Probably everyone heard that the digestion process is carried out with the participation of bile, which is constantly produced by the liver. And the gallbladder is the repository of this secret. Which side is located, which functions and what violations arise in his work, we will consider in this article.
Anatomical features
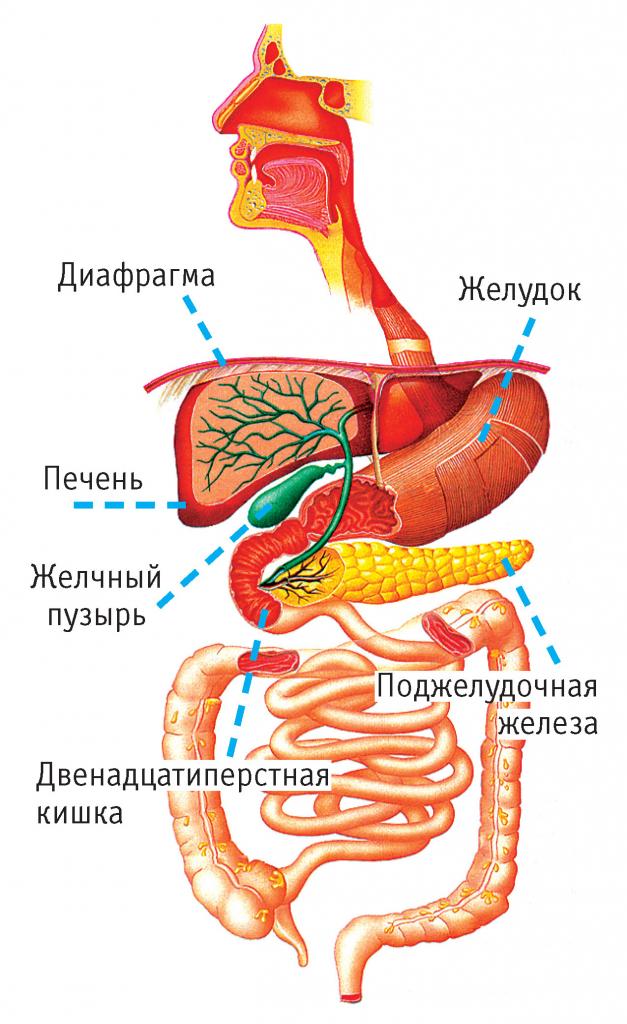
Outwardly, the gallbladder resembles a pear. It is located below the liver between its lobes. Bile, regularly produced by the liver, is essential for the digestion process. It is not required constantly, but periodically, therefore a special reservoir has been created for its storage and concentration - the gall bladder. It dispenses a dosed liquid when food appears in the stomach. It, along with pancreatic enzymes, helps digest food, is involved in the breakdown and absorption of fats, and has bactericidal properties.
The gall bladder consists of:
- cervix - the narrowest part of the organ;
- body - its length does not exceed 15, and a width of 4 cm, volume - about 70 ml;
- bottom - a wide area protruding beyond the lower edge of the liver.
The walls of the gallbladder have a multilayer structure. They contain the following shells:
- Mucous - consists of elastic fibers and glands that produce mucus.
- Fibrous-muscular - smooth muscle cells are mixed with collagen and elastic fibers.
- Serous - built of dense fibrous connective tissue.
In the normal state, the gallbladder is not palpable, and with an increase in its position, it can be determined by palpation.
Functions
Why do you need a gall bladder? Firstly, it acts as a container where bile is stored. Secondly, a concentration of liquid occurs in the bubble due to the separation of water. During the day, more than a liter of bile is produced by the liver. If necessary, it enters the duodenum through the cystic and common bile duct. The main components of bile are: water, bile acids, bilirubin, cholesterol, mucus, proteins, vitamins and minerals.
In the body, it performs the following functions:
- neutralizes gastric juice;
- enhances the activity of intestinal and pancreatic juice;
- destroys pathogens in the intestines;
- removes toxins from the body;
- improves intestinal motility.
