Syphilis has been walking the planet for centuries, and has already been studied quite well. To date, innovative methods of diagnosis and treatment have been developed, but still the number of its victims is growing. In Russia alone, over the past quarter century, their number has increased by 7 times.
Syphilis in the tongue and in the oral cavity is less common than on the genitals, but no less dangerous. The main feature of this form is that in the mouth on the mucous membranes and in the tongue it is easy to confuse it with completely harmless diseases, which is why many patients do not rush to the doctor, but are self-medicating and lose time. But with syphilis, the prognosis of healing completely depends on the timeliness of the treatment started.
Consider how syphilis manifests itself in the language, how it can be infected, how dangerous it is for others and what methods of treatment have been developed.
Pathogen portrait
Syphilis causes a microscopic microbe - anaerobic, whose name is "pale treponema." She is called pale because in reactions according to Romanovsky-Giemsa she becomes pale pink. Its microscopic body has the appearance of a thin spiral with pointed ends and the 12th or 14th, less often 8th curls. These parasites are very mobile, but not particularly tenacious. They are able to withstand the environment with t = 55 ° C for only 15 minutes, and when boiled, that is, at t = 100 ° C and above, they die instantly. They are also easily destroyed by any disinfectants, even ordinary household soap. Therefore, in order not to catch syphilis on the tongue in the household way, you just need to observe hygiene.
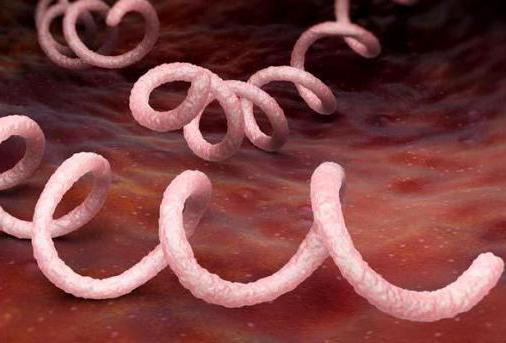
A distinctive feature of treponem is that they feel great only in warm and humid environments. In the cold, as well as under the influence of certain medications, they can form cysts and wait in the wings for years. In the heat, especially without a drop of moisture, they die as the wet substrate dries. Treponemia reproduce by simple division, and quite slowly. Usually, the process of creating a new bacterium lasts 32 hours. This feature affects the duration of the incubation period.
Infection pathways
The one who believes that syphilis in the tongue can be picked up only during oral sex with an unreliable partner is mistaken. According to WHO statistics, approximately half of patients become infected with this disease. The rest are infected with pale treponema in the mouth in other ways:
- a kiss with a patient with syphilis (traumatic, deep);
- transfusion of unverified donated blood;
- a visit to an unscrupulous dentist working with non-sterile instruments;
- injecting several people with a single syringe (mainly drug addicts);
- use of a toothbrush, spoon, glass after a patient with syphilis;
- treponem transmission from mother to fetus (congenital syphilis);
- infection of infants during breastfeeding;
- infection of health workers.
Infection mechanism
The manifestation of syphilis in the tongue is possible if the pale treponema managed to penetrate the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. In oral sex, the transmission mechanism is simple. Treponema is always massively present in the patient's semen, even if visually his genitals do not have signs of the disease.
Once in the mouth of a new victim, bacteria try to penetrate the mucous tissues. Especially beneficial for the parasite if they have wounds. In this case, infection occurs with a 100% probability. Treponema is detected in the saliva of a patient with syphilis only if he has characteristic rashes in his mouth. This determines the percentage of chance of infection with a kiss.
The spiral form of their body helps bacteria to penetrate into the intercellular space of tissues, thanks to which they “screw in” like a corkscrew, and once inside, they begin to multiply. The victim’s immune system directs antibodies, macrophages, and lymphocytes to the aggressors. If the human immunity is very strong, and contact with the patient was one-time and short-term, it is possible to stop the disease. But more often, agents of the immune system can not cope with an army of parasites that have penetrated the body, in which, to protect the body, they are covered with capsule-like mucus. Treponemas multiply, initially filling the lymphatic fissures, since oxygen in the lymph is only 0.1%. Then they penetrate the blood and begin to travel through the body, affecting other organs.
