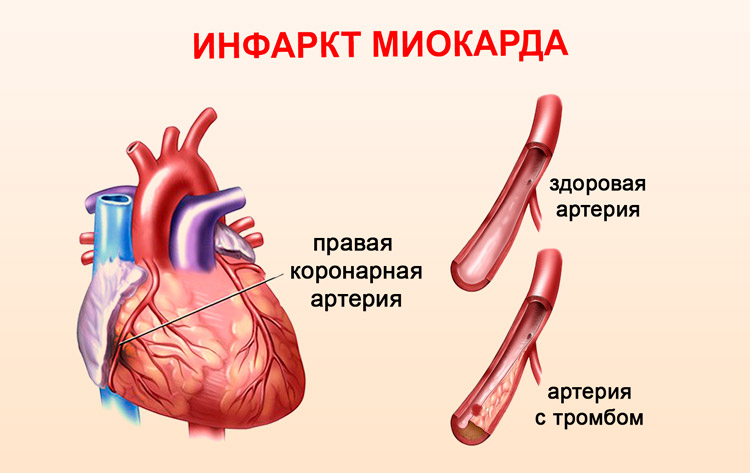
A heart attack is an acute disease that occurs due to the cessation of blood flow in one of the coronary vessels that saturate the heart. This happens in patients with atherosclerosis, when a thrombus forms in the coronary artery and gradually increases, closes the vessel, as a result, the blood flow stops. The myocardial site remains without oxygen and nutrition. Cell death begins in a quarter of an hour. Such changes lead to disturbances in the work of the heart and threaten the life of the individual. He may die immediately, or may not notice what happened. It all depends on the form of the disease.
Symptoms
With myocardial infarction, the following symptoms appear:
- severe chest pain of a pressing or stitching nature;
- burning in the chest;
- pallor of the skin;
- cold sweat;
- dizziness;
- shortness of breath, shortness of breath;
- heart rhythm failure.
In some cases, there may not be any symptoms. A person learns that a heart attack has occurred according to the results of a cardiogram at the next doctor's visit. In others, an attack begins acutely and it is important to immediately seek medical help so that sudden death does not occur.
Heart attack diagnosis
For its implementation it is necessary:
- To collect an anamnesis - information is collected about diseases, chest pains, risk factors.
- Examine the patient - attention is drawn to excess weight, a capillary network on the face, blood pressure is measured, the pulse is felt, heart rhythms are heard.
- Assign a general and biochemical blood test.
- ECG - the characteristic signs of the disease are detected: negative T wave, pathology of the QRS complex. According to the cardiogram, it is possible to determine the location of the lesion.
- Echocardiography - determines the violation of contractility of the affected ventricle.
- Coronary angiography - reveals the closure of a vessel or its narrowing.
Upon receipt of all research data, the patient is diagnosed and a course of therapy is prescribed.
Myocardial infarction: different periods
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the period of myocardial infarction. The course of each of them has its own symptoms and features, which should be considered when providing assistance. There are five periods of illness :
- Prodromal - its duration is from several hours to a month. It is characterized by recurring pain and tachycardia.
- Acute - from the occurrence of severe myocardial ischemia to the dying of a section of the heart muscle, it takes from half an hour to two hours. Most often, a characteristic chest pain occurs, which causes a feeling of fear and anxiety, there is increased sweating.
- Acute - the focus of necrosis in the heart is determined. The duration of this period of myocardial infarction is up to 10 days. The pains pass, signs of death of the heart muscle cells appear, a slight increase in body temperature occurs.
- Subacute - the patient's condition returns to normal. Pain in the heart and fever stops. Pulse and blood pressure are approaching normal, heart failure is weakening. The period lasts up to eight weeks.
- Post-infarction - duration up to six months. All painful symptoms disappear. Laboratory data are back to normal.
Complications in the acute period
The most common complications of the acute period of myocardial infarction:
- Acute heart failure is formed according to the left ventricular type. The severity is determined by the size of the area of myocardial damage. As a result of tissue necrosis, the pumping function of the heart decreases and cardiogenic shock occurs, in which almost half of the left ventricular myocardium is affected. For treatment, vasopressor drugs, Nitroglycerin, cardiac glycosides, ACE inhibitors, diuretics are used. In difficult situations, an operation is performed.
