Lipomatosis is the accumulation of fat cells in a specific area of the body. Lipomatous lesions are single or multiple, however, they are always a localized formation, with or without a capsule. Pathology can form both in the subcutaneous tissue and in the internal organs (for example, kidneys, heart, pancreas are damaged). Lipomatosis - what is it and what are its manifestations - is described in detail in this article.
The causes of the disease
The etiology of the disease, unfortunately, is not known, but there is evidence indicating a relationship between changes in the type of lipomatosis with a disorder of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, stress, hereditary (genetic) burden and external adverse factors.
It is proved that the basis of Derkum's disease is polyglandular endocrinopathy, which is obesity, the genesis of which is not known. Atrial septal lipomatosis in 80% of cases develops against the background of general obesity, and in 20% against the background of type 2 diabetes. Moreover, almost all patients with lipomatosis are patients with a cardiological profile, that is, they suffer from various pathologies of the heart (aneurysms, ischemic heart disease, and so on).
Congenital lipomatosis, Madelung syndrome, Leri-Roche disease and the plasma form of the disease are hereditary diseases in which there is a congenital disorder of lipid metabolism.
Forms of Lipomatosis
There are several varieties of the disease:
- knotty form - characterized by the formation of dense, clearly defined, painful fatty nodes;
- mixed form (diffuse knotted).
In addition, the disease is classified in accordance with the localization of the process: lipomatosis of the pancreas and thyroid glands, liver, skin, lymph nodes and so on.
There are also special forms of the disease that have a characteristic localization of formations:
- Derkuma syndrome. It is accompanied by the appearance of multiple painful (or cutting-itchy) lipomas that grow in the lumbar region and limbs, depression and impotence. Pathology is hereditary.
- Epidural lipomatosis. It is accompanied by the accumulation of fat cells between the vertebral periosteum and the dura mater. The cause of the process is often taking corticosteroid drugs or general obesity. A similar form of lipomatosis often develops along with pituitary tumors (prolactinoma) and Cushing's syndrome.
- Gram syndrome. It is considered a variant of Derkum's syndrome and represents the formation of multiple lipomas in women 45-70 years of age, obese and burdened by heredity. In this case, the formations are located on the knee joints and lower back.
- Lipomatosis of the renal sinuses. This form is accompanied by pathological growth of adipose tissue in the kidneys (their sinuses and peripheral parts), leading to atrophy of the renal parenchyma and fibrosis of the organ tissues. Most often, such lipomatosis is combined with urolithiasis and is manifested by prolonged hyperthermia (up to 37-38 degrees) and lower back pain.
- Rocha-Leri syndrome. Such lipomatosis is the lot of patients 40-60 years old. Very rarely occurs in children. Characteristic for this form is the formation of neoplasms on the buttocks and arms. In some cases, lipomas can also occur on internal (mainly digestive) organs. The disease develops as a result of trophic changes or in the presence of a genetic predisposition.
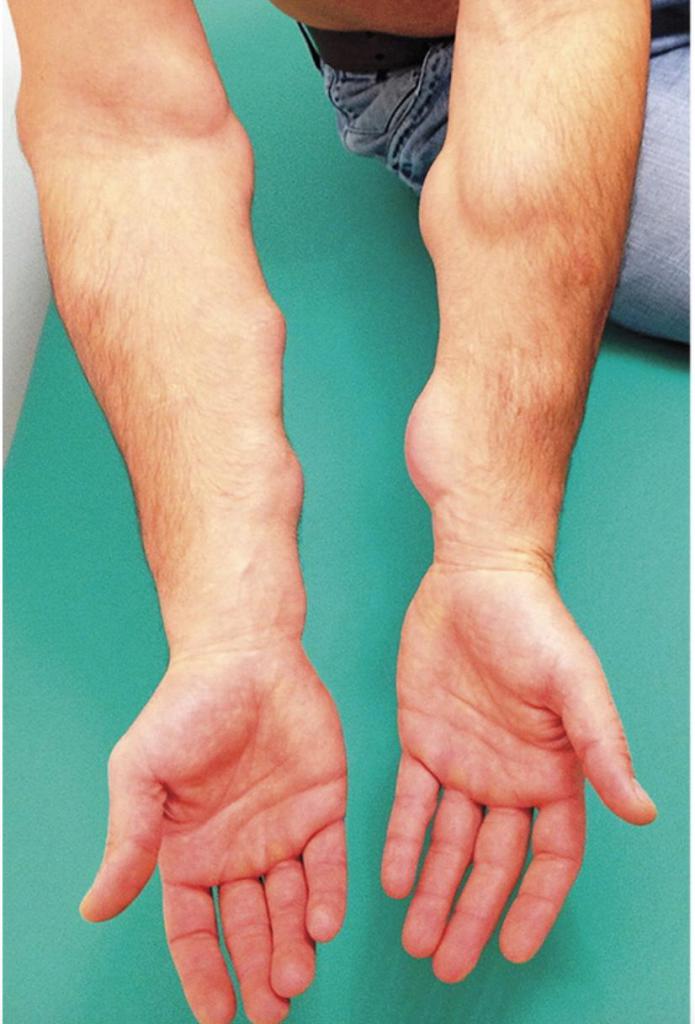
- Hypertensive subcutaneous lipogranulomatosis. The form is very rare, and therefore little studied. Obese women with GB suffer from this ailment. The disease manifests itself in the formation of rapidly growing dense nodes on the hips and lower legs, often undergoing central decay with preliminary softening.
