Chicken pox or chickenpox is a severe acute infection caused by the third type of herpes virus. This type belongs to the category of viruses with absolute susceptibility. It can take three forms: mild, moderate and severe. How does chickenpox begin? The first signs of the disease are fever and rash. It is considered a characteristic childhood infection, although adults also get sick. We will talk about how chickenpox begins, how long the incubation period lasts, and about the features of the course in children and adults.
The specificity of chickenpox virus
The chickenpox virus has a high degree of volatility and passes from person to person by airborne droplets. Dies when exposed to high and low temperatures, when exposed to ultraviolet rays. Perfectly stored at room temperature. The virus is able to exist for a long time in the air, thus covering distances of up to 20 meters.
Chickenpox incubation period
On average, the incubation period of chickenpox can last from 10 to 21 days. A number of factors affect its duration:
- The situation in which the infection occurred. Indoors, the reproduction of the pathogen occurs with greater intensity. Consequently, the virus accumulates and develops in the body faster.
- Immunity. In infants with poor immunity, the latent period is shortened, and the disease proceeds in severe forms.
- The number of viruses that enter the body.
- Age: In adults, the latent period of the illness lasts longer.
Chicken pox in children
How does chickenpox begin in children? Like other infectious diseases, chickenpox begins in infants in a latent form. After the virus enters the child’s body, it takes time to adapt. After that, the causative agent of the disease begins to actively multiply and accumulate foci in the baby's body. The next step is the distribution of the virus throughout the body. At this stage, the first visible signs of chickenpox appear.
Signs that chickenpox is starting
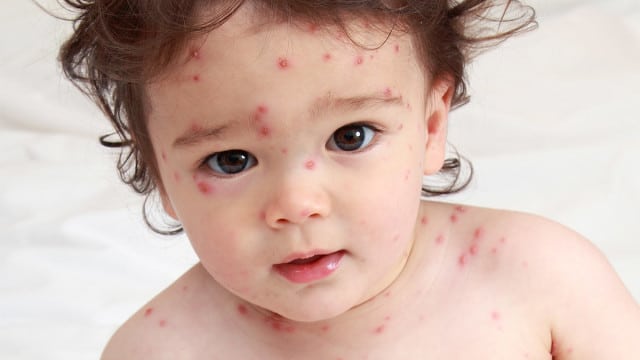
Cough, runny nose and mild fever are signs of chickenpox in children. A sick child can lose his appetite, become moody and whiny. At this stage, chickenpox can be confused with acute respiratory infections. At the next stage, rashes appear in the form of red pimples. The first rashes arise on the scalp, face and neck.
The main symptoms of chickenpox
How does chickenpox begin? Symptoms are as follows:
- The initial manifestations are similar to the common cold. Weakness, headaches, drowsiness, and loss of appetite.
- Elevated body temperature. In a patient with chickenpox, body temperature rises from 37 ° to 38 ° C. In severe form, it can rise to 39 ° C or more. An increase in temperature can last 3-5 days, sometimes a week. The entire period of the appearance of new rashes is accompanied by fever.
- Enlarged lymph nodes. In a person suffering from chickenpox, in some cases, growth of lymph nodes can be noted. This happens when the virus enters the lymphatic system and begins to actively share there.
- Rash. By this sign, anyone can recognize chickenpox. Small red spots, similar to insect bites, appear on the 2nd day after a fever. First, rashes appear on the scalp, then on the face, neck and arms. Over time, a rash can cover all parts of the body, and even the oral cavity and the whites of the eyes. The rash is filled with fluid and turns into small pimples. After a couple of days, pimples begin to dry. In this place, crusts appear, which hold for another 1-2 weeks. Typical for chickenpox is the presence of several types of rashes at once: specks, acne and crusts.
- Severe itching. The appearance of new pimples is accompanied by severe itching. To avoid serious complications, pimples can not be scratched. It is especially difficult to control babies who comb wounds.
Light form of chickenpox. Symptoms
Often in preschool children there is a mild form of chickenpox. In a baby who has chickenpox in a mild form, the temperature may not rise above 37.5 ° C or remain normal. There are few rashes and they practically do not cause inconvenience.
But even after having chickenpox in a mild form, a person receives immunity to this disease. And re-infection with chickenpox is quite rare.
How does chickenpox begin in adults? First signs
Previously, chickenpox was considered only a childhood disease, in adults it almost did not occur.
However, the deterioration of the ecological state of the environment, addictions and frequent stresses led to malfunctions of the immune system. As a result of these, the manifestations of childhood diseases in mature people today are much more frequent.
