An infectious disease that affects the elements of the temporal bone of the human skull due to the purulent inflammatory process of the middle ear is mastoiditis. What it is, for what reasons it arises and what consequences it may lead to - all issues will be considered in our article. However, in order to understand the nature of the origin of the disease, it is necessary to understand the definition of the mastoid process and the anatomical structure of the human skull.
The structure of the skull. Temporal bone
The human skull is formed by a combination of bones, which are conditionally divided into two large groups - the bones of the brain and facial bones.
In addition to these bones, in the cavity of the middle ear there are three types of paired bones - a malleus, a stapes and an anvil. Temporal bone is a bone from the group of the brain that forms the base of the skull. In the temporal bone, a whole complex of nerve trunks:
- vestibule-cochlear,
- facial,
- trigeminal nodule
- wandering,
- glossopharyngeal nerve.
The temporal bone consists of three areas: scaly, tympanic and stony. The scaly area forms the lateral walls of the skull; the drum part is an element that surrounds the auditory canal on all sides; the stony part looks like a pyramid and serves as a reservoir for the middle and inner ear, through which also pass the blood vessels. The pyramid includes three surfaces - front, back and bottom. The lower region forms the mastoid process.
The concept and structure of the mastoid process
The mastoid process is a protrusion of a conical shape located behind the ear. The internal structure of the mastoid process is a collection of bone cavities filled with air and communicating with the middle ear (with the tympanic cavity) through the mastoid cave. The cave (antrum) is the largest cell of the mastoid process. A muscle consisting of three components is attached to the
mastoid process - the sternum, clavicle and mastoid.
The structure of the appendix is individual for each person. There are three types of its structure. Pneumatic structure - the mastoid process consists of large cells filled with air. Diploetic structure - the structure is small cells filled with bone marrow. Sclerotic structure - the cellular structure is very weakly expressed.
It should be noted that the course of mastoiditis depends very much on the type of structure of the mastoid process. And in most cases, mastoiditis develops in individuals with the pneumatic structure of the mastoid process.
Mastoiditis: what is it?
Mastoiditis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the mucous membrane of a cave (antrum) or in the cellular structures of the temporal bone. Pathology is classified according to various signs. Usually, two forms of the disease are distinguished - primary and secondary mastoiditis.
As noted earlier, the mastoid process communicates with the tympanic cavity. Most cases of mastoiditis occur due to infection in the mastoid process due to inflammation of the middle ear. This clinical picture speaks of secondary mastoiditis as a complication of chronic otitis media.
The most common cause of acute mastoiditis are streptococci and staphylococci, less commonly, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. There are very rare cases in which the disease is caused by mycobacteria.
Primary mastoiditis is a pathology that can develop:
- Due to an injury caused by a gunshot wound or a fractured skull.
- With the transition of the purulent process to the bone tissue of the mastoid process from the lymph nodes.
- Due to specific diseases - tuberculosis or infectious granulomas.
The process of the onset of the disease is as follows. Injuries occur multiple fractures of thin partitions in the bone, resulting in the formation of small fragments, which, together with spilled blood, create a favorable environment for the melting of bone fragments and the development of progressive inflammation.
Stages of the disease
As a rule, the development of mastoiditis undergoes two stages:
- exudative
- proliferative alternative.
The initial stage of development of mastoiditis is exudative, it lasts 7-10 days. During this time, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mastoid process develops. The mucous swells, the cells of the mastoid structure are closed, filled with purulent mass and are separated from the mastoid cave. The x-ray at this stage of the course of the disease illustrates the barely visible partitions between the cells.
The proliferative-alternative stage of the course of the disease is characterized by the destruction of the partitions separating the cells and the emergence of separate groups of cells that merge into bulk cavities. Changes also occur in the bone marrow and vascular structures.
Sometimes the development of cholesteatoma in the middle ear can cause various pathological processes in the body, including mastoiditis. What it is? A cholesteatoma is a capsule consisting of keratinized epithelial cells.
Mastoiditis: Symptoms
The treatment of mastoiditis is a long and laborious process. Therefore, in order to achieve success in this matter, it is very important to identify the disease at the earliest stages. Depending on how the symptoms of mastoiditis are manifested, a typical and atypical form of the disease is distinguished. An atypical or latent form of the disease is characterized by a sluggish course without pronounced symptoms.
