The intestine is an organ of the digestive system that performs very important functions in the human body, but today intestinal pathologies are very common. Conducting preventive examinations of the gut comes to the fore in order to prevent the development of various diseases. In this article we will talk about what methods of examination of the intestine medicine offers, and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each of the methods.
What is the intestines for?
The intestine is an organ that is located in the abdominal cavity and is involved in the digestion process. It absorbs nutrients that later enter the bloodstream. Undigested substances are excreted in the form of feces together with intestinal gases.
The length of the human intestines reaches four meters. It is home to a huge number of bacteria that provide digestion processes, so it is very important that the microflora of the organ is in constant balance. Otherwise, the body will fail, which will entail the development of various pathologies. Disorders of the intestines can be manifested by a variety of symptoms, among which the most obvious are rumbling in the abdomen, flatulence, pain, diarrhea, stool retention, chronic constipation, etc.
Intestinal diseases, as a rule, are infectious or parasitic in nature. Infectious pathologies include syphilis, tuberculosis, dysentery, etc. parasitic - scarabiasis, diphyllobothriasis, trichinosis, intestinal myiasis, trichocephalosis, etc. Various methods of intestinal examination are used to diagnose all these diseases.
Intestinal structure
The anatomical structure of the organ is represented by two segments:
The small intestine is located between the stomach and large intestine. In it, the digestion process takes place directly. This section of the intestine is divided into the following components:
The small intestine got its name because, in comparison with the anatomical structure of the colon, it has less thick and strong walls. In addition, the diameter of the cross section of its departments is much smaller.
The large intestine is the lower part of the digestive tract, in which water is absorbed and feces are formed. Its length is approximately 1.5–2 m.
The large intestine is represented by segments:
- cecum and appendix
- colon, which includes the ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and sigmoid colon,
- rectum with a wide part and terminal tapering part.
I must say that the methods for examining the intestine are very similar for both the small intestine and the colon, although there are nuances.
Relevance bowel examination
To date, intestinal pathologies are very common. Unfortunately, severe diseases are often encountered - cancerous tumors. Each year, about 1 million new cases of colorectal cancer are diagnosed in the world. Half of the patients who have this disease are killed. Intestinal oncology occupies a leading position among all malignant tumors. Therefore, it becomes relevant to conduct preventive examinations of the colon in order to prevent the development of diseases.
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to detect various pathologies of the intestine in the early stages and begin immediate treatment, which increases the patient's chances of an early recovery or at least maintaining his quality of life at a good level. The diagnosis of diseases of the colon is more demanded, because serious disorders arise precisely in these parts of the intestine. Medicine offers patients a whole range of diagnostic methods for this organ, including:
- capsule examination,
- colonoscopy
- endoscopy
- MRI diagnostics
- irrigoscopy.
Video capsule examination of the intestines
Among all available diagnostic methods, this method is considered the most painless and at the same time quite informative. The essence of the study is that the patient swallows a capsule equipped with a video camera. Once in the human body, the “device” travels through all sections of the gastrointestinal tract, taking a photograph every two seconds. Data from the chip is processed by a special program, and medical conclusions are made based on the results obtained.
You must first prepare for the procedure. On the eve of the manipulation, eating is prohibited, the study is performed on an empty stomach. A device is mounted on the human body that will record the results of the study. The diagnostic procedure takes about eight hours, during which the patient leads a normal lifestyle - goes about his business, without disrupting the daily rhythm. After examination, the capsule dissolves and is excreted from the body in a natural way.
The most modern methods of examining the intestines today are represented using video capsules, although this method has its drawbacks. Such manipulation is very expensive. The fact is that “smart” capsules cost about 1 thousand. e., and only two countries offer them today - Japan and Israel, leaders in the market for such services. In the CIS countries there is still no in-house production of diagnostic chips.
Intestinal endoscopy
An endoscope is an optical device that is used in medicine to study the hollow organs of a person, for example, the esophagus, stomach, intestines. In most cases, it is administered through the natural opening of the body, less commonly through surgical incisions.
Endoscopic methods for examining the intestine are prescribed for suspected polyps or tumor formations in the intestine. Before the procedure, the patient should carefully prepare the body - cleanse the intestines. Today, this measure is easily carried out through special medications. The doctor introduces an ultrasound probe into the intestine, allowing you to examine in detail the mucous membrane and the condition of the walls of the organ under investigation. In order to clarify the results during the procedure, biological material can be taken for additional laboratory tests.
An endoscopic ultrasound of the large intestine is performed in most cases, with the exception of the cases when the patient has diseases of the heart and blood vessels or lungs. This is directly related to the need for special drugs. However, the feasibility of such a study is decided individually in each case.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a research method based on the use of a special device - a fibrocolonoscope - a plastic bundle with an optical system. Such a study is recommended for preventive purposes to be performed every five years by people over forty years of age and those whose heredity is burdened with intestinal oncological pathologies.
