Along with dermatological diseases such as dermatitis, psoriasis, mycosis, eczema on the hands is quite common. Questions about the medical treatment of this disease do not lose their relevance. Despite the fact that eczema is a non-infectious disease, its breadth is striking: every year eczema is diagnosed in a huge number of patients of any age, gender, social status.
To date, the pharmaceutical industry offers many drugs to combat dermatosis, but practice more often shows that pharmacy medicines do not permanently cure eczema on the hands. As a rule, the ailment is amenable to therapy, but it very quickly acquires a chronic course, subsequently alternating with remissions and relapses. In this article, we will look for answers to a question about the features of the course of eczema on the hands, symptoms, causes of this disease, and medical methods of treatment.
What is this disease
Eczema is a complex inflammatory reaction of the upper layer of the epidermis. Scientists are not yet able to say exactly what provokes this dermatological disease, but it is also known that the pathology has a neuro-allergic nature of origin. Skin lesions with this type of dermatosis are not a clinical manifestation of a bacterial or fungal infection, therefore, without a doubt, the question of whether eczema on the hands is contagious can be answered. Unlike mycoses, lichen, scabies, herpes, this disease is not transmitted from person to person.
Eczema can occur in acute, subacute and chronic form. In the first case, we are talking about pronounced signs of the disease. The subacute form of eczema is characterized by a partial attenuation of inflammation on the skin, its roughening and slight thickening. In chronic dermatosis, which, incidentally, is diagnosed in a predominant number of visits to a dermatologist, the pathological process develops slowly. But even during the period of calm of the disease, changes on the skin remain: it becomes pale, dry, acquires the likeness of a scaly structure.
Why does eczema appear?
Dermatosis can affect almost any area on the body. Most often, the manifestations of the disease are found on the face, scalp, elbows, legs, fingers and palms. The main difference between existing types of eczema on the hands are the probable causes of their occurrence. But, despite the polyetiology of the disease, one can still identify several generalizing factors that serve as a favorable soil for the development of dermatosis in the hands of any kind and form:
- hypersensitivity of the skin to allergens (sensitization);
- hereditary predisposition to skin diseases;
- weakening of immune functions.
Separately, it is worth noting the circumstances that play the role of a trigger in the development of a pathological process on the skin. In this sense, the causes of eczema on the fingers can be considered:
- Improper unbalanced diet. This implies an excess in the diet of fatty foods, processed foods, preservatives and a deficiency of nutrients entering the body from natural products.
- Lack of B vitamins, omega-3 fatty unsaturated acids.
- Helminthiasis, the presence of chronic infectious and inflammatory foci in the body.
- Exposure to allergens (detergents, cosmetics, animal hair, insect bites, synthetic fabrics, plants, etc.).
- Ignoring hygiene and sanitary standards for skin lesions.
- Unstable psycho-emotional state, stress, overstrain.
- Intestinal dysbiosis, accompanied by disorders in the digestive system.
- Failures in metabolic processes, hormonal imbalance.
- Renal pathology.
True eczema
The causes of the disease are largely the determining factors in the treatment. But, as already mentioned, scientists have only assumptions about the nature of the origin of eczema on the hands or any other parts of the body.
The biggest "mystery" for dermatologists is the etiology of the idiopathic (true) form of the disease - the main reason has not yet been established. But nevertheless, the researchers warn that those persons whose relatives were diagnosed with eczema are most prone to its development. In addition to the hereditary predisposition, the health of the endocrine system and the state of the digestive tract also play a role. Some scientists believe that true eczema on the hands occurs against a background of vegetative-vascular dystonia, lack of sleep, and mental disorders. At least, the appearance of dermatosis in the arms of women who have just given birth is often associated with this factor.
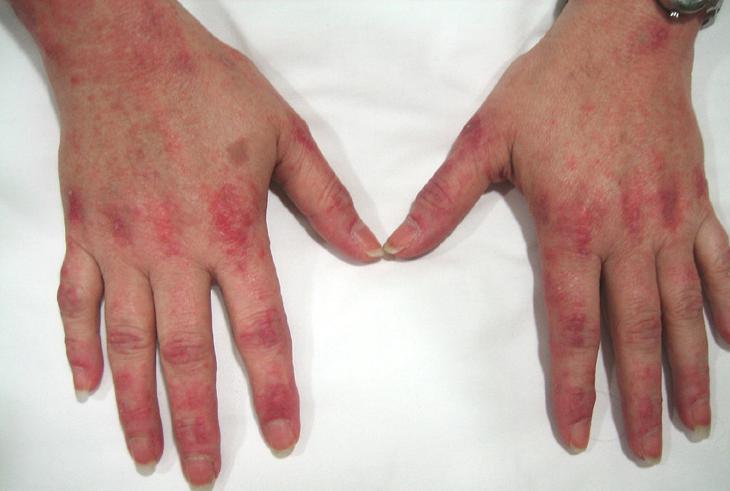
The course of the pathology is characterized by an acute onset. The patient has erythema of the affected area, mild swelling, small vesicles appear (small densified nodules). As the rash progresses, the rashes increase, the vesicles become like blisters, which, after a few days, open and leave wet serous wounds in place. When erosion begins to crust, they speak of a regression of the disease.
