The heart is one of the main organs. Circulation circles begin with it. Large vessels also flow into the heart muscle, giving rise to all the arteries and veins in the body. Therefore, cardiological diseases remain one of the most severe and take first place in the list of causes of death. Heart pathologies occur with the same frequency in both the adult population and among children. One of the acquired diseases is viral myocarditis. To a greater extent, this ailment relates to the problems of pediatrics, but it occurs in adults.
The course of the disease can be acute and chronic. In some cases, patients do not even know about the presence of pathology, since the ailment is not actively manifested. Despite the absence of severe symptoms, treatment of myocarditis should be started as soon as possible. After all, this disease belongs to one of the causes of heart failure in both adults and children.
Viral myocarditis: causes
Myocarditis means inflammation of the heart muscle, leading to rhythm and conduction disturbances. Often, the disease occurs as a result of viral infections. In other words, myocarditis is a complication of various pathologies. Pathologies preceding inflammation of the heart muscle include:
- Coxsackie V Infections
- Polio.
- Different types of flu.
- Infections caused by ECHO viruses.
- Herpes.
- Diphtheria.
- Enterovirus infection.
- Scarlet fever.
- HIV infection.
Any of these diseases leads to a decrease in the immune response and can provoke the development of myocarditis of viral etiology. According to statistics, this disease makes up about 10% of all cardiological pathologies. In pediatric practice, 2 peaks of incidence are noted. These include the infant period and age of 6-7 years. Among the adult population, mainly young people suffer from this ailment. The average age of patients is from 30 to 40 years.
In most cases, myocarditis is caused by the Coxsackie virus. This pathogen is the cause of the disease in 50% of cases. This virus has a tropism for cardiomyocytes. It not only quickly penetrates the myocardium, but also multiplies in it. Therefore, the pathogen often causes a subacute and chronic form of inflammation. In addition, influenza A and B viruses have tropism for the heart muscle. Others that have been aroused less often cause the disease. The most dangerous pathologies that provoke inflammation of the heart include diphtheria, sepsis and scarlet fever. They are the cause of acute viral myocarditis. Most often, the causative agents of these pathologies lead to heart complications in patients with reduced immunity. Acute myocardial inflammation can be fatal. In addition to these diseases, enterovirus infection, which is often found in children, is of great danger.
The mechanism of myocarditis
In most cases, viruses enter the body through the respiratory tract. They settle on the mucous membranes of the nasal sinuses or throat, and later invade the cells. Viruses multiply rapidly, causing a local inflammatory process. Some pathogens enter the gastrointestinal tract through contaminated food. With a decrease in the immune response, harmful agents penetrate the bloodstream. Thus, viruses penetrate first into the cardiac vessels, and then into the myocardium. This leads to the activation of a number of processes. The pathogenesis of viral myocarditis includes the following steps:
- The introduction and reproduction of the pathogen in the heart muscle.
- The effect of toxins on cardiomyocytes.
- Activation of immune defense and the development of autoantibodies.
- Lipid peroxidation.
- Apoptosis of cardiomyocytes.
- Electrolyte disturbances.
Upon entry, the virus binds to receptors located on the surface of cardiac cells. As a result, myocyte structure is damaged. Cardiotropic viruses multiply rapidly and infect more and more heart muscle cells. The harmful effects of pathogens are due to the fact that they emit toxic substances. Thus, an inflammatory reaction and dystrophy of the cellular elements of the myocardium develop.
Such changes lead to the activation of the body's defenses. Immune cells begin to respond to abnormalities and secrete antibodies. Unfortunately, such protection not only fights against the pathogen, but with destroyed cardiomyocytes. As a result, immune cells begin to perceive the tissue of the heart muscle as foreign particles. Such a reaction only aggravates cell damage. The inflammatory process triggers a complex biochemical reaction - lipid peroxidation. As a result, free radicals form in the cells, which irreversibly damage myocardial tissue.
With the progression of the disease, pathological reactions are exacerbated. The next stage in the development of viral myocarditis is apoptosis. It is a cell death programmed at the genetic level. All of these violations lead to hypoxia of uninfected cardiomyocytes and the development of acidosis. Thus, the electrolyte balance in the cells is disturbed and potassium is lost. Deficiency of this chemical element entails severe consequences. In addition to the inflammatory process and impaired contractility of the heart, rhythm and conduction disorders develop.
Classification of a pathological condition
All over the world there is a single classification of diseases (ICD-10), which includes various pathological conditions. Among them - viral myocarditis. ICD-10 is a classification in which each disease is assigned a specific code. The diagnosis of viral myocarditis is code I41.1.