Other varieties of the disease
- Children's diffuse lipomatosis - this disease affects only children. In this case, pathological formations are found on the forearms and hips and are often accompanied by pathological increase in muscle volume, in addition, lipomas are localized in the connective tissue, organ parenchyma and do not have clear boundaries, the course is rapid. In most cases, the pathology is hereditary.
- Hypertrophic form. It is a symmetrical generalized accumulation of adipose tissue between atrophied muscle fibers, as a result of which the patient looks like Hercules.
- Poten-Verney lipomatosis. It is manifested by the formation of nodular lipomas in the supraclavicular fossa.
- Symmetric limited shape. It is accompanied by the appearance on the arms, abdomen, hips, lower back of fatty nodes up to 4 cm. As a rule, it develops in patients 35–40 years old and extremely rarely in children.
- Pasteur lipomatosis and palmar form.
- Segmental form.
Pancreatic affection
Gland lipomatosis (whether pancreas or thyroid) is an irreversible, slowly progressing benign process in which normal organ cells are replaced by fatty cells, as a result of which its function is impaired.
Among the factors leading to the formation of this disease, we can distinguish: diabetes mellitus, various injuries and inflammatory processes, organ damage by toxins (alcohol and others). An important factor is the burdened heredity.
Process degrees
For an easier formulation of the diagnosis and the appointment of adequate treatment, doctors use the division of the process in the pancreas as lipomatosis into the degrees:
- 1 degree. The course is asymptomatic, the process is compensated, damage affects only 30% of the organ.
- 2 degree. Fat cells replace up to 60% of glandular tissue. Non-specific symptoms of digestive disorders occur.
- 3 degree. Adipose tissue occupies more than 60% of organ tissues, significantly impairing its function. That is, glandular cells do not produce a sufficient amount of hormones and enzymes, as a result of which insulin ceases to be synthesized and, as a result, the amount of glucose increases significantly and complications develop.
There is another division of lipomatosis, in accordance with which such forms are distinguished:
- small focal (diffuse);
- islet.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this disease of the pancreas comes down to an ultrasound and CT scan. In this case, a gland of normal size is found, however, its structure has increased echogenicity.
The most reliable research technique is a biopsy, during which fat cells are detected instead of normal tissue.
Condition therapy
Patients are often interested in the question of how to treat pancreatic lipomatosis.
Most often, conservative methods are prescribed for the treatment of this disease. In this case, the patient is invited to lose excess weight, adjust the diet and get rid of bad habits. Enzymatic and hormonal drugs are prescribed from medications to eliminate digestive "malfunctions" and hormone deficiencies.
In addition, concurrent treatment of concomitant ailments (diabetes, hepatitis, thyroid disease), if any, is carried out.
In cases where conservative therapy does not have the proper effect, lipomatous areas will be removed promptly.
The defeat of other organs
The formation of lipomas can occur anywhere in the body from the mediastinum to the kidneys.
The formation of lipomas in the mammary glands is quite rare. The cause of the pathological process may be weight loss or weight gain, an increase in the size of the glands during pregnancy or lactation. The diameter of the wen can be up to 10 cm, if the node is large - breast deformation is possible. The process is long, slowly progressing and asymptomatic (the only exception is the involvement of nerves in the process or their compression by lipoma, which leads to soreness). It is worth noting that lipomatosis rarely occurs directly in the mammary gland, more often this process is observed in the chest subcutaneous tissue.
The occurrence of an ailment in the liver tissue is also possible. Moreover, the process arises as a result of metabolic disorders in the tissues of organs, for example, due to excessive alcohol consumption. Fatty acids are released heavily from the surrounding fatty tissue, and then the liver itself begins to produce fatty cells. Patients complain of weakness, soreness of a dull nature in the side on the right and impaired appetite. Pathology is diagnosed during CT or ultrasound. There are small- and large-drop varieties of the disease.
Heart lipomatosis is most often found in the atrial septum and is characterized by the accumulation of fat in myocardiocytes. As a result, the myocardium does not carry out full-fledged contractions, arrhythmias and blockages can occur, the chambers are stretched, the heart grows in size and heart failure develops.
Renal lipomatosis occurs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus, amyloidosis, glomerulonephritis. It is accompanied by an increase in the organ, swelling of the cortical layer and accumulation of fat in the tubules and ultimately leads to the death of nephrocytes. The functions of the organ are violated until the development of renal failure and the complete cessation of the damaged kidney.
General principles of treatment
Often patients are interested in the question of how to treat lipomatosis.
It is worth noting that the choice of therapy depends on the form of the disease, its localization and severity.
Treatment of lipomatosis is often surgical, but after this, the disease can recur. In the case of diffuse-nodular forms, the operation may be complicated by bleeding due to damage to the developed vasculature in the formation.
Derkum's Syndrome involves symptomatic treatment. So, in the presence of hypofunction of the glands, hormone therapy is prescribed, with an increase in body weight - a diet, and with mental disorders - specific drugs that affect the mental state of the patient. Operations are ineffective due to frequent recurrence, however, surgical treatment is still carried out with severe pain or if the nodes interfere with movements or wearing clothes.
Breast lipomas are observed, removed surgically or without intervention (administration of diprospan, laser, and so on).
Risk groups
The risk groups for lipomatosis include people with immediate relatives (parents) suffering from this disease; patients with diabetes mellitus, overweight, hypertension, endocrine pathologies.
Preventative measures
Specific prevention of the disease does not exist. However, lipomatosis can be prevented to some extent by maintaining a normal weight, eradicating bad habits and timely treatment of diseases.