When it comes to diseases of the superficial veins of the lower extremities, in most cases their varicose expansion is implied. However, the spectrum of pathological processes that are associated with leg veins is much wider. It includes even more dangerous pathologies, such as, for example, thrombophlebitis. We will figure out what are the causes of such diseases and what treatment methods are used to eliminate them.
Phlebeurysm
Distinguish between superficial and deep veins of the lower limb.
All arteries of the lower extremities are distinguished by thick and elastic walls with smooth muscles. This is explained by the fact that blood is ejected through them under extreme pressure.
The superficial veins of the lower limb include:
- Profit center or saphenous vein;
- BVP - a large saphenous vein;
- skin veins located under the back of the ankle and plantar zone.
Varicose veins are a pathology of the venous walls. With varicose veins, the venous walls expand and become thinner, as a result of which the blood flow through them is disturbed. The disease is associated with decreased venous tone and insufficiency of their valves. The outflow of blood through the veins begins to weaken, the lumen of the veins increases. Venous valves also undergo deformation, become shorter, thicker and cease to cope with their basic functions. Most often, varicose veins affect the lower limbs.
Causes
The causes of the development of this disease of the superficial veins of the lower extremities are:
- genetic predisposition;
- excess weight;
- constant excessive tension of the limbs during a prolonged stay on the legs;
- passive lifestyle;
- low motor activity;
- pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalance;
- the presence of bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs);
- taking hormonal medications.
The initial symptoms of the disease include the following symptoms:
- swelling of the legs, worse in the evening, heaviness in the limbs;
- feeling of fullness in the calves.
In the morning and when walking, the symptoms become less pronounced. However, the disease progresses, and gradually there are more unpleasant symptoms: convulsions, pain, fever in the legs appear, and telangiectasias form on the skin.

For pathology of the superficial veins of the lower extremities, it is necessary to contact a phlebologist who examines and prescribes diagnostic procedures, including contrast venography and duplex scanning. Therapeutic tactics depend on the patient's condition and stage of the pathological process. Medicines, physiotherapy exercises, traditional medicine, the use of compression underwear and surgical treatment methods are used. Drug therapy involves the use of drugs that strengthen the vascular walls and thin the blood (phlebotonics, anticoagulants, venotonics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). In addition, local medicines in the form of ointments are used. At the 3rd and 4th stages of pathology, the only treatment is surgery. Patients are prescribed:
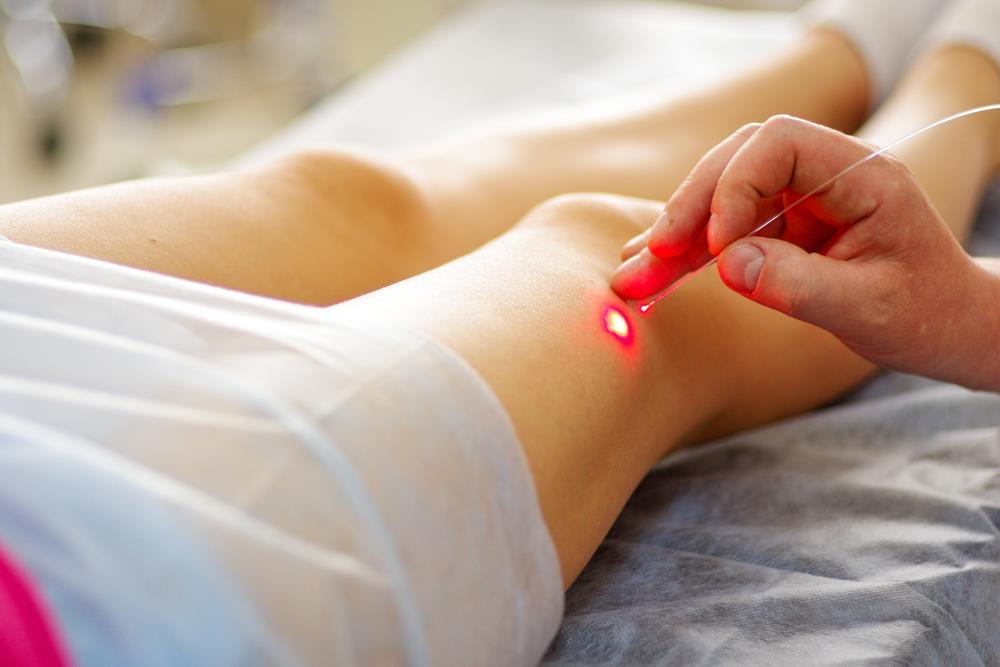
- sclerotherapy (altered vein resolves with a special drug);
- laser therapy (turning off a vein from the bloodstream);
- traditional phlebectomy (vein removal).
Phlebitis
This disease of the superficial veins of the lower extremities is an inflammatory process in the walls of the veins. In most cases, phlebitis is a consequence of varicose veins of the lower extremities. As a result of inflammation in these veins, blood flow is disturbed and blood clots form. Subsequently, phlebitis passes into a more dangerous form - thrombophlebitis. The causes of phlebitis may be the following factors:
- complications of an abscess;
- complication of varicose veins;
- chemical burns to the skin;
- streptococcal infection.