Characterization of pathologies of the gallbladder
The main diseases of the body are most often associated with malnutrition. These include:
- Gallstone disease - the formation of stones inside the body. It develops due to stagnation, when bile is retained in the bladder for a long time, or if metabolic processes are disturbed, a precipitate forms, from which solid particles form over time. As long as the stones are inside the bubble, they do not cause concern. As soon as their movement along the ducts begins, the patient experiences sudden sharp pains on the right, i.e., on which side is the gallbladder.
- Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder. It is caused by infection, intoxication, mechanical irritation of the mucosa, and most often gallstone disease. The malaise is acute or chronic. In the first case, sharp, and in the second, dull painful sensations arise. They can be given to the back of the head and neck, nausea and malfunction of the digestive organs are possible.
- Dyskinesia - the contractile activity of the gallbladder and its ducts is disturbed. Pathology contributes to malnutrition, stressful situations, gastrointestinal diseases. The pain is localized in the upper right abdomen, where the liver and gall bladder are located. With a hyperkinetic form, it is sharp and short, with a hypokinetic form, it is long, dull and bursting.
- Neoplasms - tumors are formed extremely rarely and at the initial stage do not manifest themselves in any way. With an increase, they block the bile ducts, first there is pain as with dyskinesia, then it intensifies, spreading to the entire right side of the abdomen. Malignant tumors often arise as a result of complications of chronic inflammatory processes that affect the inner membranes and ducts of the bladder. In this case, metastases quickly occur, affecting nearby organs.
If you experience any unpleasant sensations in the right hypochondrium there, on which side the gallbladder is located, it is necessary to consult your doctor and undergo an examination to prevent serious complications.
Disease symptoms
For any impaired functioning of the gallbladder, problems are accompanied with almost the same symptoms. The most basic sign indicating inadequate organ function is a strong, not passing pain under the right rib. The condition worsens when eating spicy, fried or oily foods. After all, it is also known from the school course of anatomy that the gall bladder makes. He throws a portion of the enzyme to break down fat in the duodenum. And in case of impaired function, the secretion duct is often clogged, so pain occurs.
In addition to pain, the patient may experience:
- nausea and vomiting
- diarrhea or constipation;
- allergies - skin rashes and itching;
- belching after eating;
- bloating, flatulence;
- yellowness of eye proteins and skin;
- irritability;
- insomnia
- bitterness in the mouth.
The appearance of such symptoms can not be ignored and it is advisable to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Pathology diagnostics
Concerned about the pain under the right rib. What is there? Two important organs are located in this place - the liver and the gall bladder, which is the repository of bile. When contacting a doctor to identify an accurate diagnosis, the patient undergoes an examination. The set of measures depends on the age of the individual, his complaints and chronic ailments.
The main methods include:
- History taking. In a conversation with the patient, the doctor finds out the time of onset of the disease, the features of the onset of pain, their nature.
- External examination of the patient - the presence of obstructive jaundice of the skin and eye proteins is detected.
- Palpation in the peritoneum - a check of pain at certain points on the right side.
- Complete blood count - draws attention to the number of white blood cells to determine the inflammatory process.
- General and bioanalysis of urine - the identification of the level of urobilirogen.
- Coprogram - shows digestive disorders.
- Duodenal sounding - sampling of bile to study its composition.
- Ultrasound - allows you to identify features of the anatomical structure of the gallbladder, determine the presence of polyps, inflammation, stones.
- MRI and CT are performed if in doubt after an ultrasound scan.
- Biopsy - a study of the material to determine malignant neoplasms.
Having received all the results of the tests and having carried out the necessary consultations with narrow specialists, the doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment using conservative therapy or surgical intervention.
Gallstones: symptoms and treatment
This disease can manifest itself at any age. Often it is asymptomatic and a person for a long time does not suspect about its development. Gallstones are crystals that form from abnormal bile, when the concentration of salts in it increases and the outflow from the gallbladder slows down. Stone formation is often associated with a genetic predisposition. In addition, risk factors include diabetes mellitus, a high-calorie diet, and obesity. Moreover, it is noted that women get sick more often than men.