The disease differs in the course of the pathological process, depending on the time of persistence of the pathogen in the body. According to this classification, there are:
- Acute myocarditis. It is characterized by the presence of severe intoxication syndrome. During the first 2 weeks there is an increase in body temperature, runny nose, headache. After 14 days, symptoms of inflammation of the heart muscle begin to appear.
- Subacute myocarditis. This diagnosis is made with a disease duration of less than 6 months. Symptoms of inflammation are less pronounced than with acute myocarditis. However, signs of chronic heart failure are noted.
- Chronic myocarditis The course of the pathology takes more than six months. In a chronic process, signs of exacerbation are replaced by the complete disappearance of symptoms. However, with this form of myocarditis, organic changes in the heart muscle occur, namely sclerosis and dilatation.
Another type of the course of the disease is chronic persistent inflammation. It is characterized not only by the disappearance of the clinical picture of the pathology, but also by the restoration of the normal activity of the heart. Despite this, this condition is called borderline inflammation, since cardiological failure can develop at any time in the future. Therefore, one of the most dangerous forms is considered to be persistent persistent viral myocarditis. Symptoms and treatment of the disease directly depend on the nature of the course of the pathology. Therefore, it is important to determine the form of the inflammatory process in time.
Symptoms of the disease in adults
Myocarditis caused by viruses can develop in people of any age with a decrease in immunity or under the influence of other provoking factors, such as stress. The clinical picture in the early days of the disease does not have any connection with signs of heart disease. Therefore, the pathology is diagnosed after the inflammatory process begins in the myocardium. Symptoms depend on the extent of the lesion. If a small area of the heart muscle is inflamed, then there may be no clinical manifestations. With extensive damage, severe pain and shortness of breath are noted.
Most often, pathology is observed in middle-aged people - from 30 to 40 years. How to suspect viral myocarditis? Symptoms of the disease rarely begin suddenly. Usually they are preceded by a clinical picture of the infection. Signs of the disease vary depending on the type of virus. The most commonly reported symptoms are fever, headache, runny nose, lacrimation, sore throat, and general weakness. In some types of infections, disorders of the digestive tract come first. 2 weeks after the onset of the disease, cardialgia occurs. Pain in the heart is permanent. The severity of discomfort depends on the prevalence of viral myocarditis. Symptoms in adults are less pronounced than in children. With subacute and chronic course of the disease, patients complain of shortness of breath. In some cases, this is the first sign that a person pays attention to. However, shortness of breath indicates the development of heart failure and the transition of the disease into a protracted form.
Features of the pathology in children
In cardiological practice, viral myocarditis is often found in children. Symptoms are not much different from the manifestations of the disease in adults. However, there are some features of the course of the disease. Unlike adults, symptoms in children depend not only on the prevalence of the inflammatory process, but also on the age of the child. Particularly severe illness occurs during the neonatal period. The disease is accompanied by intoxication, refusal to feed and the appearance of cyanosis. The baby's skin acquires a bluish tint, the baby constantly cries and does not sleep. With the progression of the disease, edema and shortness of breath are noted even at rest.
Viral myocarditis in young children has the same manifestations. In addition, children often complain of pain in the abdomen and chest, sometimes the pathology is accompanied by a cough. Preschool age is considered the peak of viral myocarditis. Symptoms of the pathological process become more similar to the clinical picture observed in adults. The main complaints include fever, muscle pain and weakness. Then the unpleasant sensations of tingling in the region of the heart join. Children quickly get tired of games and physical education. This is due to increasing shortness of breath associated with impaired heart function.
Diagnosis of the disease in adults and children
How to detect viral myocarditis? Diagnosis of this pathology begins with examination and physical examination of the patient. The main method to suspect myocarditis is auscultation of heart valves. When listening to a phonendoscope, a decrease in the sonority of the 1st and 2nd tone is noted. The defeat of the mitral valve is indicated by the appearance of systolic murmur. With severe inflammation of the myocardium, splitting of the 1st tone is heard. Chronic disease is accompanied by heart failure and dilatation of the left ventricle. Auscultation of this complication is expressed in the appearance of diastolic murmur.
Laboratory diagnostics includes OAC, a biochemical blood test. With inflammation, leukocytosis, lymphocytosis and neutropenia, an increase in the level of C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, and acceleration of ESR are observed. Percussion and ECG data indicate an increase in heart size. Damage to the valvular apparatus is noticeable during ultrasound examination - echocardioscopy.
