Eating is an indispensable process to ensure the vital functions of any living organism. The digestive system, consisting of many organs, is responsible for ensuring that everything goes well. Any failure in the operation of this mechanism debugged by nature itself can cause serious harm to human health. Therefore, it is necessary to deal with the prevention of diseases of the digestive system and, if necessary, be sure to contact a medical institution for help.
On a note. Statistics say that gastrointestinal pathologies are among the most common diseases in the world. For example, in Russia, according to medical reports, gastroenterological problems are in third place after oncology and cardiovascular diseases.
What is a human gastrointestinal tract?
Before we talk about the prevention of diseases of the digestive system, let's talk about what a system is, dozens of organs of which are involved in the process of grinding food, its processing, assimilation and removal of decay products and all excess (undigested food) from the body. What is this cycle called the digestion process:
- The initial stop of food on this "long" path is the oral cavity, in which the food is chewed (chopped), mixed with saliva (it is secreted as a result of the signals given by the brain) and turned into a small soft lump in volume.
- Further, after passing through the throat, the food enters the muscle tube (its length is 22-25 cm), which has a cylindrical shape, that is, into the esophagus. What prevents food from returning to the oral cavity? Two sphincters (valves) located in the upper and lower part of the esophagus.
- The next stop is the stomach. This is where the fun begins. The stomach is very similar to a cauldron in which food is mixed to a pasty state and digested under the action of gastric juice (it consists of hydrochloric acid and certain enzymes).
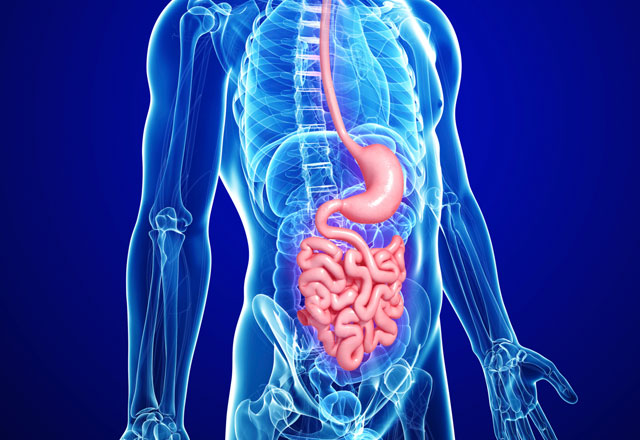
- Next, the primary processed food enters the most voluminous part of the small intestine, namely in the duodenum (duodenum). We remind you: the small intestine includes the duodenum and two more intestines (lean and ileal). So, in the duodenum under the action of enzymes, bile, intestinal and pancreatic juices, carbohydrates, proteins and fats are broken down so that they are easily absorbed by the body.
- In the small intestine under the action of enzymes and intestinal juice, the process of formation of fatty acids, monosaccharides and amino acids occurs, which are subsequently absorbed into the blood. It should be noted that the intestine can absorb about 2-3 liters of fluid in 60 minutes.
Important! After absorption, the nutrients dissolved in the water do not penetrate into the general bloodstream, but into the blood that has accumulated in the portal vein and is moving towards the liver.
- Further along the route is the large intestine, in which there is absorption of fiber, electrolytes and water, as well as the fermentation process and the formation of feces.
- The process of digestion in the rectum ends. Through the anus, bowel contents are emptied.
What other organs are involved in the digestion process?
There are several of them:
- Pancreas. It is she who produces enzymes and secrete pancreatic juice, which are so necessary for the full course of the digestion of food and the metabolic process.
- Gall bladder. The function of this digestive organ is to collect bile in itself and serve it in the duodenum, in which, together with pancreatic juice, the food received from the stomach is split. Moreover, it is processed to such a state that it can freely pass through the small intestine.
- Liver. It is located in the right hypochondrium under the diaphragm and represents the largest gland in the human body. The liver is a filter, the result of which is the purification and disinfection of blood and harmful compounds. In addition, the body regulates protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
- Kidneys and adrenal glands. They are the main organs in the process of urination. It is with the help of them that all the water coming from the colon is filtered, and it is divided into suitable for human life and urine, which contains harmful impurities.
