Diphyllobothriasis is a parasitic disease, accompanied by a predominant lesion of the digestive tract, as well as megaloblastic anemia. Its causative agent is a large tapeworm - broad tapeworm (D.latum), whose length can reach up to 10 m, as well as more than 10 species of less studied tapeworms from the genus Diphyllobothrium.
The causes of the disease
Human infection with diphyllobothriasis occurs when invasive, insufficiently thermally treated or poorly salted fish products are consumed, as well as when cutting fish and processing dishes after it is of poor quality. Moreover, the ingestion of helminths in the human body occurs according to a long chain.
Method for the distribution of diphyllobothriasis
The tapeworm eggs mature in fresh water with a temperature of 10-20 ° C for about a month. Then, coradiation embryos are separated from them, which, in turn, are eaten by small crustaceans, for example, copepods. This is the first intermediate stage of infection in which helminth larvae, plerocercoids, are formed. Then the second stage occurs, when a freshwater fish, such as pike, ruff, perch, burbot, trout, etc., eats crustaceans, and in its body the larvae complete their development to the stage of a mature individual. And only after that the helminth finds its final owner and, accordingly, the source of invasion - a person, or, less commonly, a representative of fish-eating animals, for example, a pig, fox, bear, seal, etc. It is in their organisms that a mature helminth already parasitizes, whose eggs go out during defecation and with the sewer fall into fresh water, starting a new chain of infections.
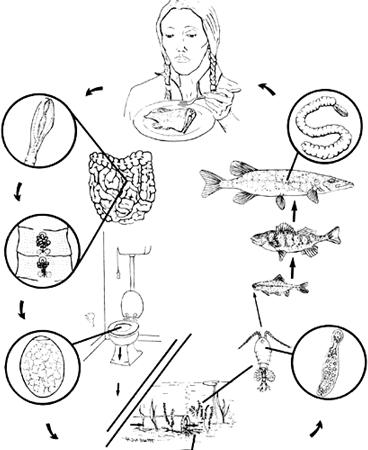
The wide ribbon in the intestine, parasitizing in the intestine, consists of several thousand segments (proglottids) containing eggs and is firmly attached to the walls of the donor’s small intestine with the help of two slits (botria) located on its head end. And although the length of the parasite sometimes reaches 10 meters, there are often cases when several worms coexisted in the same human body.
Geography of the spread of the disease
Human diphyllobothriasis is most common among residents of regions with a temperate cold climate, where the main food of the population is fish and its caviar. The disease occurs in European countries, especially in the Scandinavian, Japan, South America, Africa, USA, Canada, and Russia.
Pathogenesis and pathoanatomical picture of diphyllobothriasis
Once in the human body, a wide ribbon has a pathogenic effect on it of a mechanical, toxic-allergic and neuro-reflex nature. Firstly, it is an infringement of the intestinal mucosa by botria when the helminth is attached to the walls. As a result of this, atrophy and necrotization of the mucosa occurs. Parasite metabolism products provoke autosensitization processes. Substantial endogenous hypoavitaminosis of folic acid and vitamin B12 is observed, which, together with intoxication of the body with the vital products of the parasite, in 2% of cases provokes the development of megaloblastic anemia. The duration of the invasion is up to a dozen years.
Symptoms of diphyllobothriasis
From 20 to 60 days - this is the incubation period that has diphyllobothriasis, symptoms in a person begin to appear only after this period. It is during this period that helminths acquire sexually mature forms, attach to the walls of the intestine and begin to function. Diphyllobothriasis begins to manifest itself gradually. Attacks of nausea, belching and vomiting, bloating , epigastric pain, poor appetite, impaired stool are all symptoms accompanying early diphyllobothriasis. A photo of a person with diphyllobothriasis of a later stage will invariably depict him with a noticeable pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, and the patient himself will suffer from fatigue, dizziness, weakness, abdominal pain, paresthesia, hepatosplenomegaly, tongue fissures (later the surface of the tongue becomes smooth).
There are tachycardia, hypotension, drowsiness, systolic murmur at the apex, the noise of a top. Laboratory tests of the blood of an allegedly infected patient show the following picture: decreased hemoglobin, low red blood cells, an increase in direct bilirubin, high color score, neutropenia, leukocytosis, and elevated ESR. The severity of anemia, as well as the severity of the course of the disease, is affected by the intensity of helminthic invasion, the presence of concomitant diseases, the general resistance of the body, the quality and quantity of food consumed.
For severe form of diphyllobothriasis, funicular myelosis is characteristic, which is expressed by a violation of deep sensitivity, leg weakness, unsharp paresthesias. In some patients, allergic rashes (urticaria) appear on the skin, and the size of the liver and spleen increases. In isolated cases, epileptiform (convulsive) seizures, numbness of the limbs, instability when walking were recorded. Like these ones diphyllobothriasis has serious symptoms, and treatment of this disease should be started immediately after its diagnosis. A prolonged course of diphyllobothriasis causes intestinal obstruction.
But, it is worth noting that diphyllobothriasis, whose symptoms consist of an impressive list of ailments, sometimes has an absolutely latent (asymptomatic) course of the disease, in which infection is detected only with the detection of parasite fragments in the feces.