The development of the disease in the 18-year-old is the same as in people of retirement and pre-retirement age. But due to chronic diseases existing at this age, people over 50 have more episodes with complications.
Where does chickenpox start from?
Chicken pox begins like flu or a cold, with a general malaise. After this, reddish spots appear on the head and face. Strong intoxication of the body occurs, as a result, the body temperature rises. The rash spreads throughout the body. In an adult, rashes often occur on the genitals, this serves as a source of acute pain during urination. Initially, a rash of liquid appears on the rash, which bursts after a couple of days, leaving a dry crust. With proper treatment, it will soon disappear.
An adult develops a lot more rash than a child, and it lasts longer. The rash causes severe itching. But combing rashes during chickenpox is categorically impossible. In wounds, a secondary infection can occur that will leave scars on the body.
In adults, serious complications can occur that can affect the internal organs and even the brain.
Complications of chickenpox
The following complications are possible:
- Stomatitis. Sores in the oral cavity can lead to severe stomatitis.
- Vulvitis and inflammation of the flesh of the glans penis. Rashes and ulcers can lead to secondary genital infections.
- Loss of vision. Chicken pox may appear on the white of the eye. The bubble leaves a scar behind it, which can cause deterioration or even loss of vision.
- Tracheitis, laryngitis and chickenpox pneumonia. Dense chickenpox rashes on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract provoke a sore throat and cough. Weakened immunity can provoke chickenpox pneumonia.
- Encephalitis and meningitis. Chickenpox virus can damage nerve cells and meninges. In this case, the coordination of movement is disturbed in the patient. Possible loss of consciousness and nausea.
Chickenpox during pregnancy
The most wonderful period in the life of every woman is pregnancy. But at the same time, he is the most disturbing and exciting. During pregnancy, it is extremely undesirable to get chickenpox.
If the expectant mother suffered chickenpox in childhood, you should not be afraid. A threat awaits those women who have not met with this virus.
In women carrying a child, the symptoms and development of the disease are the same as in other people. The disease passes in the same form, pregnancy does not provoke specific complications. The danger of contracting the chickenpox virus for the expectant mother is primarily a threat to the baby. The first trimester and the last week before childbirth are considered the most critical.
How to protect yourself from chickenpox to expectant mothers? During pregnancy planning, test for antibodies to chickenpox virus. If there are no antibodies, consider vaccination. In this case, the pregnancy will need to be postponed for a couple of months.
If pregnancy has already occurred, it is too late to be vaccinated. In this case, try to exclude being in children's groups. After all, children suffer from chickenpox more often than adults. Do not contact people who suffer from shingles, because the causative agent of chickenpox is the same virus as with this disease.
If you have had contact with a chickenpox patient, consult a doctor immediately.
Features of the treatment of chickenpox
Chickenpox is a viral disease. Therefore, taking antibiotics does not give an effect. It is justified only in the case of the development of a secondary bacterial infection.
There are no specialized medicines and specific treatment for this disease. But there are several methods that can help cope with chickenpox:
- If the body temperature rises above 38 ° C, it is necessary to take antipyretic drugs. It is worth remembering that aspirin is not recommended for chickenpox. Its use can provoke liver disease.
- Frequent heavy drinking will help to quickly remove the virus from the body.
- Diet. During illness, it is advisable to exclude fried, spicy and sweet foods, alcohol and caffeinated drinks. Such a diet complicates the treatment process, the body spends a lot of energy on processing such food. Give preference to lean food, steamed.
- Do not comb chicken rash. A bacterial infection can enter the damaged wound and cause complications.
- If itching cannot be tolerated, take antihistamines.
- Avoid suppuration of chickenpox rashes with the help of antiseptic agents.
- Do not wear heavy or tight clothing. Give preference to cotton fabrics. This will allow the skin to breathe and relieve you of unnecessary discomfort.
- Change clothes and bedding more often. Take care not to sweat excessively. Wet sweaty laundry will intensify itching and speed up the spread of rash.
- Do not use a washcloth or other detergent while bathing. Take a bath with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- Create a favorable microclimate. To prevent a viral infection from accumulating in the room, ventilate every 3-4 hours. Watch for humidity and air temperature.
If a patient with chickenpox begins vomiting, breathing problems and a partial loss of coordination, consult a doctor immediately! Remember, self-medication may not give positive results, but only exacerbate the situation. Only the attending physician may prescribe suitable therapy.
If possible, a patient with chickenpox should exclude all contacts with healthy people. The isolation period should last at least a week. In pre-school and school educational institutions, quarantine lasts three weeks.