Any of the diseases of the digestive system requires a long and systematic treatment. Gastroduodenitis, the symptoms of which are caused by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, occurs in almost every second adult person. The etiology of this disease is diverse, so it may take longer to find and eliminate its true cause than to combat symptoms and treatment.
Gastroduodenitis - what is this disease?
Inflammation of the pyloric stomach and duodenal mucosa negatively affects the functionality of the entire gastrointestinal tract. As a result of the progression of the disease, the pancreas, liver and bile ducts are significantly affected, so it is extremely undesirable to delay its treatment.
In adults, the symptoms of gastroduodenitis appear without fundamental differences. In old age, this disease is extremely rare. Gastroduodenitis mainly affects adolescents, young men and women. This fact can be argued by the fact that it is this category of patients that often makes mistakes in nutrition, abuse alcohol and smoking.
Suspect inflammation of the gastric mucosa in a patient for a number of specific symptoms. Gastroduodenitis is treated after a series of diagnostic procedures, the reason for which is weight loss in a very short time and pain during palpation of the abdomen.
Types of disease
Depending on the etiological factor, primary and secondary gastroduodenitis are distinguished. Primary implies types of inflammation of the gastric and duodenal mucosa caused by external stimuli - harmful food products, aggressive chemical agents. Exogenous causes of gastroduodenitis also include infection with Helicobacter pylori, a helical bacterium that lives in the pylorus of the stomach. By the way, when this microorganism is detected, an HP-positive form of pathology is diagnosed, and in the absence, an HP-negative form.
Secondary pathology occurs under the influence of endogenous factors. Often, against the background of disorders of the endocrine and immune systems, diseases of the pancreas and liver, characteristic symptoms of gastroduodenitis in adults arise. The treatment of this ailment must be started without delay, since it can have serious complications. We will pay attention to the consequences of progressive gastroduodenitis a little later, but for now we will return to other varieties of the disease.
Depending on the duration and severity of the course, distinguish:
- Acute gastroduodenitis. The full cycle of the disease lasts no more than three months. In the acute form, the entire pyloric department and the duodenum are affected, which leads to a disruption in the motility of the digestive system, and prevents the normal passage of food entering the body. Without treatment, the symptoms of gastroduodenitis intensify, often the pathology goes into the chronic stage.
- Chronic gastroduodenitis. The disease develops mainly against the background of the acute stage as a result of untreated gastritis or the absence of any therapy at all. The duration of the course of this form of the disease can be different, therefore, drug treatment of chronic gastroduodenitis, the symptoms of which are much similar to gastritis, is carried out with each exacerbation.
The depth of mucosal lesions and the type of inflammatory process that is determined during instrumental diagnostics distinguish such forms of gastroduodenitis:
Form name | Description and features of the course |
Catarrhal | The mildest form, in which the surface of the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed, however, erosion is still absent on the membrane, the glands function satisfactorily. |
Hypertrophic | There is a thickening of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum due to prolonged inflammation, the formation of folds and outgrowths. |
Erosive | Numerous ulcerations, minor erosions on the mucosa are characteristic. With this form of the disease, intestinal cells may appear in the stomach, which normally should not be. This disorder is called metaplasia of the intestinal epithelium. |
Mixed | In many ways, the disease is similar to hypertrophic gastroduodenitis, but with a mixed form, erosive foci also occur. |
Depending on the level of acidity of the gastric environment, gastroduodenitis is distinguished:
- with increased secretory function of the stomach;
- with a normal level of acidity;
- with reduced secretion (often leads to the appearance of malignant tumors).
Provocative factors
Given that all forms of this disease can be caused by various causes and manifest uneven symptoms, treatment of gastroduodenitis in adults can also be carried out according to different schemes. However, before proceeding with the treatment of inflammation of the gastric mucosa, it is important to determine the very provocative factor. The most common causes of gastroduodenitis are:
- the inclusion in the diet of products containing chemical irritants (preservatives, stabilizers, dyes, pesticides);
- poisoning by stale food;
- long-term medication;
- regular consumption of hot spices and seasonings;
- acute infectious diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract;
- non-compliance with the diet;
- stress, frequent experiences that lead to increased secretion of gastric juice.
The mechanism of occurrence of gastroduodenitis involves the development in the pyloric department of an inflammatory reaction that impedes the natural physiological regeneration of the mucosa. In most cases, this disease occurs due to the combined influence of factors, which include nutritional errors, helicobacter pylori damage, and psychogenic disorders. In combination, their action leads to a weakening of the secretory and motor functions, therefore, with gastroduodenitis, a decrease in the tone and motility of all parts of the gastrointestinal tract is noted.
Symptoms of gastroduodenitis in adults
Treatment of a chronic form involves the neutralization of the symptoms of the disease, which interfere with normal health and performance. The uncomfortable manifestations of gastroduodenitis are extremely diverse, and their severity directly depends on the nuances of the pathology. Among the main clinical signs of this disease, it is worth noting:
- soreness in the epigastric region (aching or cramping pains);
- nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- bad taste in the mouth;
- a feeling of constant fullness of the stomach;
- constipation or diarrhea.