Important! From all of the above, it becomes clear that all the organs involved in the digestion process are extremely important. Each of them clearly fulfills the role assigned to it. Therefore, it is so important to prevent the digestive system diseases. Otherwise, problems may arise that threaten the development of various gastrointestinal pathologies.
Digestive system
Before talking about the prevention of diseases of the digestive system, let's list the possible pathologies of the digestive tract:
- Gastritis. About 70% of the entire adult population of the world suffer from this pathology. Moreover, with age, the risk of developing gastritis only increases. A consequence of the pathology can be a peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. A disease of a chronic nature, which is accompanied by irreversible processes of replacement of active liver tissue cells with fibrous ones. A decrease or increase in the organ occurs, and also it becomes rough, dense and bumpy. In most cases, the pathology is not treatable and ends in death.
- Peptic ulcer or duodenal ulcer. Statistics show that pathology is diagnosed in every 15th inhabitant of planet Earth.
- Polyps of the stomach. A rather rare disease and, as a rule, without pronounced symptoms. Polyps are a cluster on the inner surface of the stomach cells.
- Perforated ulcer (perforated). The presence of a through hole in the wall of the stomach (or duodenum) through which its contents flow into the peritoneal cavity.
- Hepatitis. A very dangerous pathology of an inflammatory nature, having a viral origin.
- Pancreatitis Pathology is characterized by an inflammatory process in the pancreas. Self-destruction occurs due to the fact that the enzymes secreted by it do not enter the duodenum, but remain in the organ.
- Colon cancer Mortality from this serious disease is about 10-12% of the total number of fatal cases from oncology.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. The histological picture of the pathology is a change in the intestine of a dystrophic nature.
- Cholelithiasis. Represents the formation of calculi (stones) in the gallbladder or its ducts.
- Appendicitis. Inflammation of the cecum, or more precisely, its appendix (appendix). A very common disease that is diagnosed in the peritoneum, requiring surgical intervention.
- Colitis. The inflammatory process of the colon mucosa. The main causes of the disease are: infection, dysbiosis and insufficient fiber in food.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Throwing back into the esophagus the contents of the stomach or duodenum. This can happen once or on a regular basis. As a result, the lower esophagus is affected.
- Enterocolitis. It is characterized by an inflammatory process in the small and large intestines at the same time. What can provoke pathology? It may be an infection; abuse of strong drinks or spicy foods; the use of antibiotics for a long time; helminths, allergies to certain products, as well as unbalanced nutrition.
- Duodenitis (may be chronic or acute).
- Bowel obstruction. It is characterized by either a partial or complete lack of patency of the contents of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Dyskinesia of the bile ducts. This functional disorder is manifested by impaired biliary motility.
- Gastroenteritis. The pathology is characterized by the inflammatory process of the stomach and small intestine and is accompanied by diarrhea, pain in the abdomen and vomiting. Most often, gastroenteritis, both its acute form (OGE) and its chronic form, can be caused by viruses (to be more precise, E. coli bacteria and rotaviruses) and other pathogens. Sometimes the cause of the pathology is in no way associated with any infection. For example, the development of the disease in children can be triggered by non-compliance with hygiene rules or weak immunity. What is the prevention of infectious diseases of the digestive system, OGE in particular? First of all, this is the observance of personal hygiene rules (for example, washing hands frequently with soap and drinking boiled water), as well as eating drinks from trusted manufacturers and clean products, including vegetables and fruits.
- Pyloric stenosis (pyloric stenosis). It represents a significant narrowing of the hole in the transition of the stomach into the duodenum.
- Liver failure. It is characterized by a violation of several functions (or only one) of the liver. Clinically, this is manifested in monotonous speech, drowsiness, uncoordination of movements and tremor.
- Gastrointestinal dyskinesia. Digestive system problems associated with difficulty moving food along the gastrointestinal tract.
- Cholecystitis. It is the most common complication of cholelithiasis. The main cause of the pathology is a violation in the process of outflow of bile.
- Intestinal dysbiosis. It represents an imbalance in the microflora of the body. Moreover, dysbiosis in itself is not a pathology, but its presence may indicate any disease.
- Constipation.
- Diarrhea.
