Polycystic ovary syndrome is a common problem that many women face. The formation and proliferation of multiple cysts is usually associated with hormonal disorders. If untreated, the disease leads to infertility. That is why it is worth learning more about this pathology.
Why does polycystic ovary syndrome occur? How to treat a similar pathology? What symptoms cannot be ignored? Is it possible to get pregnant with a similar disease? The answers to these questions are interesting to many women.
What is a disease?
What information about the pathology does the ICD contain? Is polycystic ovary syndrome dangerous? What are the symptoms associated with? This information is sought by many patients.
So, polycystic ovary syndrome (ICD-10 assigned pathology code E28.2) is a disease in which multiple small cysts form in the tissues of the ovaries. As a rule, the ailment is associated with hormonal problems.
What is the mechanism for the development of polycystic ovary syndrome? The pathogenesis of the disease is well understood. Increased secretion of estrogens, androgens and insulin leads to disruption of the growth and maturation of eggs. From immature follicles, cystic structures begin to form.
The neoplasms themselves are small, with a dense shell and liquid contents inside. In most cases, cysts appear in two ovaries. The presence of such structures in approximately 25% of patients leads to infertility.
Two forms of pathology are distinguished depending on the origin.
- Primary polycystic ovary syndrome is the result of congenital malformations. This form can occur in girls during the formation of menstrual function.
- The secondary form of the disease develops in adulthood and, as a rule, is associated with acquired pathologies of the endocrine glands or previously transferred inflammatory lesions of the organs of the reproductive system.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Causes
Unfortunately, this is a very common pathology. Why does polycystic ovary syndrome develop in women? In fact, the reasons may be different.
- Often the disease develops against the background of pathologies of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. The fact is that in the pituitary gland follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones are synthesized, which are responsible for the growth and development of follicles, ovulation processes. Against the background of an increase in the level of these hormones, overproduction of androgens in the tissues of the ovary is observed, which leads to the appearance and development of cysts.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome may be associated with insulin resistance of cells. An increase in insulin levels affects the functioning of the entire endocrine system. In particular, the amount of synthesized androgens and luteinizing hormone increases. Such changes lead to an active growth of follicles. However, none of these structures matures - premature aging of the follicles sets in, which increases the likelihood of the formation of multiple cysts.
- Risk factors also include an excess of male sex hormones, which also disrupts the growth and maturation of eggs in the ovaries.
- There is a genetic predisposition. To date, there is no data that would confirm the hereditary transmission of the disease. Nevertheless, women in the family who had people with a similar ailment are at risk.
- It is worth noting that taking certain medications is also a risk factor. It is also proved that against the background of obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome proceeds in a more severe form. By the way, according to statistics, about 40% of patients are overweight.
- Risk factors also include stress, a sharp change in climate, transferred infectious diseases (if the patient has the prerequisites for the development of pathology).
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Symptoms
Sometimes the pathology proceeds without the appearance of any specific signs - in some patients the disease is diagnosed by chance. But in most cases, a number of disorders appear that indicate the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome. Symptoms in women can be different.
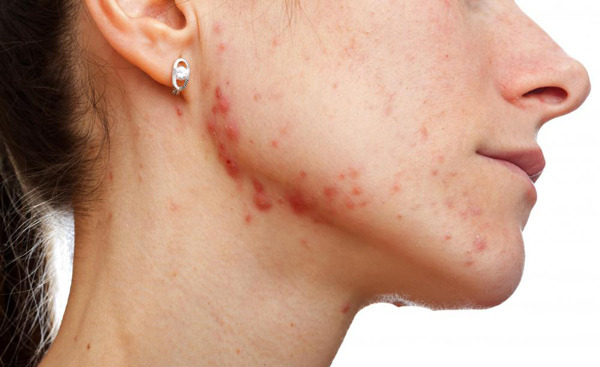
- Pathology primarily affects the menstrual cycle. It becomes irregular - prolonged periods of menstruation are possible up to their complete absence (amenorrhea). There are violations, and sometimes the disappearance of ovulation. Sometimes long delays of menstruation are replaced by full uterine bleeding.
- Since the processes of egg maturation are impaired and there is no ovulation, women develop infertility.
