Renal tuberculosis occurs when an organ is infected with mycobacterium. The causative agent belongs to the group of anaerobic, is transmitted with blood, spreads through the body with lymph flow. When infected with mycobacterium, a person does not always get kidney tuberculosis. A disease is observed if several significant factors influence at the same time.
Basic information
In order for kidney tuberculosis to appear (except for infection with pathological microflora), weakening of the organ parenchyma, usually due to a deterioration in blood flow quality, is necessary. It is more likely that the infection will end in the disease, if a person has lowered immunity, kidney tissue is the area of localization of inflammatory foci. If the disease occurs, it leads to a deterioration in the functionality of the organ. Some forms of mycobacteria are characterized by increased resistance to antimicrobials. Such a variant of the disease with a greater degree of probability leads to insufficient functioning of the organ.
According to doctors, kidney tuberculosis in half the cases (and sometimes even a little more often) takes a destructive form. Symptoms appear on average six years after the initial infection. Timely diagnosis and clarification of the case before this period is extremely difficult.
How to notice?
The first signs of kidney tuberculosis are divided into local, general. A person often feels tired, often the temperature rises relative to the norm. Concerned about high blood pressure. Studies show macrohematuria, an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. When studying the renal parenchyma, it is possible to detect foci of destructive processes, the release of pus.
Local symptoms of kidney tuberculosis in adults (and children) include lower back pain. Analyzes show pyelonephritis, the study of the renal parenchyma gives an idea of the destructive processes.
Disease development
The first signs of kidney tuberculosis usually appear only after 5-7 years from the moment of infection of the body with mycobacteria. The duration of the incubation period is one of the main obstacles to timely diagnosis of the condition. Certain difficulties are associated with a reduced sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics. If during the incubation period the patient uses antimicrobial drugs to eliminate other inflammatory processes, then this increases the resistance of mycobacteria, that is, creates difficulties in the future for treating the disease. About 70% of cases during the incubation period do not manifest themselves with any phenomena.
About a third of patients in the early years are faced with some symptoms, the first signs of kidney tuberculosis. The temperature rises to subfebrile, but not higher than 38 degrees, the patient often feels tired, weak. From time to time, a pain syndrome is localized in the lower back.
One of the characteristic signs is urine with tuberculosis of the kidneys, containing inclusions of pus. Laboratory studies can show the presence of a pathogen in the secretions, sometimes there are protein fractions, red blood cells, white blood cells. No specific effects of renal tuberculosis occur. The urine is acidic, when sowing, infection can be established in a two-week period, but it is extremely rare that such an analysis is prescribed to a person during the incubation period - there is simply no reason for this.
Disease progression
Usually indicate the need for treatment of symptoms of advanced tuberculosis of the kidney. The process is accompanied by complications, precisely because of their reason, the patient usually seeks medical help. Tuberculosis can provoke inflammation of the prostate, urethra, and appendages. Dysuretic disorders are possible, lower back pain becomes very severe, blood fractions are observed in urine. Such symptoms indicate the development of the disease.
Acute symptoms are extremely rare. With pathology, an increase in pressure, a general condition of poisoning is possible. When kidney tuberculosis spreads to the upper areas of the ureter, the bladder, dysuretic failures are possible. Another symptom is paranephritis.
Additional symptoms
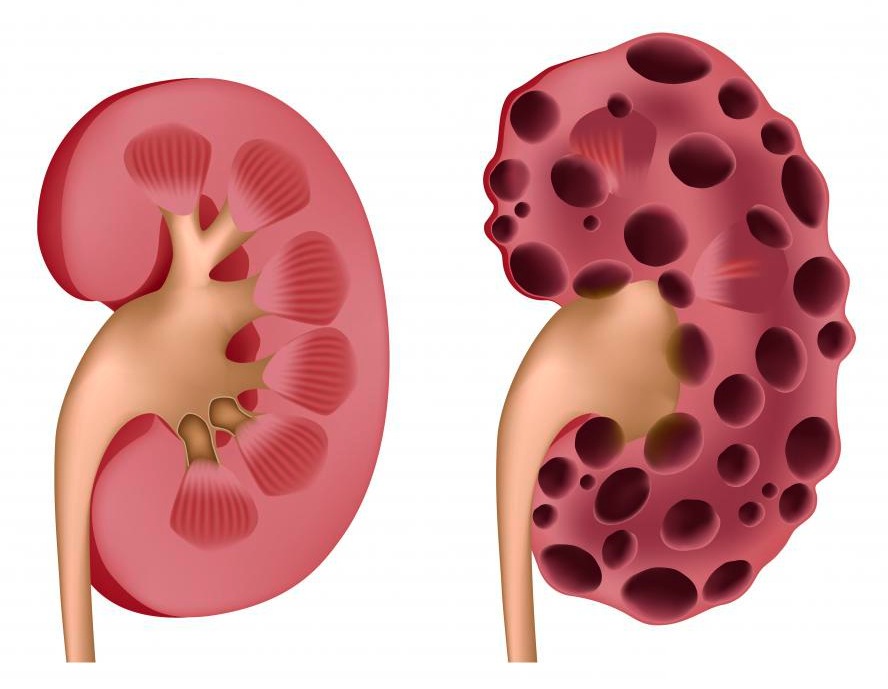
With renal tuberculosis, pyelonephritis, pyonephrosis, paranephritis are possible. In some patients, caverns and papillitis are revealed. At the terminal stage, the disease leads to kidney failure.