Classification
In world practice, the following classification of syphilis is used:
- primary;
- secondary (early and late);
- congenital.
Each of these forms has its own symptoms of syphilis of the tongue.
More commonly used is a simpler classification:
- early syphilis (easier to diagnose, more contagious, symptoms may disappear without leaving a trace);
- late syphilis (spread to all organs, although it could start in the oral cavity).
In medicine, there is a slightly different classification of syphilis:
- primary (seronegative and seropositive);
- secondary (fresh, hidden, recurrent);
- tertiary (open, hidden);
- congenital (early and late);
- visceral.
The process of the disease is divided into four stages:
- incubation;
- primary;
- secondary;
- tertiary.
Let's consider them in more detail.
Incubation period
There are no signs of syphilis in the tongue at the very beginning of the disease. This is a hidden stage, which lasts from the moment of penetration into the mucous membranes of the microbe until the first visual symptom appears.
At this time, treponemas increase their numbers and slowly spread with lymph flow through the body. The immune system is still able to wage active struggle with them, significantly reducing their number. A person does not yet feel that he has become infected, although for others he is already becoming dangerous. The incubation period can last from 15 to 60 days. It is considered to be average terms of 20-21 days. Faster symptoms appear in people weakened by other diseases (tuberculosis, AIDS, alcoholism). Symptomatic delay is observed if the patient takes antibiotics during the period of syphilis infection, treating tonsillitis, gonorrhea, and other concomitant ailments.
Primary period
It occurs with the advent of hard chancre, and ends with its disappearance and the appearance of a rash. The word "chancre" in translation from Old French means "sore." This formation, as a rule, is painless, dense, appearing at the site of the introduction of treponem into the tissue. On the surface of the chancre, erosion that does not cause painful sensations may be located.
Similarly, syphilis in the tongue appears in the primary period. The photo shows a solid chancre on the surface of the tongue. It goes through several stages of development, starting with a small red spot. Within two or three days, a seal appears in its center, which gradually increases in diameter. In parallel with this, in the center of the chancre, the tissue is necrotic and acquires a red (meat) color.
If you take a scraping from such a place, thousands of treponemas will be found in it. Sometimes ulcers in the center of the chancre are covered with a whitish coating. When it is located in the area of the folds of the tongue, some people experience crevice erosion. When located on the back of the tongue, it usually protrudes above its surface.
Another important symptom is regional lymphadenitis (enlarged lymph nodes). If syphilis occurs in the mouth, the lymph nodes increase under the jaws and chin, and sometimes in the neck.
Features of the primary period
Tongue ulcers in syphilis, if there are no other symptoms of infection (malaise, fever, headache, etc.), many patients take for anything (for example, stomatitis), but not for a sexually transmitted disease. This is especially true for people who have not entered into dubious sexual relations and who have become infected by the household. Therefore, they begin to treat their ulcers with rinses, they burn them with iodine. Treponema does not kill such methods, but a person who has chancres on the tongue or on other parts of the oral cavity (on the gums, lips) becomes very contagious, because bacteria from the ulcer constantly enter the saliva. However, when coughing and sneezing, syphilis is not transmitted, only through a kiss, a cigarette, dishes.
The analysis for RW (Wassermann reaction) at the first stage can be either negative (seronegative form) or sharply positive with four pluses (seropositive form).
Secondary period
It is marked by the disappearance of chancre, which many people perceive as a "cure for stomatitis." With classical syphilis at this stage, a rash appears on the palms, feet, throughout the body. In addition, there is a lesion of the nervous system. About the same symptoms characterize syphilis in the tongue. The photo shows how rose spots appear, which can appear along with papules (plaques). If they occur in the area where the papillae are well defined, they protrude above the surrounding tissues in the form of grayish foci with clearly defined or, on the contrary, uneven edges. But more often there are no papillae at the site of the lesion, and then the papule becomes like a glossy, pinkish-cyanotic, located below the neighboring sites. The tongue at the same time begins to resemble a meadow slanted in separate pieces.