- An increase in androgen levels leads to an increase in sebum production. Patients suffer from seborrhea, increased greasy hair. The skin is covered with acne and blackheads. Such violations are permanent and practically do not respond to symptomatic treatment.
- A very characteristic sign of polycystic is obesity. The patient’s body weight increases sharply by 10-15 kg for no apparent reason (the woman continues to eat in the usual way). At times, body fat is distributed evenly throughout the body. But due to an increase in the level of androgens, male obesity is possible. Excess fat accumulates in the waist and abdomen.
- Obesity, metabolic disorders of carbohydrates and lipids sometimes lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Enhanced body hair growth is possible: an increase in the level of male sex hormones leads to male-type hair growth - “antennae” appear above the upper lip, hair growth is observed on the chest, abdomen, and inner thighs.
- Many women complain of chronic pain in the lower abdomen. Soreness is moderately pronounced, pulling in nature. Sometimes the pain spreads to the pelvic region and lower back.
The presence of such violations cannot be ignored. If untreated, the pathology leads to complications.
Possible complications
How dangerous can polycystic ovary syndrome be? The reviews of experts indicate that with early diagnosis and proper treatment, the disease can be dealt with. However, in some cases, the disease leads to the development of certain complications.
- Pathology is accompanied by hormonal disorders, as a result of which the patient does not ovulate. This, in turn, causes infertility.
- A prolonged course of the disease, the lack of therapy may result in the appearance of malignant tumors in the tissues or cervix.
- It is also believed that polycystic ovary, coupled with diabetes and obesity, increases the likelihood of developing breast cancer.
- Hormonal disruptions lead to a disruption in the normal metabolism of fats. Overweight, coupled with metabolic disorders leads to disruption of the heart and blood vessels. That is why atherosclerosis, stroke, myocardial infarction are included in the list of complications.
Diagnostic measures
What to do if you suspect polycystic ovary syndrome? The symptoms described above are a good reason to see a doctor. Do not self-medicate or try to determine the problem yourself, as this can be dangerous.
How to identify polycystic ovary syndrome? Diagnosis in this case includes a number of procedures.
- First, an anamnesis and a general examination are necessary. The doctor draws attention to the physique, examines the skin and mucous membranes, notes the nature of hair growth, notes all the symptoms that may indicate hormonal disorders.
- The following is a standard gynecological examination and palpation of the abdomen. So the doctor may notice a tightening or enlarged ovary.
- Mandatory is an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. During the procedure, you can notice an increase in the ovaries, confirm the presence of cysts.
- Dopplerography helps to evaluate the nature of the blood flow in the ovaries.
- The patient also gives blood for analysis. It is necessary to determine the level of estrogens, progesterone, androgens, cortisol, insulin, pituitary hormones.
- Also, the blood is checked for the presence and level of lipids - this makes it possible to detect metabolic failures.
- Magnetic resonance imaging gives the doctor the opportunity to get an accurate image of the ovaries, determine the size, location and number of cysts.
Based on the results, the doctor can make a diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome. Treatment in this case will depend on the form and stage of development of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Conservative treatment
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely get rid of a disease such as polycystic ovary syndrome. In this case, treatment is aimed at restoring the normal cycle, stimulating the ovulation process (if the patient wants to become pregnant), reducing the external manifestations of the disease (skin inflammation, hairiness), normalizing the metabolism of carbohydrate and fat metabolism.

- If there is a violation of the metabolism of carbohydrates, then patients are prescribed hypoglycemic drugs, for example, Metformin. Drugs help normalize blood glucose levels.
- If the patient tries to become pregnant, stimulation of ovulation is necessary. For this purpose, as a rule, the drug "Clomiphene" is used, which ensures the release of the egg from the ovary. As a rule, the medicine begins to be taken on the 5-10th day from the beginning of the menstrual cycle. According to statistics, such therapy in 60% of cases ends with ovulation. In approximately 35% of patients, it ends in fertilization.
- To restore the normal menstrual cycle, combined hormonal contraceptives are used.
- Sometimes the drug "Veroshpiron" is included in the treatment regimen. This is a potassium-sparing diuretic, which also reduces the level of androgens in the body of a woman, blocks their effect. Such therapy lasts at least six months and helps to get rid of uncharacteristic hair growth, normalize the sebaceous glands.