Tuberculosis progress is slow but steady. Symptoms are gradually getting stronger. The spread of the pathogen in the kidney is usually observed against a background of damage to the respiratory system. If mycobacterium is detected in the lungs, it is highly likely that after 5-7 years, kidney damage will be detected.
Pathology spread
More often, symptoms of kidney tuberculosis occur when the pathogen enters the human body with blood. Pathological organisms are localized in the parenchyma. If the foci are small, and the immunity is strong, then it is possible to independently scar the area without specific treatment. There are no symptoms in this case. With a decrease in immune status, the infection is able to infect the crust of the kidneys, the brain layer of the organ. At this stage, tuberculous papillitis appears. Mycobacteria gradually infects the pyramids of the kidneys.
Without specific symptoms, tuberculosis of the kidneys gradually spreads to the internal structures, disrupts the cups and pelvis of the organ, and leads to caverns. The foci become places of accumulation of calcium, it can be detected by x-ray examination of the organ.
Gradually, the process from the kidneys spreads to the bladder and the path of the urine duct. The patient has chronic pyelonephritis, possibly the appearance of kidney stones. There are frequent cases when diseases are considered independent, a course is prescribed for their treatment, but it is not possible to determine that the root cause is tuberculosis.
Step by step: forms of the disease
The first stage is parenchymal. This is followed by papillitis, followed by the formation of caverns. The next stage in the development of the disease is pyonephrosis, after which post-changes are observed.
The initial stage is the defeat of the renal parenchyma without destructive foci. The disease can be manifested by an increase in the concentration of leukocytes in urine. It is impossible to find the causative agent in the secretions, since bacteria cannot go through the process of glomerular filtration. It is possible to establish the disease at this stage by PCR and certain types of microscopy. The prognosis is best if the pathology can be determined on time.
Papillitis is the second stage of development of tuberculosis. In urine, you can find mycobacteria. The most accurate method for diagnosing kidney tuberculosis is sowing. Therapy is conservative. A possible complication is a decrease in the lumen of the ducts for urine.
A cavernous developmental step can be detected by ultrasound of the organ. A single cavern appears. When the lesion is bilateral, the prognosis is negative. To clarify the case, a biopsy is necessary.
The terminal stage is the presence of several caverns. Secondary infection is accompanied by purulent fusion. The likelihood of complications is high.
How to clarify?
Analysis for kidney tuberculosis - Mantoux test. If a disease is suspected, an ultrasound scan is prescribed to assess the condition of the ureter and tissues nearby.
To identify mycobacteria in the discharge, the patient takes urine samples for inoculation. Quite accurate information about the state of a person can be obtained by PCR. The blood of a person suspected of having tuberculosis is infected with a guinea pig to assess the development of the situation. Clarification of the case is possible through luminescent microscopy.
Kidney tuberculosis in children and adults can manifest itself as purulent fractions in the urine, which is a secondary symptom that simplifies the diagnosis. Also indirect manifestations include macrohematuria, a calcium coating of the cavity, the appearance of specific tubercles on the mucous membranes of the urinary system.
How to fight?
Conservative treatment of renal tuberculosis is possible with the first and second degree. For each patient, 0.3 g of Isoniazid or 0.3 g of Rifampicin or 0.4 g of Ethambutol is prescribed for every day. Drugs are used three times daily. In the third and fourth stages, the patient can only be helped by surgical intervention.
