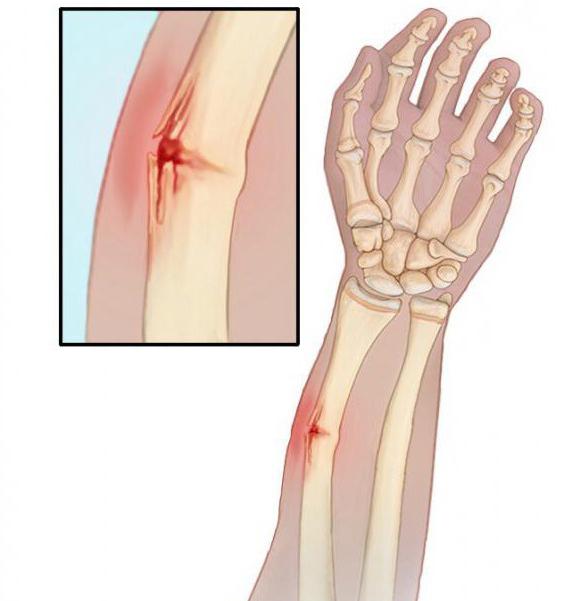
The forearm is the part of the arm, including the radius, ulna. In fact, this is a continuation of the shoulder. The joint joint is the ulnar joint. The forearm connects to the hand with the wrist joint. According to the ICD, a fracture of the forearm is encrypted with the S52 code. Such an injury is a serious injury, requiring an urgent medical attention. One of the important stages of care is immobilization in case of fracture of the forearm. This must be done quickly, carefully, without worsening the patient's condition.
Fracture: causes
A fracture is provoked by injuries received by the bones, the causes of which are:
- unsuccessful falls;
- direct hits;
- arm twisting.
The risk of getting a forearm fracture is higher if the patient is characterized by:
- older than average age;
- low muscle mass;
- bone disease
- sports activity.
High probability of fracture of the forearm in those who experience violence or do not receive enough nutrition.
How to suspect?
With an open / closed fracture of the forearm, patients complain of:
- pain
- swelling;
- deformation of the affected area.
A diseased arm cannot move in a normal range.
In the presence of such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. At the initial examination, the specialist interviews the patient, collecting information about both the symptoms and previous events that provoked a fracture of the forearm. The doctor also examines the damaged area to make an accurate diagnosis.
Define a fracture
To diagnose a closed / open fracture of the forearm, an X-ray is first done. This allows you to get information about the internal structures of the human body, gives an idea of the state of the bones. The doctor can pinpoint the problem area.
Another effective and accurate method of obtaining data is computed tomography. In testing, they use a computer and a powerful x-ray, which allows you to get an accurate picture of internal damage and the structure of bones, muscle tissue. Tomography allows you to get an idea of the condition of tendons, cartilage. If the fracture of the forearm is complex, then tomography becomes an indispensable assistant to the doctor involved in bone restoration.
You can deal with the problem
Modern medicine allows you to treat a fracture of the forearm bones, however, success depends on what the injury is: where exactly it is located within the body, how difficult it is. Doctors usually carry out activities aimed at:
- the return of bones to their original state, which is often accompanied by anesthesia, surgical intervention;
- keeping the affected area stationary until the bones are fused.
Effective Techniques
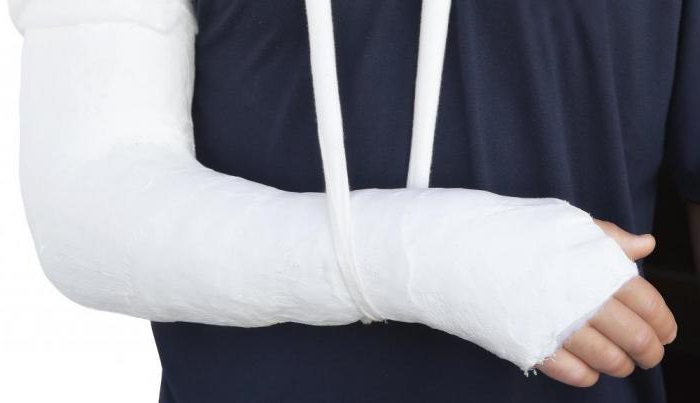
In order for the splint to prove effective in fracture of the forearm, it is applied using one of the following methods:
- plaster bandage applied before surgery, as well as in cases where the invasive method is not needed;
- metal plate (installed during the operation);
- screws (installed invasively).
To reduce pain, anesthetics are injected. After the operation, the patient's condition is regularly checked by tomography or x-ray to monitor the healing process. In the event of an unexpected bone displacement, you can immediately diagnose this and take appropriate measures.
What's next?
When first aid was provided during a fracture of the forearm, the operation was done and the patient began to recover, it is necessary to do special exercises. Their main task is to strengthen muscles, restore the body's ability to move. The main task of the patient and doctors is to restore the ability to function on the shoulders, fingers. Physiotherapy is usually prescribed and sports and any heavy loads are prohibited.
Usually a fracture of the bones of the forearm heals in about 10 weeks, sometimes faster. If there was an open or fracture of the forearm with a shift, then the duration of treatment and rehabilitation is longer. In some complex cases, full recovery will not work. However, in any case, the success of events is largely determined by how clearly the patient follows the instructions of the doctors. If there is a violation of these, the likelihood of complications is high.
How to prevent?
Of course, the ability to help with a fracture of the forearm is a useful and important skill, but it is even more useful to know how to prevent this situation. As a preventative measure, they recommend:
- Avoid dangerous situations that can cause injury;
- control the content of vitamin D, calcium in food;
- regularly do bone strengthening exercises;
- train muscles;
- at work, in sports, observe safety rules.