- Infectious diseases of the digestive system: botulism, dysentery, salmonellosis, cholera, helminthic invasions.
Let us dwell on some points in more detail.
Gastritis and its symptoms
This pathology is characterized by the inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa, which can be triggered by a trauma of a psychological nature, bacteria, improper use of medications. As a result, the shell of the organ loses its ability to withstand the action of pepsin and hydrochloric acid, which are a necessary attribute of food processing.
Gastritis can occur in acute form, and can turn into chronic. Moreover, depending on the level of acidity of the gastric juice, the pathology is divided into hypoacid (with a low content of hydrochloric acid in the stomach) and hyperacid (with an increased amount).
On a note! The last type of gastritis is much more common and is characterized by the fact that over time, erosion appears on the mucous membrane.
Symptoms of gastritis:
- The presence of general lethargy, drowsiness and weakness.
- Nauseous condition, sometimes turning into vomiting.
- Pain in the hypochondrium.
- Fast weight loss.
- Failure of the heart muscle.
- Dizziness.
- Lack of appetite.
- The presence of certain problems with the stool.
- Frequent irritability.
- Violation of taste.
- Restriction on the ability to actively move.
Important! Symptoms in the presence of which should be wary and call an ambulance: plaque on the tongue, belching with the smell of food that has been eaten for a long time, as well as severity or pain in the stomach.
Therapy of ailment
Before talking about the prevention of diseases of the human digestive system and in particular gastritis, we will talk about its treatment. The most important thing in this process is taking antibiotics prescribed by a doctor, as well as an adequate diet, selected by a specialist.
Medications should be taken within 10-14 days. Dosage must be determined by your doctor. Several drugs may be included in the treatment regimen. For better healing of the gastric mucosa, a medicine such as Solklozeril is suitable, and Motilium will give a good effect for activating the organ's motor function.
If the patient has hyperacid gastritis, then the following recommendations should be followed:
- What should the patient refuse? From salty, spicy and fatty dishes; as well as salt, garlic, spirits, coffee, smoked meats, radishes and mushrooms.
- The food should be warm, in no case hot.
- Dairy products with a low percentage of fat, meat and fish of low-fat varieties, Borjomi mineral water (drink one glass 30 minutes before meals), mashed potatoes and jelly are welcome.
If hypoacid gastritis is diagnosed , then the following recommendations should be followed:
- You should eat at a strictly defined time.
- Nutrition should be frequent, 5-6 meals per day.
- Sour-milk products, milk, cottage cheese, all kinds of mashed potatoes, fruit juices, as well as meat and fish, steamed or simply boiled are welcome.
- Food should be thoroughly chewed, and this should be done in a hurry.
Traditional medicine in the fight against gastritis
Before we talk about preventive measures for diseases of the digestive system (in particular gastritis), let's talk about recipes of traditional medicine, which quite effectively help to cope with the disease. Here are some of them:
- We steam the rose hips in the oven and eat them warm.
- Mix 10 percent propolis tincture and sea buckthorn oil in a ratio of 1:10. We use a mixture (20 drops) three times a day along with mineral water or milk.
- Fill wheat grains (approximately 100 grams) with water. After the sprouts appear, cut them off, wash them in running water and scroll in a meat grinder. We use green mass in combination with vegetable oil (several tablespoons) on an empty stomach every day.
- Pour the fruits of bird cherry (1 tablespoon) with boiling water (1 glass), cook for 15 minutes, cool, add 10% propolis extract to alcohol (40 drops) and drink three times a day in a glass.
Important! Before you start using traditional medicine, do not forget to consult your doctor about your actions.
Preventive measures to prevent gastritis of the stomach
Prevention of diseases of the digestive system, for example gastritis (both its acute form and chronic), includes the following measures:
- We follow a corrected and balanced diet. We refuse pizza, hot dogs and other types of fast food.
- Eat every 3-4 hours at a well-defined time. The number of receptions should not be less than 5.
- We monitor the amount of servings, which should be no more than what can fit in the palm of your hand.
- We pay great attention to the quality of the food on the table. It is desirable that it be freshly prepared and warm.
- When eating, take our time and do not chew food quickly.