- Rupture of the interventricular septum occurs in the first five days. This complication of the acute period of myocardial infarction mainly occurs in older people with a high heart rate and hypertension. Surgical treatment is carried out, endovascular methods are used, vasodilator drugs are prescribed.
- Mitral insufficiency - mild or moderate form is more often formed. A severe form is very dangerous when the papillary muscle ruptures in the first twenty-four hours after a heart attack. With this pathology, an emergency operation is performed. In severe form, the cause of which ischemia, do coronary angioplasty. In other cases, drug therapy is used.
- Rupture of the free wall of the left ventricle occurs in the acute period of myocardial infarction with its transmural form. To assist, an urgent operation is performed to close the defect.
- Thromboembolism occurs with anterior localization heart attacks in the first ten days. With extensive heart attacks, “Heparin” is administered intravenously on the first day, and then “Warfarin” is administered anticoagulant therapy.
- Early pericarditis develops with transmural infarction in the first four days. To relieve symptoms, take "Aspirin" up to six times a day.
- Arrhythmias are observed in most individuals in the acute period of myocardial infarction. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation or left ventricular fibrillation occurs. Heart contractions may stop and cardiac arrest will follow. In this case, cardiac defibrillation will be required.
- Acute aneurysm of the left ventricle - severe heart failure and shock are possible. They use vasodilator drugs, intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation, ACE inhibitors, and sometimes surgical treatment is used.
- Pulmonary edema occurs in the first week of the disease, occurs against the background of acute heart failure. For treatment, glycosides and diuretics are used.
Acute period
Symptoms in the acute period of myocardial infarction are pronounced and do not go unnoticed. The main symptom is severe pain, which has a burning, dagger character. It appears after emotional stress or physical exertion and lasts more than half an hour. Often, pain is given to the lower jaw, shoulder blades, arms, neck area. They cannot be eliminated even after taking nitroglycerin or other vasodilators repeatedly. The individual has a strong sense of fear of death, a sharp weakness, and sometimes fainting.
The patient has a faster pulse, a disturbed heart rate, a fever, a sharp pallor, and a sticky cold sweat appears. Urgent medical attention is needed. On the first day, a focus of necrosis is formed, and for the acute period of myocardial infarction on the ECG, elevation of the ST segment above the contour is noted, which merges with the positive T wave. The R wave decreases proportionally to the severity of damage in height.
Acute myocardial therapy
Treatment of acute myocardial infarction is focused on the fastest restoration of blood flow through an artery blocked by a blood clot. When this goal is achieved, chest pains do not bother, the process of dying of the cellular tissue of the heart muscles stops, and the supply of the heart with nutrients and oxygen is resumed. The faster this process ends, the greater the likelihood that a heart attack will pass without complications.
Treatment of myocardial infarction in the acute period is as follows:
- thrombolytic therapy - taking medications that help dissolve blood clots;
- anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents - drugs that prevent the formation of new blood clots;
- angioplasty - the procedure for opening the affected artery using a catheter, which is inserted into the vessel to preserve the lumen and ensure blood flow;
- taking medications that reduce oxygen consumption by the heart muscle;
- medications that help normalize heart rate.

The patient spends an acute period of myocardial infarction in a hospital. Initially, he is in the intensive care unit. When the condition improves, he is transferred to a regular ward. Most importantly, the patient needs to behave properly. In the first three days you can not sit and get out of bed. As a result of the disease, part of the heart muscle becomes soft. Even with a small load, it can rupture, which threatens with death, or stretch, which will cause heart failure and disability. Only compliance with bed rest and timely treatment will help accelerate rehabilitation after illness.
Drug therapy in the subacute period
The following drugs are used to treat a subacute period of myocardial infarction:
- Acetylsalicylic acid. It is used to treat all patients in the absence of contraindications. If the drug is intolerant, “Clopidogrel” is prescribed. In case of impossibility to use both drugs, indirect anticoagulants are used .
- Beta blockers. Assign to all patients in the absence of contraindications. The purpose of admission is to reduce the number of heart contractions to 60 beats per minute at rest, to reduce systolic blood pressure to 100 mm r. Art.