Some patients at the beginning of the secondary period appear weakness, headache, fever, which is perceived as a mild cold. Patients make this “diagnosis” especially confident if their merging red spots spread to the tonsils and throat, which is very similar to a trivial sore throat. The main difference is that with syphilis there is no pain when swallowing.
The secondary period begins at about 9–10 weeks after infection and at 6–7 weeks after the appearance of the first chancre, and lasts from two years or more. At this stage, there is a systemic lesion of all internal organs, and the rash and spots on the tongue with syphilis can either completely disappear or appear again.
Tertiary period
In the advanced state of the disease, many internal organs (bones, liver, heart, spleen) are affected. The patient's immunity is weakened and cannot significantly affect the course of the disease. However, exacerbations and remissions at the tertiary stage can be traced. They are caused by trauma, stress, poor nutrition, and other diseases, such as an elementary cold.
Classically, the tertiary period begins 4.5–5.0 years after infection, but many cases are known when it began 10 or more years later. The main sign of its onset is the appearance of gum - nodes in tissues that significantly deform organs. The tongue looks quite characteristic with syphilis of the Tertiary period, therefore it is no longer possible to confuse this sexually transmitted disease with a cold or sore throat.
Gummas in the tongue can cause nodular or diffuse glossitis. The latter is considered the most severe complication of syphilis in the mouth. Due to diffuse infiltration, the patient’s tongue thickens, becomes denser, which is inconvenient when pronouncing sounds. Subsequently, scar tissue appears at the site of the infiltrate, the tongue becomes even more dense, the papillae are smoothed, the surface becomes tuberous, and painful cracks and ulcers appear on it, which can give rise to malignant tumors. Despite such unpleasant symptoms, the patient is less dangerous for others, since there are almost no treponemes in the gums.
Diagnostics
An experienced doctor can determine syphilis in the tongue by external manifestations, but most often a number of tests are prescribed to the patient. The most common, but also the most inaccurate, is RW. At the serological stage, it can give a negative result in a sick person, and in a healthy one, with positive conditions such as:
- pregnancy;
- tuberculosis;
- malaria;
- blood diseases;
- after anesthesia;
- during menstruation.
PCR analysis is more accurate, but it gives the correct answer only at the primary and secondary stages of syphilis development. In addition, such reactions are used to detect treponema: RIBT, RIF, RPGA, RIT, RPR, KSR.
None of these methods are 100% accurate, so two analyzes are usually performed to get the right result. For their conduct, the patient gives fasting blood from a vein. The second type of test for syphilis is scraping from solid chancre, papules and nodules of the rash, but it is effective only in the primary and secondary stages of the disease.
A positive result is indicated by “++++” or “+++”. In addition, one more confirmatory analysis is required.
The dubious result is indicated by “++” or “+”. In this case, the diagnosis is repeated after 10-12 days.
Syphilis treatment in the tongue
Since treponema is very sensitive to mercury, syphilis was previously disposed of with drugs based on it. With the discovery of penicillin, to which treponema is also very sensitive, this practice is a thing of the past. For several decades, penicillin preparations have been used to treat syphilis. Only if the patient has an allergy to them, they are replaced with "Erythromycin", "Cephalosporin", "Tetracycline." Sometimes aminoglycosites are also used, which are also able to suppress treponemal growth, but they must be taken in too high doses, which is unsafe for the patient.
In addition to treating a person who has been diagnosed with syphilis, all who were in contact with him should undergo a diagnosis and, if necessary, a course of therapy.
Forecast
The primary and secondary stages of syphilis of the tongue with proper therapy can be cured by almost 100%, but keep in mind that treponemas are able to protect themselves from the effects of drugs. If the situation is unfavorable for them, they stop violent activity, form cysts and begin to wait. As soon as the treated person has a decrease in immunity, they again form the usual spiral-shaped forms and begin to multiply. Therefore, after completing the course of therapy every 3 months, patients pass control tests. It lasts 2 years. Then, for another year, tests are submitted every 6 months. After this, a complete examination of the patient is carried out, with good results it is deregistered.
The tertiary stage of syphilis is also being treated now, but the begun deformations of the tongue are no longer being restored. Also, the deep stellar scars remaining after gum do not disappear.