For the treatment of renal tuberculosis, Isoniazid is sometimes used with a frequency of once every seven days, twice a week or every other day. "Rifampicin", "Protionamide" is often prescribed daily or every two days. If "Pyrazinamide", "Ethambutol" are prescribed, they are usually used 1-2 times a week or every other day.
The frequency of taking Streptomycin Sulfate, Capreomycin varies from once a week to use every second day. Once every two days use "Cycloserine". If the doctor recommends staying with fluoroquinolones, such drugs are used daily or once every two days. After a day or 1-2 times in seven days, Kanamycin Sulfate is taken.
Treatment features
Do not try to cure tuberculosis with medications at your discretion, without consulting a doctor. Only a doctor can prescribe the optimal program, choose a dosage. When choosing the rules of admission and specific names, the doctor evaluates the background diseases, the presence of complications, patient tolerance, the quality of kidney function.
If the drug course is ineffective, the disease has progressed significantly, surgical intervention is necessary. To prevent the spread of infection, the diseased kidney is removed. The installation of an artificial ureter allows you to avoid serious difficulties with the drainage of urine.
The duration of the treatment course for renal tuberculosis often reaches two years. After diagnosis, the patient is put on the first accounting group for inpatient treatment. In the absence of activity of mycobacteria for two years, the group is changed to 3B. In the chronic course of the disease, a second group of accounting is assigned.
Consequences and warning
Tuberculosis can cause kidney failure and fistula development in the lower back. The cavern can break through. There is a chance of increased pressure in the aorta. Tuberculosis can provoke paranephritis.
The main method for preventing renal tuberculosis is to increase the immune status and minimize the risk of contact with a carrier of a pathological microorganism. In practice, it is practically impossible to exclude such an interaction: medical studies have shown that only in public transport a person faces at least two carriers of infection every day. Even strong immunity cannot provide resistance, but at present there is simply no other method of minimizing risks.
To reduce the danger, it is necessary to avoid bad habits, give yourself a good night's rest, eat well. Any diseases, infectious and inflammatory processes must be treated in a timely manner.
Relevance of the issue
Among all forms of tuberculosis localized outside the lungs, it is the renal variant that occurs most often. As a rule, the disease is secondary, appears against the background of damage to the respiratory or musculoskeletal system. Tuberculosis is one of the most common diseases. It is no secret that it is possible to get infected with different forms by aerosol route and even by touching an object used by the patient. Blood flow, lymph flow allow pathological microflora to penetrate the kidneys. In this organ, blood moves through the vessels rather slowly, since the liquid is filtered. In addition, there are many vessels themselves. All this forms a convenient environment for the propagation of mycobacteria, the likelihood of developing an infectious focus is significantly higher than in other organs.
Tuberculosis develops in representatives of different age groups, with different sexes. Up to 2% of patients are children under the age of ten, one patient out of ten is a patient under the age of twenty. Isolated cases of renal tuberculosis in infants are known. In childhood, most often due to infection with pathological microflora, the kidneys and the respiratory system or bones and kidneys suffer.
Note!
Koch sticks in the initial stages of the disease can be detected only by accident, if the patient passes urine for research for another reason. Often, infected foci independently heal, but subsidence of pathological microflora is possible, which remains passive for a long time. The resumption of progress begins when a favorable situation develops, several factors affect the human condition. In addition to lowering immunity, general hypothermia or exhaustion, an infectious disease can provoke the growth of a colony. Tuberculosis can activate a disease localized in the urine ducts if this leads to impaired fluid excretion.
Most often, an accurate diagnosis of tuberculosis can only be made in a specialized institution. You should contact the dispensary if purulent fractions are observed in urine for some time. Particularly attentive should be persons often suffering from cystitis, pyelitis, pyelonephritis.
The nuances of the disease
If tuberculosis is suspected, urine must be passed for examination. The most accurate results will be when taking fluid according to the technique developed for this. Women put a catheter into the bladder, receiving samples of the discharge. The following technology has been developed for men: first, two vessels are filled with an equal amount of urine during one continuous urination, then the fluid from the first container is checked for leukocyte concentration, and the second for the presence of markers of inflammatory processes in the prostate gland. When detecting purulent fractions, we can confidently talk about the pathological process localized in the kidneys, urinary system.
If the kidneys are functioning normally, there is no symptomatology indicating a lack of functioning, there are no protein inclusions and cylindruria, the patient is shown urography. It is possible to determine tuberculosis by conducting angiography, radioisotope analysis, and ultrasound examination of internal organs.