In a typical form of mastoiditis, patients may complain of a sharp pain in the ear and head, which extends to the back of the head or forehead; swollen area of the mastoid process. With a sharp swelling of the tissues, especially when a purulent process forms in them, the auricle protrudes markedly.
In this case, the presence of the disease can also be indicated by altered indicators of a blood test due to the inflammatory process that has occurred.
The course of mastoiditis may be accompanied by the development of Gradenigo syndrome, in which paralysis of the abducent nerve occurs. The patient has limited mobility of the eyeball from the side of the affected ear.
Photophobia may develop. These symptoms often indicate limited inflammation of the meninges, the symptoms of which are manifested in vomiting, dizziness, and unilateral headaches.
Signs of mastoiditis are similar to symptoms of furunculosis of the outer ear, as well as inflammation of the lymph nodes located behind the auricle. Since these nodes are located in the central region of the mastoid process, they provide lymph movement throughout the auricle. In a healthy state, each lymph node is easily palpated. With the disease, all lymph nodes are smoothed. With mastoiditis, pressure on the nodes does not cause pain, on the mastoid process - it causes; with adenitis, everything is exactly the opposite.
Compared with the course of the disease in an adult, mastoiditis in children can be characterized by nonspecific signs and can be expressed in loss of appetite, diarrhea, increased irritability, discharge from the outer ear.
Atypical forms of mastoiditis
In addition to the typical forms of the disease, atypical forms of mastoiditis are distinguished in medicine. The most common forms include:
- zygomaticitis,
- apical cervical mastoiditis with four subspecies,
- squame
- petrozite.
Zygomaticitis is a type of mastoiditis in which the inflammatory process extends to the zygomatic process, there is swelling of the cheekbone in the area in front of the auricle. After edema, an abscess forms.
In childhood, “false” forms of zygomatic cells can occur - an abscess that does not affect the cells of the root of the zygomatic process. Since only a cave is well developed in children, they often develop anthritis - an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane of the antrum of the mastoid process. Previously, this disease led to high infant mortality.
Squamate is a purulent process that affects the temporal bone.
If the inflammatory process begins in the pyramidal region of the temporal bone, petrositis occurs. By the way, petrozites develop slowly.
Types of apical cervical mastoiditis
The apical cervical mastoiditis includes:
- Betzold mastoiditis is a pathology in which pus spreads to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and a swelling occurs in the area of the apex of the mastoid process. The focus of the pathology may not be visible on the lateral projection of the tomography of the temporal bone. The symptom of this form of mastoiditis in the initial stage is poor neck mobility.
- Chetelli's mastoiditis is a pathology in which pus penetrates the posterior surface of the mastoid process.
- Mastoiditis Mure - a disease in which pus spreads between the muscles of the neck due to inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes, an abscess forms. In this case, a swelling of the neck is observed, subsequently fistulas may form.
- Orleans mastoiditis is a pathology in which edema is formed in the region of the upper section of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, with pain when pressed. However, there is no discharge of pus from the ear, in contrast to the Betzoldovsky mastoiditis.
Diagnostics
As a rule, the diagnosis of mastoiditis is established based on the patient’s medical history. In this case, transferred ear pathologies, ongoing therapy, the presence / absence of complications are taken into account; violation of the general state of health is assessed. In addition, the patient’s complaints, examination and palpation of the ear area, the results of otoscopy, audiometry, laboratory studies of ear discharge, ophthalmoscopy and eye biomicroscopy play an important role in the diagnosis. Computed tomography is a standard method by which mastoiditis is diagnosed. What it is? This type of diagnosis allows you to clearly consider all the structures of the skull and evaluate the extent of development of purulent processes and their distance from the brain and facial nerve. This technique is based on a phased study of the structure of an object - the effect of the influence of x-ray radiation on tissues of excellent density is compared. The data obtained are subjected to complex computer processing.