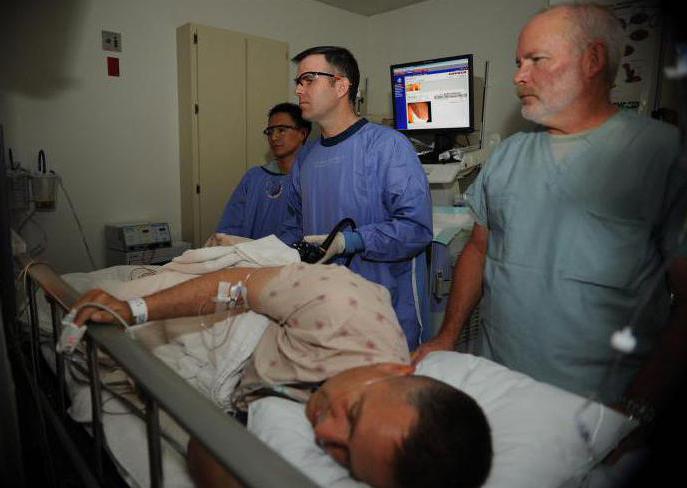
Before the procedure, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines with the help of medications. Typically, a colonoscopy lasts no more than 30-40 minutes, but it is a rather unpleasant procedure. The patient may be uncomfortable due to the fact that the intestines are filled with air, and the person has a feeling of bloating. Methods of examining the intestines with a fibrocolonoscope also allow sampling of biomaterial for histological analysis. In addition to diagnostic functions, colonoscopy allows you to remove polyps or benign tumors of small size. Using this technique, it is also possible to identify adhesions in the intestine. The results of the study are ready, as a rule, immediately after manipulation.
Irrigoscopy
The method of irrigoscopy is a method of examining the intestine using x-rays. Before the procedure, the patient must carefully prepare the body - cleanse the intestines, while eating is not allowed. Immediately before the study, a liquid is introduced into the body, in the composition of which there is a radiopaque drug - barium sulfate. The essence of the study is as follows. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, the solution fills all areas of the intestine and allows the images to evaluate the contours and the degree of lumen of the intestine. The procedure can be supplemented by another manipulation. After the contrast agent is removed from the body, air is pumped into the intestine - this gives an additional opportunity to examine in detail the contours of the departments of the organ.
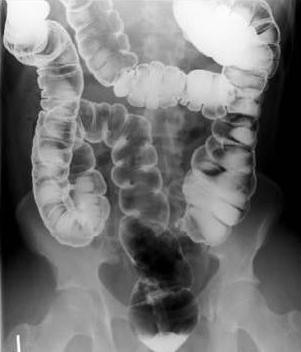
This technique makes it possible to diagnose fistulas, birth defects, ulcers, scars, but it is considered not sufficiently informative. The procedure is considered conditionally safe, since during the study, the body is exposed to radiation exposure.
Intestinal MRI
Another way to diagnose intestinal diseases is magnetic resonance imaging, which is based on the use of a magnetic field in the study. This procedure is painless and is considered safe, since it does not carry a radiation load on the body. The day before, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines, and immediately before manipulation - to introduce a contrast agent into the body. The study itself takes no more than ten minutes and allows you to identify serious disorders in the intestine, up to malignant tumors.
I must say that the diagnosis should be carried out comprehensively, therefore, methods of clinical examination of the intestine are added to the above manipulations. To detect dysbiosis, a feces test is done, in addition, rectal and bacteriological studies can be performed. Blood is taken from the patient - as a rule, both biochemical and clinical analysis of the material is performed. Modern diagnostic methods, however, will not replace digital
rectal examinations.Examination of the small intestine: methods
As noted earlier, most often serious pathologies affect the departments of the colon, however, diseases of the departments of the small intestine also occur. Diagnosis, as a rule, begins with a study of the duodenum located between the stomach and large intestine. For these purposes, fibroscopy or endoscopy is prescribed, they may additionally resort to irrigoscopy or radiography. A few days before the manipulation, the patient is recommended to adhere to a certain diet.
With the help of endoscopy, you can not only diagnose the intestines, but also remove polyps, stop bleeding, and install a probe for food intake. Two-balloon enteroscopy, which is performed under general anesthesia, is considered the most modern method for diagnosing diseases of the small intestine. This procedure is considered severe enough and is performed only in a hospital setting. Enteroscopy is prescribed for bleeding in the small intestine, with obstruction.
Thus, capsule examination, endoscopy, colonoscopy, irrigoscopy and MRI are the basic methods by which the intestines are diagnosed and examined. I must say that in general, the pathological conditions of the organ are diagnosed more often in women, but this is only due to the fact that the beautiful half of humanity carefully monitors their health and consciously undergoes a medical examination for preventive purposes. There is still an opinion that such diseases are inherent in wealthy people, because they are more likely to afford refined food.