Diagnosis of diphyllobothriasis
The basis for the diagnosis of "human diphyllobothriasis" are the patient's complaints and relevant laboratory data. Blood eosinophilia (with recent invasion), as well as thrombocytopenia and leukopenia, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate and hyperchromic anemia can be a suspected disease. A megaloblastic type of hematopoiesis is characteristic of the disease. The analysis indicates a large number of young forms of red blood cells (megaloblasts, normoblasts, polychromatophiles, poikilocytes, etc.). An important role in the diagnosis is played by the epidemiological history: the facts of the patient being in the endemic zone, eating raw freshwater fish or under-salted caviar. But the final analysis is put only when the analysis of feces of the patient shows the presence in it of eggs or segments of a wide ribbon.
There are cases when patients come who notice fragments of the parasite in their own feces.
It is important not to confuse Addison-Birmer anemia and diphyllobothriasis, whose symptoms are very similar. For this purpose, gastric contents are checked for the presence of Castle factor, absent in anemia.
Diphyllobothriasis: treatment
If the patient is diagnosed with diphyllobothriasis, treatment is carried out immediately in a hospital. With severe anemia, a course of vitamin therapy (B12, folic acid, iron) is prescribed before the start of helminth excretion procedures. Vitamin B12 is administered as an intramuscular injection of 200-500 mcg 2 or 3 times a week. The duration of vitamin therapy is 30 days.
For deworming, drugs such as Biltricid, Praziquantel, Nicklozamide or Azinox are used. Also, the drug "Fenasal" can be used to remove the parasite. All drugs are taken orally and have a paralyzing helminth effect. As a result of this, the parasite loses its ability to stay inside the intestine and goes outside. It is very important to make sure that the tape comes out completely. To achieve the final result, cleansing the intestines with an enema is possible.
The effectiveness of such drug treatment is about 95%, only in rare cases complicated by intestinal obstruction, dehelmentation is carried out operatively. Patients with a diagnosis of diphyllobothriasis, whose treatment has successfully passed the stage of deworming, go to the follow-up with a fecal analysis every month for six months.
Folk remedies
In folk medicine, pumpkin seeds and a decoction of them are traditionally used to expel helminths. Pumpkin seeds, raw or dried, are ground with water and honey and taken in an amount of 300 g. on an empty stomach in portions for an hour. This method perfectly fights such a problem as human diphyllobothriasis. Feedback on successful deworming using pumpkin seeds allows you to verify the effectiveness of this method.
Diet, nutrition
During the treatment of diphyllobothriasis, the patient must adhere to a sparing diet, excluding products that have an irritating effect on the intestinal mucosa. It is advisable to include in the diet foods with a high content of vitamin B12, as well as folic acid.
Features in children
Helminthic infestations by children are much more difficult, the symptoms of anemia and hypovitaminosis in young patients are more pronounced.
Prevention of diphyllobothriasis
If you are a lover of freshwater fish and live in the northern regions near water bodies, then in order not to fall on the hook of such an unpleasant disease as human diphyllobothriasis, its prevention should become your life rule No. 1.
In order to avoid infection with diphyllobothriasis, freshwater fish only well-cooked or fried, as well as its caviar, only qualitatively salted, should be eaten. It is necessary to strictly observe the rules of hygiene when cutting fish and preparing dishes from it.
You should know that when salting fish, depending on the concentration of salt, the larvae die only after 2-7 days. Helminth eggs during salting of eggs die in half an hour at 10% of the mass fraction of salt in relation to the weight of the eggs. If salt is 5%, then the product becomes safe for food no earlier than 6 hours, at 3% - no earlier than two days.
Helminth larvae also die during deep freezing (for 2-4 days at a temperature of -18 ° C, a week later at a temperature of -6 ° C).
When making a diagnosis to a patient, it is imperative to examine all members of his family, since in this case they are at risk.
On a global scale, in order to minimize the likelihood of infection, it is necessary to reduce the percentage of intermediate carriers in water bodies by reducing or eliminating the discharge of feces into lakes and rivers, ensuring sanitary control over this process, as well as the general condition of coasts, beaches and fish products coming to food enterprises industry and store shelves. Care should be taken in medical facilities to monitor the occurrence of symptoms inherent in a disease such as diphyllobothriasis. Treatment with confirmation of the diagnosis should be started immediately and with a mandatory check of all family members for the presence of invasion.
Features in pregnant and lactating
Helminthic invasion, namely, hypovitaminosis and anemia with it, is a great danger to both the health of the expectant mother and the development of the fetus. Pregnant women should be especially careful when eating fish and caviar. It is important not to miss the first signs of a disease such as diphyllobothriasis, symptoms that can easily be confused with the manifestation of toxicosis (preeclampsia), and urgently apply for a laboratory examination of feces for the presence of helminth eggs in it.
Treatment of the disease in pregnant women is carried out by a method that is safe for the health of the unborn child. So, for deworming to pregnant and breast-feeding women, such drugs as Biltricid are not prescribed, but they use a safe folk remedy - pumpkin seeds. In some cases, breast-feeding with a diagnosis of human diphyllobothriosis treatment It is recommended that medications be taken by the method of taking standard drugs for diphyllobothriasis, and infants are transferred to artificial feeding.