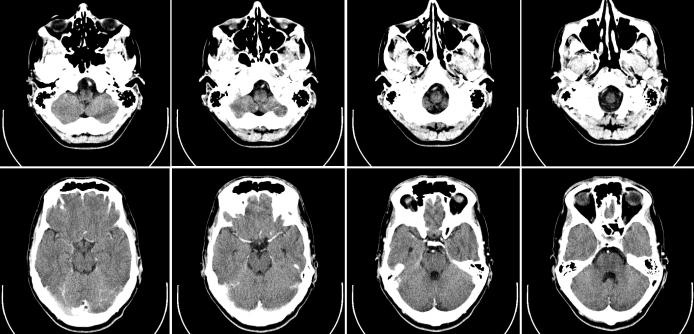
for example, helps to identify fuzzy cell walls as a result of the inflammatory process, which clearly indicates the development of mastoiditis. In addition, with suspected mastoiditis, a clinical analysis of blood and pus from the ear for sensitivity to antibiotics is performed.
In order to make a diagnosis of "mastoiditis", you may need to consult not only an otolaryngologist, but also other specialists - a neurologist, dentist, ophthalmologist, surgeon.
Conservative treatment
Usually, pathology can be stopped at the initial stage. If a person immediately seeks help from a specialist and receives timely therapy (use of antibiotics), the spread of infection ceases and it can be assumed that the patient will not have complications in the future that cause mastoiditis.
Treatment is performed according to the following scheme. First, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. Further, in accordance with the results of laboratory studies of biological material, specific antibiotics are prescribed, which have a narrowly targeted effect on the identified aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Complete elimination of the infection may require long-term antibiotic therapy. This is due to the fact that antibiotics hardly penetrate into the structures of the mastoid process. In addition, relapses of the disease are not excluded, chronic mastoiditis may occur.
At the initial stage of treatment of mastoiditis in the absence of complicating factors in combination with the therapy, physiotherapy (UHF, microwave) can be prescribed. Compresses on the behind-the-ear area have a good healing effect. By the way, they can be both warming and cold.
The widespread use of antibiotics in developed countries has sharply reduced the incidence of mastoiditis and has led to the advantage of conservative treatment methods over surgical ones.
Surgery
Often, drug therapy does not improve the patient’s health. In such cases, resort to surgical treatment of pathological processes that cause mastoiditis. An operation, however, does not negate concurrent conservative treatment.
Among the surgical methods, the most common are myringotomy - an incision in the tympanic membrane - and the introduction of a tympanostomy tube, which allows pus to be removed from the ear. After a certain period of time - from two weeks to several months - the tube spontaneously is removed from the eardrum, and the incision naturally heals.
Antromastoidotomy is an surgical intervention in which the antrum is opened and the mastoid process is trepanized. The purpose of surgery in this case is the complete removal of the affected tissue. There are frequent cases when during surgery the entire process is removed along with its apex. Such a manipulation is called mastidectomy. It is quite complex and resort to it in case of complications or in the absence of positive dynamics in treatment. Children under three years old perform an antrotomy - manipulations on the antrum, since they still have a poorly developed mastoid process.
Complications of mastoiditis. Prevention
If there is no or insufficient treatment, the infection passes to neighboring tissues, which can lead to various complications, for example, hearing impairment, labyrinthitis and, as a result, dizziness, hearing loss. Infection can affect the facial nerve and cause paralysis of the facial muscles. Mastoiditis is often the cause of subperiosteal abscess, the trigger in the development of zygomatitis, squamite, petrozite, otogenic paresis. If the inflammatory process affects the lining of the brain, meningitis develops. The presence of any of the above complications in a patient is an indication for surgical intervention.
The task of both the medical specialist and the patient is to prevent the development of mastoiditis. Disease prevention is closely related to the prevention of middle ear abscess - a pathology called otitis media. Mastoiditis is a disease that cannot be started. Its symptoms and causes must be eliminated in the early stages. Treatment should be qualified and sufficient.
Not the last role is played by human immunity, its ability to resist infection. It is important to care for the nasal cavity and the mouth, to prevent inflammatory diseases in the nasopharynx. An early diagnosis of ear diseases and proper antibacterial therapy helps in the prevention of mastoiditis.
The article highlights information about what mastoiditis is; symptoms, treatment of the disease and its prevention. However, I want to note that the material presented above is purely introductory. Therefore, with any suspicion of a disease, you must immediately seek medical attention from a specialist.