Dyshidrotic eczema
Another skin disease, the origin of which is partly a mystery to doctors. The main reasons for its development are still unknown. At the same time, dermatologists believe that dyshidrotic eczema often occurs in people with increased sweating. Rashes are localized mainly on the fingers, palms, lateral areas of the hand, soles.
This type of dermatosis proceeds according to the scenario described above. True, unlike true eczema on the hands, the wetting stage does not last so long. Lingering, erosion turns into a compacted brownish crust. The skin at the site of the lesion coarsens over time.
Microbial eczema
This type of dermatosis is provoked by the activity of pathogenic microflora. Usually, the pathological process develops in the area of damage to the skin, around wounds, cuts, burns infected with microbes due to non-compliance with hygiene rules. Treatment of microbial eczema on the hands is carried out with the mandatory use of antibacterial drugs.
Externally, dermatosis is manifested by exfoliation of the upper layer of the epidermis along the edges of the wound, peeling or secretion of exudative fluid, followed by the formation of a crust. A characteristic feature of microbial eczema is purulent elements, severe itching.
A subspecies of this type of disease is mycotic dermatosis. Its name speaks for itself: this eczema is provoked by a fungus. Considering that any yeast is an alien organism for us, like the products of their metabolic processes, immunity begins to actively fight them. However, if the protective functions are weakened, too many antibodies are produced, which eventually begin to “attack” the tissues of our body.
Many believe that microbial and mycotic eczema on the hands is a contagious disease. In fact this is not true. Dermatosis is not transmitted from one person to another, but pathogenic microbes and fungi may well infect by penetrating tissues through wounds on the surface of the skin.
Allergic types of disease
This group of dermatoses includes atopic and occupational eczema. The atopic form is provoked by the reaction of the immune system to an irritant, which can be anything you want, starting from household dust and animal hair in the house, ending with food and medicine. Externally, atopic eczema is different from previous varieties of dermatosis. This ailment manifests itself in the form of an abundant vesicular rash on hyperemic edematous areas of the skin, but passes the stage of weeping. Atopic eczema can be distinguished from other skin lesions by the painful dryness of the integument, peeling and intolerable itching.
Occupational eczema also has an allergic nature of origin. This type of dermatosis is associated with labor, as eczema occurs against the background of prolonged contact with chemicals, dyes, formaldehydes. Most often, exposed areas of the skin suffer, so the disease is mainly localized on the palms and fingers.
Unlike microbial and idiopathic therapy, treatment of eczema of an allergic group does not always imply the use of medications. Often with an uncomplicated course of the disease, it is enough to simply exclude contact with the stimulus.
How to cure eczema on the hands
Therapy for this skin disease is specific in nature due to the causes. In addition, an infection can join the skin lesions in the true, allergic or dyshidrotic form, which will complicate the course of the disease and prolong the duration of treatment. Dry eczema on the hands usually heals faster than wet.
The treatment regimen is developed by a dermatologist individually for each patient, taking into account the type and form of the disease, the stage and nature of the course, the characteristics of the patient’s body, age. But no matter what drugs the doctor prescribes, the success of treatment will depend on how thoroughly the patient himself approaches the solution to this problem. In addition to using medicines to treat hand eczema, it’s important to:
- follow a diet;
- Do not ignore the rules of hygiene;
- lead a healthy lifestyle without stress and bad habits.
After the onset of remission, you can not lose vigilance, since the disease can worsen at any time when exposed to any adverse factor. For prophylactic purposes, it is advisable to use safe hypoallergenic detergents with natural ingredients.
Ingestion
Therapy of dermatosis in the hands consists of two components: systemic treatment and the use of local drugs.
Drops and tablets for eczema on the hands are taken in order to eliminate hypersensitivity to irritants, to have a desensitizing effect. First of all, it is necessary to exclude neurogenic factors of the disease. With a mild form of the disease, plant-based sedatives are prescribed:
- Persen
- Sedasen
- Novo-Passit;
- tinctures of valerian, motherwort, peony.
If they do not bring a real therapeutic effect, tranquilizers are prescribed to the patient (Nozepam, Phenazepam, Chlozepide).
In order to relieve intoxication, enterosorbents are prescribed to the patient. In most cases, use:
- "Multisorb";
- Enterosgel;
- Atoxil
- "Filtrum";
- Polysorb.