Symptoms of superficial gastroduodenitis in adults, the treatment of which seems to many to be unnecessary, over time, general manifestations may join. The most common - increased fatigue, pallor of the skin, irritability, dizziness, weight loss, insomnia. Signs of the disease become more pronounced after its transition to erosive gastroduodenitis. The treatment and symptoms of this form of the disease are different from the manifestations and therapy of catarrhal inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Pain with an erosive type of gastroduodenitis is more intense, often accompanied by severe heartburn, vomiting, and difficult to stop even with medications.
In contrast to the acute stage, the chronic course is less pronounced. With a prolonged course of the disease, the patient experiences mild, but constant pain, which intensifies during the relapse. For the chronic form of gastroduodenitis is characteristic of:
- discomfort in the stomach, manifested after eating;
- nausea;
- yellow plaque on the tongue, slight swelling;
- pain in the peritoneum during palpation;
- upset stool;
- irritability;
- losing weight;
- fast fatiguability.
What is dangerous gastroduodenitis
At first sight? it may seem that this disease does not pose a particular threat to health, and therefore its treatment can be postponed until later. In fact, the consequences of gastroduodenitis can significantly complicate life.
A patient who is diagnosed with catarrhal gastroduodenitis should be wary of the transformation of superficial mucosal inflammation into ulceration. The erosive chronic form has specific clinical manifestations, including intense and prolonged pain, dyspeptic syndrome, heartburn, and intestinal disorders. If the disease progresses, the wounds begin to bleed. Ignoring the need for diet and treatment, the symptoms of gastroduodenitis in adults are supplemented by internal bleeding. At an advanced stage, the disease can degenerate into an ulcer, affecting the walls of organs. Peptic ulcer disease is a favorable condition for the formation of a cancerous tumor.
In chronic gastroduodenitis with low acidity, iron deficiency anemia often occurs, immunity weakens, and pathologies such as:
- enterocolitis;
- dysbiosis;
- diarrhea;
- pancreatitis
In addition, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum often leads to deterioration of the condition of teeth, hair, nails, and skin.
How to recognize pathology
Symptom descriptions for treating chronic gastroduodenitis in adults are not enough. The doctor must necessarily examine the patient, listen to his complaints, draw up a detailed medical history and, on the basis of the received picture of the disease, prescribe additional instrumental and laboratory diagnostics. A set of research procedures:
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy - an examination of the stomach and duodenum with an endoscope, thanks to which you can objectively assess the condition of the mucosa and the walls of organs.
- Fluoroscopy. This research method is not carried out in every case. If necessary, they resort to it to differentiate gastroduodenitis from other pathologies with an identical clinical picture. X-rays with a contrast agent also make sure the evacuation properties of the stomach.
- Clinical blood test. The results of this study can indirectly confirm the symptoms of exacerbation of gastroduodenitis. They say about the treatment of pathology if the patient has overestimated leukocyte and ESR.
In addition to the above procedures, to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor can prescribe anthroduodenal manometry - a study conducted to study the motor function of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment
Symptoms of gastroduodenitis in children and adults can have a different degree of severity, which is due to the etiology and form of the course of the disease in each case. If the disease proceeds without complications, its therapy can be carried out at home. With erosive gastroduodenitis and severe symptoms of superficial gastroduodenitis, treatment is carried out in the department of gastroenterology.
To stop an exacerbation, one medication course and a strict diet are enough. In the event of repeated episodes of the disease, one can not do without repeated consultation of the doctor, drawing up a plan of proper treatment and nutrition. The symptoms of gastroduodenitis can be dealt with using a therapeutic program based on compliance with:
- bed rest for two weeks;
- the strictest diet (table number 1);
- the regimen of taking drugs, in particular antibiotics against Helicobacter pylori and drugs that regulate the secretory function and motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
Gastroduodenitis Medication
The choice of medications depends on the concentration of the acidic environment, impaired motility of the intestines and stomach, the degree of damage to the mucous membrane. It is impossible to engage in self-medication - this can only aggravate the course of the disease. The use of any of the drugs indicated in the article is possible only after the recommendation of a doctor. The specialist will not only select the appropriate medicine, but also correctly determine the individual dosage, duration of the course.
With severe and uncomfortable symptoms, treatment of gastroduodenitis with drugs gives good results after the first use. With this disease of the stomach are used:
- Antimicrobials and antibiotics (Flemoxin Solutab, Klacid, Rulid, Furazolidone, Azithromycin, Metronidozole). Their purpose is a direct effect on the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Together with an effective effect on pathogenic microorganisms, antibiotics partially destroy the beneficial microflora, provoking intestinal dysbiosis.
- Antacids. Preparations of this pharmacological group reduce acidity and envelop the mucous membrane with a protective film, protecting it from damaging factors. In addition, antacids are prescribed for severe heartburn. The most effective and popular drugs are Almagel, Gastal, Maalox, Fosfalugel, Vikalin, Vikair, Omez, Nolpaza.