The human factor (unsuccessful sclerotherapy) can also become a trigger for the development of the disease. Symptoms of this disease are:
- pain syndrome;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- general weakness;
- hyperthermia;
- swelling of the limbs.
Chronic form
In a chronic form, the symptoms of pathology appear less intensely. They periodically subside, then reappear. The treatment of phlebitis consists in the complex application of conservative techniques. If the lesion is localized only in the superficial vein, hospitalization is not required. In other cases, the patient is subject to hospitalization. His legs should be at a certain elevation and at rest. A phlebologist prescribes medications whose action is aimed at strengthening the walls of the veins and reducing blood density. Also, the treatment of superficial veins of the lower extremities involves the elimination of the inflammatory process. When the exacerbation subsides, the patient is prescribed to wear compression underwear and the use of elastic bandages. Prevention of the disease is the timely treatment of injuries, pustular diseases and all kinds of inflammations.
Thrombophlebitis
This pathology is the main of the possible complications of varicose veins. Thrombophlebitis is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process on the walls of veins and the formation of blood clots. Doctors believe that one in four people is at risk. The most common place to localize the lesion is the lower extremities (the region is from the lower buttock to the lower part of the calf).
Reasons that can provoke an increase in blood density and, following it, the formation of blood clots:
- pregnancy;
- excess body weight;
- injuries
- genetic factor;
- respiratory viral infection;
- reduced motor activity;
- overheating of the body;
- diabetes.
The disease, as a rule, is preceded by the following pathological conditions:
- inflammation of the process on the venous wall;
- increased blood coagulation;
- blood flow disturbance.
Symptoms of thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities are pain in the area of the veins (the pain gradually becomes more intense and does not stop even at rest), high body temperature, general malaise, redness of the skin, tightened areas, weakness in the lower extremities, a feeling of cold in toes, lame when walking. Often the pathological process proceeds aggressively, accompanied by a rise in temperature and severe pain in the veins.
Swelling
Swelling is gradually increasing, and the skin on the affected areas begins to redden. Body temperature can reach 38 degrees. As a rule, in the acute stage of thrombophlebitis, such symptoms last for 10-30 days. Further, the disease is transformed into a chronic form. Diagnostics begins with an examination. The doctor determines the painful areas and the nature of the changes on the skin. To confirm the diagnosis, a blood test for coagulability is prescribed. In addition, radiopaque phlebography and duplex scanning are performed. Therapeutic measures for this disease are divided into 2 groups: operational and conservative.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment of thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities is carried out on an outpatient basis if the thrombus has not advanced beyond the lower leg. If the pathology is caused by an injury to the venous wall, anticoagulants or alcohol compresses are prescribed. To stop the pain, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. The following groups of drugs are prescribed in the treatment of thrombophlebitis: phlebotonics (Venosmin, Detralex), angioprotectors (rutin), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Sinmeton, Meloxicam), anticoagulants (Sincumar, Warfari ) Surgical treatment is indicated in case of danger of complications, as well as in cases where the pathology has spread to deep veins. Surgical treatment methods include:
- thrombectomy (removal of a thrombus);
- ligation of pathological vessels;
- phlebectomy (removal of veins).
What else leads to the expansion of superficial veins of the lower extremities?
Thrombosis
This pathology develops as a result of violations of the venous walls of the deep veins. The cause of thrombosis is most often an infectious, mechanical or chemical damage to a vein, as well as an allergic reaction. The danger of this pathology also increases with increased blood coagulation, which leads to a decrease in blood flow velocity. Another prerequisite for the development of this disease is stagnation in the veins of the legs as a result of a long stay in a standing position or low physical activity. Thus, inactivity is the main cause of varicose veins of the superficial veins of the lower extremities and thrombosis.
In the lower part of the leg, the thrombus is not dangerous, which cannot be said about cases of its localization in its upper part. The higher the thrombus rises, the greater the likelihood of a blood clot breaking off from the vessel wall. If a blood clot enters the lungs or heart, it blocks blood flow and thromboembolism occurs, leading to severe shortness of breath, cardiac arrest and death. If a blood clot enters the arteries of the brain, this causes a stroke.
initial stage
At the initial stage, symptoms of pathology can be mild. Over time, there are more and more symptoms of thrombosis:
- swelling of the extremities;
- a change in the shade of the skin on the leg affected by a blood clot;
- cramps, most often occurring at night;
- soreness in the thigh, foot and lower leg (pain subsides when the leg is horizontal);
- fever;
- venous insufficiency.
At the acute stage, thrombosis proceeds rapidly: the blood flow through the vein partially or completely stops, the legs and hips increase in size, the saphenous veins significantly expand, cyanosis and hyperthermia are noted.
Diagnostics
The phlebologist during the diagnosis conducts an examination and a tourniquet test with an elastic bandage. Duplex scanning, phlebography, reovasography of the lower extremities and ultrasound of the veins are also prescribed.
Treatment tactics
The tactics of treatment depend on the stage of the pathology, the condition of the patient, the localization of the thrombus. The main task in this disease is to avoid the spread of thrombosis and the occurrence of pulmonary embolism. Therapy is carried out in a hospital. The patient is prescribed bed rest and medications, including fibrinolytic and thrombolytic drugs, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. Surgical treatment is carried out in cases of a threat to life.