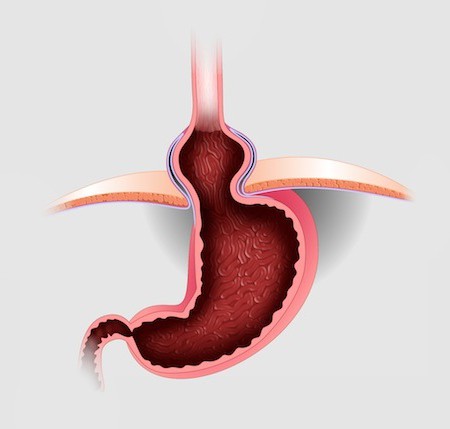
Hernia of the esophagus of the diaphragm (a photo of the pathology is presented below in the article) and reflux esophagitis are quite dangerous diseases. Against the background of these conditions, stretching of certain sections of the gastrointestinal tract is noted. In particular, changes occur in the ligaments that support the stomach and esophagus, a photo of which is also presented in the article. As a result of stretching, displacement occurs. In particular, the upper gastric part extends into the thoracic region. As a result, the functioning of the sphincter connecting the stomach and esophagus is disrupted (the photo illustrates this area).
Probable risk
When the angle of His is changed and the activity of the esophageal (lower) sphincter is disturbed, the acidic contents of the stomach or bile are thrown into the esophagus from the duodenum. The process is accompanied by the development of inflammation, restructuring of the mucosa. This greatly increases the risk of cancer. Of particular importance in the development of pathology is a sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. The operation is the only available method to eliminate this violation. However, surgical intervention has its own nuances. Next, we will analyze in more detail what a hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm is. The degrees, types and manifestations will also be described in the article.
General information
A hernia in the esophageal opening, as a rule, develops in combination with gastroesophagic disease. GREB is accompanied by a complex of cardiological, pulmonological and dyspeptic disorders. They occur mainly due to a hernia and gastroesophageal reflux. In accordance with the data of the American and European associations, in the presence of HPA in humans for 5-12 years, the likelihood of cancer after five years increases by 270%, and after 12 - by 350-490% (depending on age).
Pathology prevalence
HAP, according to some authors, is considered to be the same often diagnosed disease as, for example, cholecystitis or an ulcer of the esophagus. In terms of their prevalence, these pathologies occupy leading places among gastrointestinal diseases. HHAP, like an ulcer of the esophagus, is considered a rather dangerous disease that requires timely diagnosis and careful monitoring.
Classification
There are three main categories of GPOD. These include:
- Axial hiatal hernia. This pathology has another name. The common name is a sliding hiatal hernia. This type of pathology is detected in almost 90% of patients. The condition is characterized by the occurrence of a cardia above the esophagus. In this regard, there is a sharp violation of the closure function.
- Paraesophageal hernia. This form is found in approximately 5% of patients. The pathology of this type is characterized by the invariance of the position of the cardia and significant curvature of the stomach.
- Short esophagus. As an independent, this pathology is extremely rarely diagnosed. The disease is an abnormality in development. As a rule, this syndrome is accompanied by a sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. It is also characterized by inflammatory and scarring processes.
Sliding hernia
This form of the disease has several features. In general, a sliding hernia is a protrusion in which one of the walls is a partially covered peritoneal organ. This can be, in addition to the area considered in the article, the bladder, ascending and descending intestine, and so on. At the same time, there may not be a hernial sac . The protrusion in this case is formed by areas of the body that are not covered by the peritoneum.
Mechanism of occurrence
In accordance with this sign distinguish:
- Congenital hernia. In this case, the organs, for whatever reason, by certain departments that are not covered by the peritoneum, gradually descend to the area of the internal gate by retroperitoneal tissue. In this case, they exit the cavity. This process can begin in the embryonic period. As a result, the displaced sections become a protrusion component without a hernial sac.
- Acquired violations. Hernias of this type are formed as a result of mechanical constriction of the intestine or segments of the bladder. They lack serous cover and are adjacent to the peritoneum.
Inguinal sliding hernias in the large intestine, as a rule, are protrusions of a large size with wide gates. Diagnosed, as a rule, in old age. It is detected using x-ray methods for examining the large intestine. A sliding hernia in the bladder is manifested by dysuric disorders. Patients have double urination. First, the emptying is carried out as usual, and then, when pressing on the protrusion, another urge appears, and the patient urinates again. When diagnosing, catheterization and cystography are performed. During these procedures, the shape and size of the hernia, the absence or presence of stones in the bladder are revealed.