- Antispasmodics and painkillers. The action of these drugs is to eliminate spasms and pain in the digestive tract - "No-spa", "Drotaverin", "Duspatalin."
- Enzyme preparations (Mezim, Panzinorm, Abomin, Penzital, Creon). They are prescribed if gastroduodenitis occurs against a background of pancreatic damage.
- Vitamin complexes and fortifying drugs.
Nutrition rules
With timely initiation of therapy, the absence of exacerbations and the implementation of all medical prescriptions, the prognosis will be favorable. However, in addition to taking medications, it is equally important to follow a diet and a proper diet. Otherwise, after some time, all the symptoms of gastroduodenitis in adults will return, and treatment with drugs will be useless.
In the predominant number of cases, patients are advised to adhere to table No. 1. When observing this diet and treating gastroduodenitis, the symptoms will gradually disappear, but in order to prevent their return, the patient will have to adhere to dietary restrictions for a long time. In addition, the diet is designed to normalize the liver and bile secretion.
The essence of the diet for gastroduodenitis is the minimum consumption of refractory fats, but a sufficient intake of proteins and carbohydrates. All products must undergo heat treatment, be it meat, fish, fruit or vegetables. You can’t eat food fresh. Vein meat and vegetable fiber must be crushed to a puree state. It is important to remember that:
- Food consumed should be at normal temperature, not too hot or cold.
- Chew food thoroughly.
- It is necessary to eat fractionally: in small portions with small intervals (no more than 2 hours).
The gastroenterologist makes an individual diet for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of his digestive system, general condition and other factors. So, for example, with erosive gastroduodenitis it is allowed to eat cottage cheese, non-acidic and low-fat kefir, cream is allowed. As main dishes, patients are recommended mucous porridges, soups, egg omelets. Of meat products, preference should be given to boiled or steamed river fish, chicken, rabbit meat. Fruits and vegetables (pumpkin, beets, carrots, cauliflower, apple) should be eaten only in baked or stewed form.

If the patient suffers from gastroduodenitis with high acidity, it is necessary to abandon bread, vegetables (especially tomatoes), coffee, black tea. With low acidity, the basis of the diet should be hard cheeses, dry biscuits, soups on low-fat broth, but the vegetables in them should be chopped as much as possible. It is also recommended to eat greens, berries and fruits, drink fermented baked milk and kefir.
With the catarrhal form of gastroduodenitis, the basis of the daily menu should be boiled or baked vegetables, low-fat sour-milk products, jelly, stewed fruit, mineral water without gas.
ethnoscience
It is not worth hoping for the effectiveness of alternative methods alone, however, as an auxiliary method that will help fight the symptoms of gastroduodenitis, treatment with folk remedies is ideal. Before using any of the recipes described below, you should always consult your doctor:
- A decoction of fresh mint. You can use dry vegetable raw materials. To prepare one glass of a medicinal drink, you need 1 tsp. peppermint. You need to drink the broth on an empty stomach, while it is important that it is not hot.
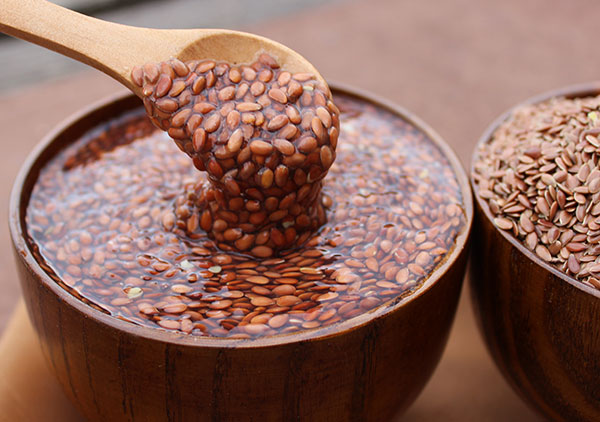
- Flaxseed infusion. Preparing a tool in this ratio: 3 tbsp. l seeds of 1 liter of boiling water.Literally in 15-20 minutes the mixture will swell and acquire a jelly-like consistency. The substances that are contained in flax seed have an enveloping property, so you need to drink the infusion every day for half a glass on an empty stomach.

- Oat broth. This folk remedy for the treatment of gastroduodenitis has a healing effect. To cook it, you need unpeeled oats. Grains (1 tbsp. L.) Pour cold water and put on fire. The broth must be boiled for 15 minutes, and then removed from the stove. Before using the drink you need to brew. Take 100 ml before meals.
- Infusion of calendula. The healing properties of this herb have long been known. One tablespoon of plant material will be enough to prepare 500 ml of infusion. Take three times a day, 100 ml.
A few words about the prevention of gastroduodenitis
In order not to get sick with this ailment, it is important to follow a few simple rules:
- Eat regularly and avoid long time intervals between meals.
- From night snacks should be abandoned once and for all.
- Daily use of fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese.
- Minimize the intake of fast carbohydrates.
- Exclude the use of alcohol, sweet soda, fast food.