop. It usually develops a second time.
Loopback syndrome: pathogenesis of the disease
The mechanism for the development of the afferent loop syndrome consists of several links. First of all, there is a violation of the anatomical and functional interactions habitual for the body. As a result of "artificial" alteration of the digestive system, the process of food evacuation changes. Food caught in the “turned off” intestinal loop cannot go any further. Therefore, there is its reverse cast - reflux. In addition, an inflammatory process is present in the pathogenesis. It occurs due to stagnation of the digestive masses and hypotension of the duodenum. The result is secondary intestinal dysbiosis. Subsequently, it leads to inflammation of the digestive tract: cholecystitis, pancreatitis, esophagitis.
Clinical picture in adherent loop syndrome
The main manifestations of this complication are pain and vomiting. Unpleasant sensations in the abdomen may appear immediately after surgery or over time. In the first case, there is a primary, acute afferent loop syndrome. It is characterized by pains of a cramping and bursting nature in the right hypochondrium and in the epigastrium. In chronic afferent loop syndrome, the clinical picture is not so pronounced. Pain occurs mainly after eating, more often when eating fatty foods. Regardless of the time the complication occurred (acute or chronic period), the disease is manifested by vomiting. It appears after an increase in pain in the abdomen, usually following a meal. Due to frequent vomiting, up to 500 ml of bile per day is possible. The consequence of this is the progressive depletion of the body. Patients quickly lose body weight, experience general weakness.
Loopback Syndrome: Diagnosis of Pathology
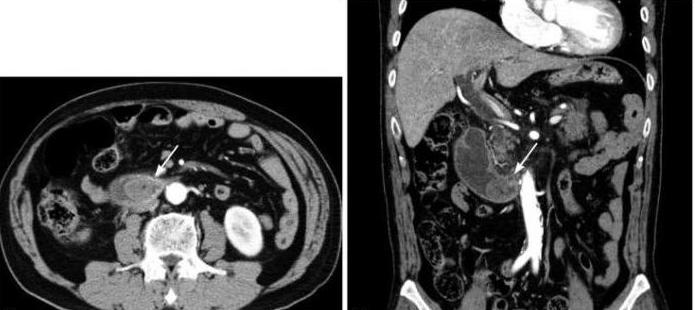
Diagnosis of the disease begins with a medical history (transferred stomach resection) and examination of the patient. First of all, you need to learn about the nature of pain and the frequency of vomiting, its relationship with meals. On examination, you should pay attention to the asymmetry of the abdomen: the right section protrudes. This symptom disappears after vomiting, as the contents of the loop go outside. Another sign is yellowness of the sclera and skin.
In addition to evaluating clinical data, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are performed. Changes can be in KLA (B-12 deficient anemia), blood smear, coprogram (the appearance of white blood cells, undigested fat). With x-ray radiation, a symptom of a niche in the region of the adductor loop, hypermotor dyskinesia, is noted. A contrast agent fills the lead loop. An endoscopic examination is also performed. In chronic afferent loop syndrome, inflammatory changes in the gallbladder and ducts are often noted. In some cases, pancreatitis develops. In this case, the pancreas also undergoes inflammation. When sowing the contents of the intestines, bacterial flora, a disturbed ratio of pancreatic enzymes are noted. The severity of the disease is determined by the depletion of the body, the amount of bile loss, the condition of the patient.
What is the danger of afferent loop syndrome: complications
It should be remembered that the afferent loop syndrome is a dangerous complication of gastric resection. As a result of constant loss of bile, severe depletion of the body can occur. Food that enters the body cannot be digested normally (due to the "shutdown" of the duodenum and part of the small intestine), and beneficial substances are not absorbed. As a result of the development of intestinal dysbiosis, the gastrointestinal tract undergoes inflammatory processes. With the development of reflux esophagitis, the pains behind the sternum and the feeling of a “coma in the throat” are added to the listed symptoms. Cholecystitis is accompanied by the appearance of bitterness in the mouth, nausea. If inflammation of the pancreas is attached, the pain can intensify, have a girdle character. With prolonged ongoing pancreatitis, diabetes may develop. Complications of acute afferent loop syndrome include peritonitis and intestinal obstruction. These diseases require immediate surgical attention.
Loopback syndrome treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the condition of the patient, the data of laboratory and instrumental studies. It is important to know the severity of the afferent loop syndrome. Treatment can be conservative and prompt. With a mild degree, a special diet, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are prescribed (medicines Cefriaxone, Ciprolet). In some cases, repeated gastric lavage is required. For moderate to severe surgical treatment is necessary. It should be aimed at eliminating stagnation of food. Most often, anastomosis is reconstructed. When the lead loop is bent, it is given the correct position and is hemmed to the peritoneum. The volume and type of surgical treatment may be different and depends on the cause of the complication.
Prevention of adherent loop syndrome
Currently, they are trying to replace the Billroth-2 operation with other surgical procedures. This is done in order to preserve the physiology of the digestive tract. If the Billroth-2 operation was nevertheless performed, it is necessary to carry out all the preventive measures prescribed by the doctor. First of all, diet refers to them. After resection, fatty and heavy foods should not be consumed. You need to take food 6-7 times a day in small portions and in a semi-liquid state (cereals, soups).