Basically, hormones for eczema are applied locally to the affected areas of the skin. But at the advanced stage of the disease or in the case of the attachment of a bacterial infection, glucocorticoids in tablets are indicated:
- "Corticotropin";
- Prednisolone
- "Dexamethasone";
- "Triamcinolone."
Hormonal drugs have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect, trigger the process of regeneration of the skin, but they can not be used independently. The thing is that the drugs of this group have a list of contraindications and side effects, drink them in short or intermittent courses. In addition, with uncontrolled use, steroids can be addictive and they are suitable only for the treatment of dry eczema on the hands.
In parallel with anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of eczema, antihistamines are taken. Their use is an important component of complex therapy, because it is anti-allergic medicines that fight swelling, burning and itching with eczema on the hands. Among the antihistamines that are used for dermatoses, it is worth noting:
- Ebastin
- "Cetirizine";
- "Tsetrin";
- "Zodak";
- Loratadine
- Claritin
- Lorahexal;
- Erius
- "Desal."
During the lull of the disease, patients are advised to seriously engage in strengthening the immune system. Vitamin-mineral complexes containing vitamins of groups E, B, C, folic and nicotinic acid can help in this. More often they are prescribed in combination with immunomodulators:
- "Polyoxidonium";
- "Immunofan";
- "Plazmol";
- "Timogen";
- echinacea extract.
External treatment
Local therapy is carried out by applying external funds. They help relieve itching, reduce the severity of inflammatory edema, hyperemia, trigger tissue repair processes and strengthen local immunity. When choosing an effective ointment for eczema on the hands, it is important to consult a doctor, since not all of the drugs available in the pharmacy assortment can be bought without a prescription and used independently.
With the development of microbial eczema, antiseptic and antibacterial solutions (Gentsianviolet, Methylviolet), ointments (Polcortolon, Levovinisol) are used, lotions are made with Resorcinol. If a small surface area is affected, pharmacy formulations with an anti-inflammatory effect are used:
- Zinc Sulfate
- "Copper sulfate";
- "Silver nitrate";
- "Phenol solution";
- "Podophyllin ointment";
- Diphenhydramine Paste.
In the subacute stage of eczema, an indifferent type of drug is used (Galascorbin, Boric Acid, Tanin, Boric Zinc Ointment, Ichthyol Ointment). Their application can give a good result in the absence of puffiness, ulcers, weeps.
In chronic eczema, the use of non-hormonal formulations based on zinc, tar, and ichthyol is often sufficient to inhibit the course of the disease. However, in the case of disease progression and the development of relapse, glucocorticosteroid ointments are often indispensable:
- "Elokom";
- Prednisolone
- "Hydrocortisone";
- "Celestoderm";
- Advantan
- Lokoid
- Sinaflan
- Afloderm;
- "Flucinar."
If an infection joins the pathology, combined hormonal preparations with an antibiotic are selected:
- Lorinden S;
- "Trimistin";
- "Travocort";
- Cremgen.
What needs to be changed in the diet
Limited nutrition for eczema can alleviate the course of the disease and significantly reduce the severity of its symptoms. Ideally, a diet should be not just a necessary measure for the period of recurrence of chronic dermatosis, but a completely new and constant style of nutrition in patients whose dermatoses are allergic in nature.
Diet with eczema on the hands implies an exception to the daily menu:
- hot spices and seasonings;
- canned and pickled dishes;
- sausages and fast food;
- fruits and vegetables of red color, including tomatoes, strawberries, bell pepper, apples;
- chocolate and its derivatives;
- mayonnaise, ketchup, various sauces;
- honey;
- nuts
- whole milk;
- egg white.
In addition, during an exacerbation of dermatosis, it is advisable to abandon rich meat broths, fatty fried meat, smoked meats, cheeses, alcohol and coffee.
To alleviate your condition with eczema, not following a diet, is almost impossible. During relapses of the disease, you should adhere to a safe hypoallergenic diet, consisting mainly of plant and fermented milk products. Preference should be given to:
- low-fat kefir, cottage cheese;
- boiled chicken, turkey, rabbit;
- vegetable oils;
- cereals;
- fresh vegetables and fruits.
In conclusion
Today, there should not be any difficulties in choosing drugs for the treatment of eczema, because among the current pharmacy range you can find a suitable option for any type of disease. In this case, it is not necessary to self-medicate, and to select medicines only after consulting a doctor.
Remember, eczema on the hands is not a contagious disease. At the same time, a person suffering from dermatosis needs to be careful not to use personal hygiene items to prevent infection and, as a consequence, exacerbation of the disease. Especially vulnerable are patients with eczema at the stage of weeping - the immune system weakens, and erosive foci serve as an affordable, almost unhindered entrance for pathogens.