Pregnancy and childbirth are associated with metabolic disorders and predispose to the formation of deposits in the gallbladder. Signs of the disease begin to appear when the stone moves out of the bladder through the ducts. In this case, the following symptoms appear:
- Intense pain, which is localized in the right hypochondrium, i.e., on which side is the gallbladder. It is so strong that it does not stop with antispasmodic drugs. Often gives back to the lower back, shoulder blade and arm. Then the acute pain passes, but aching and pulling appear, which intensify when eating fatty and spicy foods.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Elevated temperature - as a rule, an inflammatory process occurs.
- Weakness, fatigue, irritability.
- Yellowness sclera of the eyes, dark urine, discoloration of feces.
- Diarrhea.

If you have colic and pain in the right side, you should consult a doctor. Ultrasound will help determine the disease. If gallstones are identified, symptoms can be treated with medication or surgery. The decision is made by the attending physician. For conservative treatment, preparations based on bile acids are used. They are used when the stones are small and the gall bladder remains operational, and the ducts remain passable. The treatment is long, but if the reduction in the size of the stones does not occur within six months, then it stops, the individual begins to prepare for surgery.
Types of operations
Currently, there are several types of surgical intervention that are used to remove the gallbladder:
- Cavitary - is carried out when serious lesions of the pathways leading to bile have been identified, rupture of the neck of the gallbladder or blockage has occurred, peritonitis has begun. Its advantages are direct access, good visibility, and the ability to examine nearby organs. This type of intervention is used in emergency and severe cases. After it, complications and a long recovery period are possible.
- Laparoscopy is one of the most common methods. Its advantages are: small incisions, less painful, reduced risk of infection, short recovery period.
- Mini access cholecystectomy - used for patients for whom other types of intervention are contraindicated for medical reasons. The path to the gallbladder, which is under the right rib, is provided through a small incision in this area.
- Transvaginal method - used for women through an incision about a centimeter long, which is done in the posterior vaginal fornix. Its advantages: there is no pain after surgery, motor activity is fully preserved, hospitalization is one day, there are no external scars.
The choice of the type of operation to remove a diseased organ is determined by the attending physician.
Gallbladder Surgery
Intervention by laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. Its duration is an average of forty minutes. The essence of the operation to remove the gallbladder in this way is as follows:
- Carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity with a special tool to create space for working with the instruments.
- Special tubes, trocars, are introduced into the abdominal cavity through minor incisions. In them, the surgeon puts the necessary tools for work.
- A laparoscope with a video camera is introduced into the area near the navel.
- On installed monitors with a forty-fold increase, the operating team monitors the progress of the operation.
- The cystic artery and duct are clamped with titanium clips.
- Separate the gallbladder from the liver and take it out. Pre-spend crushing stones.
After surgery, a drainage device is left to drain the liquid, which, if a favorable outcome, is removed the next day. The patient is in the hospital for no more than two days.
Rules for diet after surgery
Nutrition after removal of the gallbladder plays an important role. Immediately after surgery, it is advisable to refuse food. Dry mouth wipes the lips with a swab dipped in boiled water, and after five hours, rinse your mouth. On the second day, it is allowed to drink a little alkaline water, weak tea or low-fat kefir. Light meals are suitable for food: vegetable broth, boiled chicken meat, low-fat cottage cheese. Take food in small portions, observing an interval of 3-4 hours.
In satisfactory condition, mashed potatoes, boiled fish and vegetable soup are allowed on the third day. At the end of the week you can eat cereals on the water, low-fat cutlets and meatballs. The diet after laparoscopy of the gallbladder must be observed both during the recovery period and throughout life. It is advisable to use the following foods:
- dietary meat - rabbit, chicken, turkey, veal;
- fish - pike perch, cod, pike;
- cereal cereals;
- mashed soup with vegetable or lean meat broth;
- steamed or steamed vegetables;
- low fat milk and dairy products;
- egg - once a week;
- fresh fruits, organic drinks and compotes;
- dry, lean cookies and white crackers.