Proper diet
A sharp increase in body weight is one of the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome. Clinical recommendations apply to nutrition. During therapy, it is very important to normalize the metabolism and maintain body weight within normal limits.
- Per day, patients are advised to consume no more than 1200-1800 kcal.
- Food should be fractional. Women should eat often (at least 5-6 times a day), but in small portions.
- Be sure to include fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet. They are rich in vitamins and fiber, but also low-calorie.
- It is important to provide the body with proteins. The menu recommends the inclusion of cottage cheese, low-fat meats, fish, seafood.
- The amount of animal fat should be limited. The daily norm should not exceed 80 g. You can replace these products with vegetable fats, which are more useful.
- It is necessary to sharply cut or refuse sugar, baking, honey, jam, sweet drinks, in a word, from everything in which there is a large amount of glucose.
- Experts also recommend abandoning canned foods, spices, spices, sauces, pickled products, smoked meats.
- 1-2 days a week you need to spend fasting days. For example, you can eat all day only apples, cottage cheese, kefir. Almost any mono diet will do.
- It is recommended to give up alcohol, since ethanol negatively affects the work of the whole organism.
Physiotherapy
It is worth noting that taking medications is not the only thing that is required with a disease such as polycystic ovary syndrome. Doctors' recommendations also relate to the patient's lifestyle.
Of course, an important part of therapy is proper nutrition. In addition, physical activity is recommended. It's about feasible activity, whether swimming, Pilates or long walks. The fact is that subcutaneous fat deposits are an additional source of androgens. Weight loss will not only positively affect the figure and well-being, but also help to normalize the hormonal background.
Galvanophoresis using lidase is effective. This procedure allows you to activate the enzymatic system of the ovaries. It also improves the functioning of organs. The course of treatment, as a rule, consists of fifteen daily procedures.
It should be understood that therapy with such a disease must necessarily be comprehensive. Do not count on a quick and complete cure.
Surgical intervention
In most cases, medical treatment, coupled with physiotherapy and a proper diet, is enough to maintain the normal functioning of the endocrine system. Nevertheless, sometimes you can not do without surgery. Surgery is usually used to treat infertility. Most often, laparoscopy is performed. Special equipment is introduced through small incisions. There are two methods of surgery.
- A wedge-shaped ovarian resection involves the removal of ovarian tissue in which androgen hormones are synthesized.
- Electrocauterization of the ovaries consists in the point destruction of the structures of the ovaries, which are responsible for the synthesis of "male" sex hormones. This is a less traumatic procedure that allows you to maintain the maximum number of healthy tissues.
It is worth noting that during a laparoscopic operation, the doctor has the opportunity to eliminate the mechanical causes of infertility, for example, cut adhesions between the walls or eliminate the obstruction of the fallopian tubes. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and is considered safe.
In the future, conservative treatment is carried out. Often, two weeks after the operation, the first ovulation occurs. However, the restoration of a normal menstrual cycle sometimes takes 6-12 months. If ovulation is still absent for 2-3 cycles, then the patient is prescribed the same “Clomiphene”.
It is worth noting that even after successful fertilization and the birth of a child, the risk of relapse is high. According to statistics, often polycystosis is activated 5 years after undergoing therapy. That is why the patient should be registered with a doctor, undergo examination twice a year and take tests. The sooner a relapse is detected, the easier it is to stop its symptoms and prevent the development of possible complications.
Preventive measures and forecasts
It is worth noting that it is impossible to completely get rid of such a pathology. Nevertheless, the therapy started in the early stages allows women to avoid such an unpleasant consequence as infertility (they inevitably end with polycystic ovary syndrome). IVF, taking hormones, stimulating ovulation - all this helps a woman to become a mother.
Unfortunately, specific prophylaxis does not exist. Women are advised to monitor the health status and regularity of the cycle, and if there are disturbing symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. Remember that once every six months you need to undergo a preventive gynecological examination. It is also important to monitor the diet, keep fit, treat inflammatory and infectious diseases on time.
During puberty, the girl must be explained what should happen to her body. Since cysts often begin to form during the formation of the menstrual cycle, girls are also advised to undergo preventive examinations and periodically undergo tests.