- Speaking about the prevention of diseases of the digestive system, we can not say about such bad habits as smoking and drinking alcohol. We unequivocally refuse them. Moreover, the use of their low quality leads not only to inflammation of the gastric mucosa, but sometimes to poisoning.
- If the type of activity is associated with the inhalation of chemical vapors, then we must use personal protective equipment (gloves, masks and glasses).
Botulism and its symptoms
Before you learn about the prevention of diseases of the digestive system, such as botulism, we will talk about the causes of its development and symptoms.
This is one of the most dangerous infectious pathologies that can be triggered by toxins of the botulism bacterium that lives in the soil and multiplies in an oxygen-free environment, while emitting a toxic substance. The disease is characterized by a serious damage to the central nervous system (central nervous system), and more precisely, the spinal cord and medulla oblongata. Very often, pathology is accompanied by a malfunction of the heart muscle. Disputes enter the human digestive system with poor-quality meat or fish products, canned goods, mushrooms or vegetables (especially with home-made preparations). Sometimes botulism can develop as a result of bacteria entering the wound.
Important! You should not be afraid of a person who has become ill with botulism, for those around him it is completely safe.
The initial symptoms of the pathology: headache, vomiting (it can be repeated), diarrhea, pain in the abdomen (while the temperature, as a rule, is not observed).
Further, the pathology develops rather rapidly, and after 24 hours the patient may develop a dry mouth, diarrhea can be replaced by constipation, muscle paralysis, loss of vision, and other negative manifestations, including death.
On a note! Sometimes, instead of botulism, a patient is diagnosed with angina due to such a manifestation as the bright red color of the pharynx and nasopharynx. Moreover, in the area above the larynx there is an accumulation of viscous, thick mucus, which at the beginning of the process is transparent, and subsequently becomes cloudy.
Botulism treatment
Before we talk about the prevention of diseases of the digestive system, for example botulism, we dwell on the methods of treatment of the disease. Such a pathology is treated exclusively in a hospital. What can be done while waiting for the arrival of the ambulance brigade? We perform the patient’s washing of the stomach with boiled water and collect vomit so that they can be examined later. In the hospital, special probes are used for these purposes. Next, antitoxic anti-botulism serum is administered to patients and drugs are prescribed that have the ability to bind and retain a variety of toxic substances (enterosorbents). It is also possible treatment with diuretics.
To suppress the vital activity of bacteria, all patients are shown “Chloramphenicol”, “Tetracycline” or “Ampicillin”. In the event of respiratory muscle paralysis, doctors may decide to connect the patient to a ventilator.
Recovery with botulism is a long process (it is easier to take care of the prevention of infectious diseases of the digestive system). One of the first signs that improvement is occurring is the presence of salivation. Over time, recovery of muscle strength and vision occurs (it can be weakened over several months).
On a note! Despite the fact that in the process of the disease the patient had serious neurological disorders, after recovery they are almost all restored.
Botulism Prevention
Preventive measures against infectious diseases of the digestive system, such as botulism, include the following:
- Absolute compliance with the rules of storage and preparation of fish and meat semi-finished products, as well as all kinds of canned food (for example, vegetable).
- Can boiling botulism be prevented by boiling? A vegetative form can be: it is enough to boil canned foods for 5 minutes, and the bacteria die. But it is difficult to fight the spore form, since even boiling for 5 hours does not always give positive results.
- No measures for the prevention of diseases of the digestive system will help if you indiscriminately purchase and eat obviously spoiled foods. Be careful and attentive.
Important! Measures for the prevention of infectious diseases of the digestive system - this, of course, is very good. But if you still have signs of the disease, what should I do? First of all, contact the infectious diseases hospital for help (in extreme cases, call an ambulance team) and turn in products of “suspicious quality” for laboratory testing.
Conclusion
What is the prevention of diseases of the digestive system? Briefly about this, for example, about gastritis and botulism, read above. The most important thing in therapy is taking medications and following a diet. An important role is played by timely appeal to a medical institution and diagnosis. Primary prevention of diseases of the digestive system is also extremely important. It includes not only a balanced and adjusted diet, but also an active lifestyle, regular passage of such a procedure as ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, and the ability to abstract from all kinds of stressful situations.