Medicine is impossible without knowledge of human anatomy, the structure of his bones and skull. In turn, the structural features of the skull are studied by analyzing its functions. The knowledge that we have the opportunity today to receive thanks to the medical atlases created many years ago, makes it possible for physicians to diagnose pathologies of the development of bones, veins and blood vessels of the brain. This is especially true for modern traumatologists, neurosurgeons. The knowledge gained helps in making an accurate diagnosis, conducting complex operations and prescribing appropriate treatment.
The human skull is the oblique base of the head, which consists of twenty-three bones. It has many channels and holes through which the nerves, arteries and blood vessels pass. Among them, there is the so-called torn hole , which is located on one of the bones of the skull, complex in the anatomical structure - the sphenoid bone. It plays an important role in the life of the body.
History reference
For the first time about this hole became known in the eighteenth century thanks to Jacob Winslow. It received the name “Winslow occipital foramen” due to its relation to the spinous process of the vertebra of the sphenoid bone, in particular, its large wing. In literal translation from Latin, foramen spinosum means "a prickly hole", but in medicine the definition "ragged hole" is used.
Location
There are many holes in the middle cranial fossa, through which vessels and nerves pass. Among them, a ragged hole can be distinguished, which is located in the lower part of the skull and bone of a wedge-shaped shape. It is located in front of the spine across the oval opening. Through this gap pass the middle meningeal artery and vein, as well as the meningial branch of the nerve of the lower jaw.
Pathology
The ragged hole that passes through the sphenoid bone can be different in size. In some cases, there is no gap, so the middle meningial artery passes through an oval hole into the cranial cavity. This can be observed in about half of the world's population. At the same time, in 1% of people, the hole can be duplicated, as well as the artery that passes through it. Also, a torn gap can be at the top of the spinous process or along its surface.
Development
In newborns, the ragged hole has a length of 2.2 mm and a width of 1 mm, in an adult - 2.5 mm and 2.1 mm, respectively. The diameter of the hole in the gap is on average about 2.6 centimeters in an adult. Perfect round formation was observed in childhood, from eight months to seven years. In numerous studies of the skulls, most of the holes were round. In animals, in particular large monkeys, the ragged hole is not in the sphenoid bone, but in the temporal bone, in some cases it is completely absent. Passing through the lacerated gap of the above arteries and nerves allows a person's back to rotate.
Medical relevance
In neurosurgical practice, access to certain formations of the cranial cavity is often necessary, so there is a need to focus on standard points. This hole is used as a guideline in neurosurgery, as it has a close relationship with other holes. Torn hole allows you to see the location of the oval and round fissures, nerve of the lower jaw, trigeminal ganglion. This is of great importance during surgery for hemostasis.
What passes in the torn hole of the skull
We already know that the middle artery meningeal (meninges), the mandibular nerve branch, pass through this hole. Through the membrane (fibrous cartilage), which closes this hole, pass the facial nerves, muscle, which contributes to the tension of the tympanic membrane, as well as the nerve innervating it. There are also small veins that connect the facial sinus to the veins of the base of the external skull , the carotid internal artery, one of the branches of the pharyngeal artery, some of the emissary veins that connect the plexus in the form of a wing with a cavernous sinus. They represent a possible route of infection to the brain, and also allow nasopharyngeal cancer to metastasize into the cavernous sinus, affecting the cranial nerves.
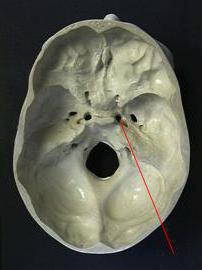
Thus, the lacerated gap serves as a guideline for neurosurgeons in conducting surgical intervention. We already know what goes through a torn hole, thanks to medical atlases that were created many years ago. It is located near the top of the pyramid of the temporal bone and is closed by cartilage.
In medicine, a large role is played by the study of the anatomy of the human skull. Thanks to the knowledge gained, specialists can carry out diagnostics, treatment and surgical interventions for various diseases and injuries. For the first time they spoke of a torn hole in the eighteenth century. Today, this discovery helps save the lives of many people.