Axial hiatal hernia
This pathology is a displacement of the stomach or other abdominal organs into the chest cavity. The disease is detected in 5% of the adult population. At the same time, about half of the patients do not notice any manifestations. This course of pathology is due to the fact that a sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm has erased signs of a typical shape, since the protrusion is located inside the body and it is impossible to detect it during a routine examination. The disease affects women more often than men. In children, the pathology is mainly congenital in nature.
Forms of the disease
A sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm is divided into:
- Cardiofundal.
- Total gastric.
- Cardiac.
- Subtotal gastric.
Paraesophageal hernias are classified into:
- Gastrointestinal
- Stuffing box.
- Intestinal.
- Antral.
- Fundamental.
Pathology stages
A sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm can be classified in accordance with the volume of the stomach penetrating into the chest cavity:
- First stage. In this case, the abdominal section of the esophagus is located in the chest cavity above the diaphragm. The stomach is in this elevated position. It is adjacent directly to the diaphragm. And at her level is the cardia.
- Second stage. In the chest cavity is the abdominal section of the esophagus, the stomach is located directly in the area of the diaphragmatic opening.
- Third stage. Above the diaphragm are the cardia, the gastric body and the bottom (sometimes the antrum), the abdominal esophagus.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of pathology are very similar to the manifestations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract associated with impaired functioning. Against the background of deterioration in the activity of the esophageal (lower) sphincter, catarrhal reflux is noted (reverse reflux of gastric contents). After a while, due to the aggressive influence of the masses, an inflammatory process develops in the lower part of the esophagus. The patient begins to complain of heartburn after eating and worsens with physical strain or in a horizontal position. Often there is a sensation of a lump in the throat. After eating, pain may appear. They have a different character. Soreness can spread to the shoulder blade, give it to the neck, sternum, heart region or lower jaw. These manifestations are similar to signs of angina pectoris, with which a differential diagnosis is made. In some cases, soreness appears at a certain position of the body. Patient complaints about bloating of the upper abdomen, a feeling of the presence of a foreign body are likely.
Effects
More severe cases are characterized by a number of complications. One of them is bleeding from the esophagus vessels. As a rule, it proceeds in a latent form and manifests itself in the form of progressive anemia. Bleeding can be chronic and acute. In some cases, even infringements of the protrusions in the esophagus and esophageal perforation are detected. The most common consequence of pathology is reflux esophagitis. It can transform into a peptic ulcer in the esophagus. With prolonged therapy, this condition provokes an even more serious complication - cicatricial stenosis (narrowing) of the organ.
Diagnostics
Pathology is identified using several methods. Among the main ones should be called: esophagogastroduodenoscopy, x-ray of the stomach and esophagus, intraesophageal PH-metry. Ultrasound, computed tomography, and esophagometry are also used.
Pathology treatment
Various measures are being taken to alleviate the manifestations that accompany a sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm: diet, medications. Conservative methods are aimed at eliminating the symptoms of pathology: relieving pain, heartburn, nausea. In this case, medications are prescribed that lower the acidity of the gastric juice. Such funds, for example, include the drug "Kvamatel." One of the conditions for the effective treatment of patients who are diagnosed with a hiatal hernia is a diet. The diet limits the presence of fatty, spicy, fried foods, alcohol, chocolate, coffee, and foods that promote the production of gastric juice. Eat should be in small portions, often. To prevent reflux, it is recommended that the patient sleep with a raised upper torso, as well as avoid heavy lifting.
Surgery: General
It should be said that the above measures do not eliminate the reason why there is a sliding hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. Surgery is the only way to restore the anatomical relationship between the parts of the digestive tract. During the intervention, an antireflux mechanism is created that prevents the backflow of the contents of the stomach. During the operation, the hernia gate is eliminated by suturing the enlarged aperture to the normal size.
Applied Surgical Techniques
Today, experts use two methods of intervention:
- Open access. In this case, Nissen fundoplication or Tope plastic can be performed. In the first case, the risk of developing many complications is high. Therefore, plastic is preferred by Tope.
- Laparoscopic access. This is the least traumatic method of intervention. After the operation in this way, the patient recovers faster and easier.
It should be said that laparoscopy with a hernia in the esophagus is often performed in conjunction with operations of other organs in the abdominal cavity. For example, cholecystomy is performed with calculous cholecystitis in the chronic stage, proximal selective vagotomy - with an ulcer in the duodenum.