To identify the etiological factor, immunological diagnostics is performed. It allows you to determine the titer of antibodies to certain types of viruses. The material for analysis is biological fluids, in most cases blood. PCR is also performed to isolate the DNA and RNA of the pathogen.
Differential diagnosis
The appearance of pain in the heart can indicate a variety of cardiological diseases. First of all, myocarditis is differentiated with heart attack and angina pectoris. According to the clinical picture, these pathologies differ in the intensity and nature of the pain. With myocardial ischemia, unpleasant sensations occur suddenly and increase within a few minutes or hours. The pain is localized behind the sternum and radiates to the left arm and shoulder blade. In some cases, angina pectoris or small focal infarction have less pronounced symptoms. Special studies, in particular ECG and venous blood test for troponins, help to eliminate ischemia.
In addition to angina pectoris and myocardial infarction, myocarditis should be differentiated from other diseases accompanied by heart failure. These include acute and chronic rheumatic fever. This disease is accompanied by damage to the valvular apparatus of the heart. Unlike infectious myocarditis, rheumatism has other characteristic symptoms. Among them are erythema on the skin, behavioral changes (small chorea) and joint damage.
Sometimes pain in the heart occurs with pathologies of the digestive and nervous system. Cardialgia can be confused with an exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis or the initial period of herpes zoster. With these pathologies, changes on the ECG and echocardiography will not be observed. In addition, during auscultation of the heart, normal, unchanged tones will be heard.
Viral myocarditis: treatment of the disease
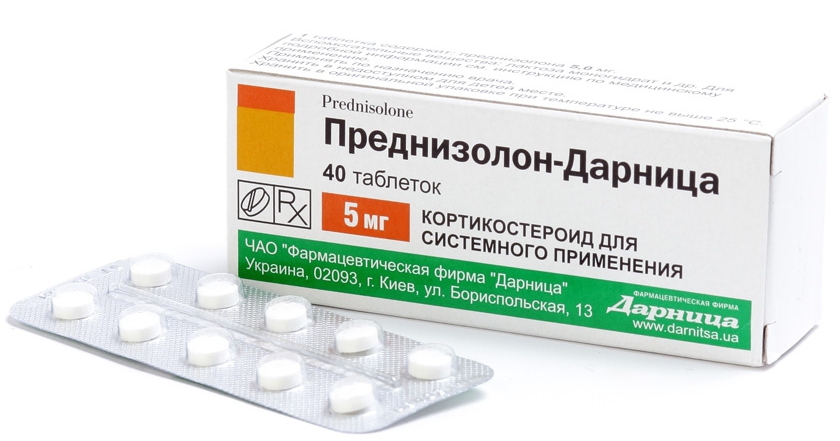
Despite the fact that the cause of infectious myocarditis can be identified, etiological therapy is rarely used. This is because the pathogen penetrated the cells and heart damage has already occurred. Therefore, the treatment of viral myocarditis is aimed at the pathogenesis of the disease. To improve the condition of the patient and stop the development of pathology, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Among them are the medicines Indomethacin, Diclofenac. They not only eliminate inflammation, but are also painkillers. With the progression of the disease, small doses of hormones are used. These include the drug "Prednisolone."
Treatment of chronic viral myocarditis is aimed at combating heart failure. For this purpose, cardioprotectors are prescribed, for example, the drug "Preductal". Vitamins for the heart and antiplatelet agents are also needed. With edematous syndrome , the use of diuretics is indicated. In severe rhythm disturbances, the installation of a pacemaker is required.
Recovery period after myocarditis
Since the disease often becomes chronic, in order to avoid exacerbations, adequate recovery after myocarditis is required. Patients are shown physical and psycho-emotional rest. It is required to exclude salty foods from the diet and add foods rich in potassium. It is recommended to eat lean meat and fish, fresh vegetables and fruits, kefir, baked potatoes, nuts.
Young women are interested in the question: is it possible to become pregnant with viral myocarditis? It depends on the severity of the disease. Naturally, with an exacerbation of the inflammatory process, pregnancy is contraindicated, as it can lead to a deterioration in the condition of the future mother and abnormalities in the fetus. As you recover and recover, you can think about replenishment. However, pregnancy should be planned in conjunction with a gynecologist and cardiologist after a full examination.
Primary prevention of myocarditis
In order to prevent the development of myocarditis, it is necessary to adhere to generally accepted preventive measures. First of all, it is necessary to avoid colds and timely take antiviral agents for infection. Additional methods include: walking and airing the premises, wet cleaning, taking vitamins and giving up bad habits.