The diet is not very strict, but restrictions must still be observed. Food will have to be baked, boiled, stewed or steamed. Fried foods and grilled foods should be discarded.
Neoplasms in the gallbladder
Often, during an ultrasound examination, polyps are detected - this is a benign proliferation of the epithelium in the lumen of the gallbladder. They are formed in the form of small, large or mesh large-scale formations. There are four types:
- Inflammatory - formed on the inner shell of the bladder when a bacterial infection enters.
- Cholesterol - overgrowth of the mucosa occurs in connection with the deposition of cholesterol.
- Adenomatous - formed from glandular tissue, often degenerate into malignant.
- Papillomas are nipple growths of a small size on the mucosa.
The causes of the formation of polyps are: hereditary predisposition, inflammatory processes, metabolic disorders or contractile activity of the bladder, malnutrition. When the growths are significant, the patient has the following symptoms:
- Aching, dull pain - the volume of the organ exceeds the norm of the gallbladder due to increased growths and accumulating bile. The condition worsens after stress and fatty foods.
- Hepatic colic - associated with a neck clamp or torsion when polyps hang from the walls of the bladder. Severe, cramping pains cause increased pressure and palpitations.
- There is a bitter aftertaste in the mouth, vomiting after eating, nausea.
In addition, the patient begins to lose weight, yellowness appears on the mucous membranes, urine acquires a dark color, itching and dry skin appear.
How to treat polyps in the gallbladder?
Therapy largely depends on the type of neoplasm. Most often, cholesterol growths appear. They have a loose structure, a small height of up to 1 cm and can, under the influence of bile, dissolve independently. To speed up the process, medications are prescribed that stimulate the quality and secretion. The course of treatment is long and is at least three months. In this case, the following drugs are used:
- "Simvastatin" - purifies the blood of cholesterol.
- "Holiver" - enhances the production of bile.
- “No-shpa” - relaxes the smooth muscles of the bladder and ducts.
- "Allohol" - weakens inflammation and stimulates the synthesis of bile acids.
Be sure to consult a doctor before starting treatment, otherwise you can only do harm. In addition, vitamin complexes to strengthen the body are included in the course of treatment. But when asked how to treat polyps in the gallbladder, doctors say that only surgery is the most effective method. Neoplasms respond poorly to conservative treatment, they have to be constantly monitored so that they do not increase and cannot degenerate into stones or a malignant tumor. The operation is carried out in a gentle way - laparoscopy, after which the patient quickly recovers and gets to work. The only condition after surgery is a lifetime diet.
The interaction of the two digestive organs
The gallbladder and pancreas are located next to each other. The most basic thing is that the bile duct and pancreatic duct join together and enter the duodenum (duodenum). Their functions are aimed at digesting the incoming food. The role of these organs during the digestion process is not the same, but both of them contribute to the breakdown of food components, providing the body with useful substances and energy. The pancreas produces pancreatic juice, which contains a large amount of enzyme substances. When they enter the duodenum, they are activated and affect the digestion of the food contained in it.
The main functions of the gallbladder, the shape of which is similar to an elongated pear, accumulate bile constantly produced by the liver and penetrate into the duodenum. Accumulated secretion, when a food coma enters, is released into the duodenum and is involved in the breakdown and absorption of lipids. Digestion of food cannot occur both without the secret of the pancreas and without bile. Failures in their production and entry into the duodenum cause digestive diseases and provoke complications.
Conclusion
Now you know why you need a gall bladder. To keep it in a healthy state for a long time, it is necessary to take care of your health: move a lot and exercise, do not smoke or abuse alcohol-containing drinks, limit the consumption of spicy and fatty foods. Particular attention should be paid to maintaining health when there is a family predisposition to ailments associated with the gallbladder.