Conservative and invasive
Fracture of the forearm can be treated either surgically or conservatively. The second option is possible if there is no bias or if the patient's condition is such that the operation carries great risks to life. The conservative method involves a long stay in a plaster cast, which can provoke incorrect fusion. In many patients, thus treating a fracture, the affected limb functions much worse than before the fracture. There are also unstable fractures in which it is difficult to achieve accurate reposition.
The operation is recognized by many traumatologists as the best treatment option known in our time. There are minimally invasive methods that allow you to operate the ulna, radius. The doctor during the event repositions of bones and fragments, placing them physiologically correctly, and then fixing the position with special devices. Small invasion is achieved by the fact that only small punctures are made for the manipulations, and all movements are controlled through x-rays. Soft tissues remain intact, recovery takes a relatively short time period, before you can be discharged from the hospital. In addition, with such an operation, the risk of complications is reduced.
Latches and consequences
For fractures of the forearms, various fixatives are used. One of the most effective is intraosseous rods, indispensable for damage to the diaphysis. When using such fixatives, you can achieve results with minimal muscle damage. The operation that accompanies the installation of the retainers leaves scars, but they are very small, almost invisible even to doctors.
Another popular type of retainer is a plate attached to the bones with screws. Osteosynthesis is a kind of "gold standard" of medicine. The most modern plate models allow you to fix bone fragments in the most correct position and hold them until the fracture heals.
It is important!
In the event of an open fracture, it is impossible to avoid surgery. Intervention involves the use of special devices that fix the forearm from the outside. This allows you to stabilize the patient's condition, after which you can proceed with further activities.
When the wound heals, the apparatus is removed and the bones are fixed with plates or rods. This approach minimizes the likelihood of purulent complications.
be careful
To operate the forearm zone is not an easy task. This area is rich in nerves, blood vessels, damage to which can adversely affect the patient's condition. Upon receipt of additional injuries, the likelihood of complications is high, which can lead to an irreversible loss of motor activity or sensitivity. Most likely a malfunction of the hand. To avoid complications, the surgeon must carefully plan and implement the intervention.
Danger of healing
The diaphysis of an adult heals for a long time. After six weeks, an X-ray of the damaged area is done to check for bone marrow. Four weeks later, a strength test is performed. Normally, the bone should gain up to 80% of the strength before fracture. Tissue remodeling and complete healing take years.
As the damaged area splices, a metal retainer can be removed. This event is not necessary, but sometimes the presence of a metal element causes discomfort or even pain, which is an indication for removal. Plates, rods are removed from the human body two years later. A prerequisite - on x-rays should be obvious signs of consolidation.
Typical fracture
Usually typical is a Smith or Wheel fracture. With this damage to the bone, the fragments do not move. After an X-ray examination, a plaster cast is applied to the patient to immobilize the affected part. The plaster cast begins at the tips of the fingers, up to the third of the forearm. Immobilization of the arm lasts about a month. When the gypsum is removed, physiotherapy is prescribed to develop the muscles of the wrist. With the normal development of the situation, recovery takes from one to two weeks.
A simple fracture complicated by displacement requires a traction reduction when the bones are normalized by pulling on a damaged arm. The event requires anesthesia - local, conductor. The assistant doctor pulls a brush on himself, another assistant pulls the limb in the opposite direction, holding the elbow. Gradually, the bone fragments are pulled in such a way that they create a distance between them, and the doctor manually puts in place all the fragments, pushing them to take the correct position.
What's next?
When the reposition is completed, make a cast of plaster, while maintaining the tension of the hand, to avoid repeated displacement. When the gypsum dries, the tension gradually decreases.
If it was not possible to successfully move the fragments or it was revealed that the fracture is accompanied by a very large number of fragments, if displacements reappeared or the joints are badly damaged, then an operation is urgently needed. Osteosynthesis is performed, metal fixatives are used, and then a plaster cast is applied. Usually, with such a fracture in a cast, you will have to spend a month or a half, and rehabilitation takes 2-4 weeks.
Fracture: Implications
Fracture provokes the consequences of varying severity. They depend on the location of the damage and its complexity. If the fracture is easy, then everything heals quickly and leaves no visible traces, does not provoke complications. But the displacement of the fragments is a signal of increased danger of additional problems. If an open fracture with bias is diagnosed, then the situation is classified as very complex.
The following consequences of fractures are usually observed:
- impaired functioning of the nerves;
- osteomyelitis;
- embolism;
- splicing pathology;
- bleeding.
The latter complication occurs most often and is provoked by soft tissue damage. The main difficulty is that it is internal, and is visually reflected by a bruise or invisible to the eye in principle. The physician must consider that bone fragments can injure blood vessels and soft tissue.
Internal bleeding often accompanies closed fractures with displacement. With open fractures, vascular damage is more significant, since the fragments are strongly displaced, and external bleeding appears.
Impaired nervous activity
This consequence of the fracture is quite common and is classified as quite severe. It is provoked by the fact that during a fracture, bone fragments damage the structure of nerve trunks located near the bones. More often, nerve damage is recorded if the fracture with displacement is open. At that moment, when the bone gets damaged, mechanically it touches the nearby nerve trunks, because of which they lose their normal working capacity.
Violation of nervous activity is manifested by a loss of sensitivity, including pain and temperature. In addition, the fingers or the entire hand lose mobility, the limb is numb, joint functions are blocked.