- ACE inhibitors. The treatment period for myocardial infarction begins with the onset of the disease and continues in most patients for life. Preference is given to medicines that have a long half-life. Start taking with small doses, gradually increasing it to the maximum allowable.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After the operation on the heart, the patient goes through a long recovery period. For several days he was in the intensive care unit. Further, with the improvement of his condition, he is transferred to the general ward. A very important role in the postoperative period of myocardial infarction is played by the diet, which the doctor prescribes to each patient individually. Initially, only light cereals and broths are included in the diet. After the fourth day of surgery, the patient is transferred to the department, and his diet may consist of the following products:
- cereals from coarse cereals - barley, pearl barley, unpolished rice;
- dairy - low-fat cheese and cottage cheese;
- fruits and vegetables - baked and fresh;
- meat - poultry and rabbit, boiled or steamed;
- fish - fresh varieties;
- various low-fat soups.
The patient observes the diet under the supervision of doctors while he is in the hospital. After leaving the hospital, many forget about it, which leads to a deterioration in well-being.
In addition to diet, the patient is advised to exclude intense physical activity, however, light exercise should be present. Be sure to observe the regimen of activity and rest and do not forget about drug supportive therapy. Subject to all recommendations, health problems are minimized.
Complications of myocardial infarction in periods
Myocardial infarction is dangerous because complications can develop at any stage of its course. By periods, their list looks like this:
- Prodromal - there are various types of arrhythmias, progressive angina pectoris.
- The most acute is extrasystole, paroxysmal tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, left ventricular heart failure.
- Acute - arrhythmias and blockades, cardiogenic shock, cardiogenic pulmonary edema, pericarditis, cardiac rupture, acute cardiac aneurysm, early post-infarction angina pectoris.
- Subacute - during this period of myocardial infarction, there is a violation of the heart rhythm and conduction, chronic circulatory failure and cardiac aneurysm, thromboembolic complications, post-infarction syndrome occur.
- Reconstructive - possibly repeated damage to the heart muscle, chronic heart failure, chronic heart aneurysm, arrhythmias, and blockade.
Patients hospitalized 6-12 hours after the onset of an attack when thrombolytic therapy was not performed are especially prone to complications. In the case of complicated heart attack, the probability of death increases.
Myocardial infarction: rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation is important during the recovery and return of the individual to everyday life. It includes:
- Drug treatment. After a heart attack, patients need long-term, and sometimes lifelong drug therapy. To normalize blood pressure, maintain heart muscle and prevent complications, the doctor recommends ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers, and to lower cholesterol - statins.
Dietary nutrition. The menu of individuals who have suffered myocardial infarction should be strictly controlled. It must contain products that help restore heart function. To do this, you need to include more vegetables, fruits, various cereals in the diet and exclude animal fats, smoked meats, fried foods and sausages from consumption. Must be present fish and bird. It is advisable to cook food steamed.
Physiotherapy exercises. The patient begins to perform light exercises in a hospital under the supervision of medical personnel. Then he visits a specialized center where an experienced specialist will select an individual set of exercises and determine the optimal load. Six weeks after the disease, it is possible to diversify physiotherapy exercises by swimming, bicycle ergometry, therapeutic running, walking.
Psychological support. Patients who have had a heart attack need the support and attention of relatives and friends, and some require the help of a psychologist and psychotherapist. Many individuals after myocardial infarction during the rehabilitation period develop depression and fear of relapse.
Dispensary observation. Some complications develop a long time after treatment, so patients need long-term follow-up.
Tips for preventing myocardial infarction
Leading cardiologists of the country give the following recommendations for the prevention of myocardial infarction:
- The patient should be provided with medical care within 6-12 hours from the onset of the attack. After this time, necrosis of myocardial tissue begins. The patient needs to get to the clinic as soon as possible, and not wait until the condition improves. Doctors say that every third heart attack passes without symptoms or with mild signs, so you need to carefully monitor your health.
- After a heart attack, a lifestyle changes. Modern medicine is able to return the patient to the system very quickly, and he does not have time to realize that he was ill with a serious disease. He lives an active life and feels like a completely healthy person. Cardiologists warn that it is necessary, following recovery, to follow the recommendations of doctors and continue drug therapy for life.
- Everyone who has had a myocardial infarction should understand that this is an ongoing process. The disease continues all the time. In the period after myocardial infarction, atherosclerotic plaques grow in the vessels, and blood clots form on them.
The body can be affected by both medication and other means. It is necessary to abandon bad habits: alcohol and smoking. Give the body feasible physical activity, increasing them gradually. Eat right: eat high-grade proteins, eat more vegetables, herbs and fruits. Reduce or minimize sugar, salt, and smoked meats. All this will help to remain in service for a long time. The above tips are not recommended to be neglected.