The brain is the main organ of man. In the lower part, directly in the bone pocket, is the pituitary gland. The latter is an endocrine gland. Refers to the endocrine system. The pituitary gland is responsible for the production of hormones that perform important functions. Some of them are responsible for growth, others for reproductive ability, and still others regulate metabolism. This is exactly what happens in a healthy person. But in these processes, failures can occur. Such violations lead to uncontrolled proliferation of cells that are transformed into tumors. In most cases, these formations are benign and, with proper treatment, do not pose a threat to life. However, rarely, but nevertheless, malignant tumors are also found. People call them pituitary cancer. They can lead to quite serious consequences. Therefore, in no case should you delay the visit to the doctor. In time to pay attention to changes in the body will help familiarization with the symptoms of the pituitary tumor. In this material they will be described in detail. Also, the reader will be able to familiarize themselves with alternative methods of treating this pathology.
Neurological aspect
As mentioned above, a tumor in the brain is formed due to abnormal reproduction of pituitary cells. A neoplasm is localized on the posterior or anterior surface and directly affects the production of hormones. Violated their balance in the body. The consequence of this are various neurological problems.
According to statistics, a pituitary tumor is diagnosed in men and women with the same frequency. It cannot be argued that any of them is more susceptible to such a disease. However, most patients come with pathologies at the age of 30-40 years, so they can be put at risk.
The brain membranes can provoke the development of a tumor. They grow into the pituitary gland, exerting a negative effect on it. In some cases, it is not possible to diagnose a pathology in the early stages, since it can develop asymptomatically. A person does not feel any changes. With this clinical picture, the formation is detected by chance during a comprehensive examination, since there are no obvious signs of a pituitary tumor.
This pathology, according to statistics, accounts for 15% of the total number of intracranial formations. Some types of tumors respond well to treatment. However, it is important to understand that a positive result is possible only with timely diagnosis.
Classification
In medicine, a pituitary tumor of the brain is divided into two types:
As mentioned above, the latter are much more common. They are called adenomas. Malignant tumors are rarely diagnosed. Modified cells of a benign formation are able to perform the functions of healthy, albeit partially. Tumors of this type increase in size slowly, so they do not cause a sharp deterioration in health. Upon detection, they are deleted. Relapses are extremely rare.
Malignant tumors not only grow, squeezing the tissue, but also have the ability to penetrate into them, which is a serious danger. The treatment options for these formations will vary depending on the species.
Causes
At the moment, medicine still does not know the exact causes that provoke the development of a pituitary tumor. Most scholars suggest that heredity plays an important role. If someone in the family already had this disease, then you need to regularly undergo an examination in order to respond in time.
In addition to the hereditary factor, doctors identify a number of other reasons that can lead to the beginning of the growth of education. These include:
- brain injury;
- impaired functionality of the peripheral glands of the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases of the nervous system;
- genetic disruption of cells;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- an abundance of hypothalamic hormones;
- adverse factors affecting the baby in the womb.
Adenoma
This pituitary tumor, the symptoms of which will be discussed below, is benign. It occurs quite often. It varies in size:
- diameter from 40 mm and more - giant adenomas;
- more than 10 mm - macroadenomas;
- less than 10 mm - microadenomas;
- not exceeding 3 mm - picoadenomas.
These formations are classified not only by size, but also by functional activity. By this criterion distinguish:
- hormonal inactive - damaged cells do not participate in the synthesis of hormones;
- hormone-active - education produces hormones.
Types of hormone-active adenomas
Those formations that produce hormones are divided into types depending on the active substance. Let's take a closer look at them.
- Prolactinomas are tumors that produce the hormone prolactin in excess. He is responsible for the secretion of the mammary glands and the work of the ovaries. Symptoms in men with a pituitary tumor of this type are galactorrhea and gynecomastia. The first pathology manifests itself in the form of secretions, which are similar to breast milk. And gynecomastia is the growth of mammary glands in men. Women have similar symptoms. The chest becomes painful, increases in size. Milk production begins. There are the same sensations as during pregnancy. In addition to these signs, women have a lost menstrual cycle. Amenorrhea that can lead to infertility may even develop.
- Corticotropinomas are formations that produce excessive production of corticosteroid hormones. In large quantities, they can cause Cushing's disease. Affect the work of the adrenal glands. In patients with such a tumor, the following symptoms appear: emotional disorders, changes in the shape of the face, bruising, age spots and stretch marks, excessive hair growth appear on the skin.
- Somatotropinomas. This type of formation synthesizes growth hormone - somatotropin. Symptoms in men with a pituitary tumor of this type - an increase in the size of the feet, thickening of the bones. These symptoms may occur in women and children. In a child, pathology leads to gigantism, which is manifested by excessive growth.
- Thyrotropinomas. Education stimulates the production of thyroid stimulating hormone. It is necessary for the thyroid gland to function properly. In large quantities, it provokes the development of hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. As for the latter pathology, the following symptoms are observed with it: weight loss, decreased appetite, sleep disturbance, dry skin, and nervous disorders. Symptoms in hypothyroidism are somewhat different. Such a pathology is manifested by excessive skin moisture, freezing of the extremities, a decrease in mental abilities, and slowness.
- Gonadotropinomas - excessive production of gonadotropin hormone, which is responsible for sexual functions. Symptoms in women with a pituitary tumor of this type: cycle disturbance or complete cessation of menstruation, uterine bleeding. Men are more likely to develop impotence, gynecomastia.
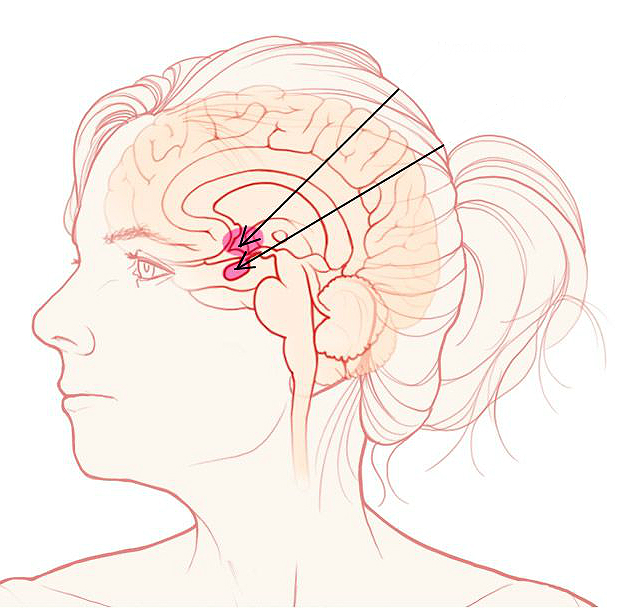
Malignant tumors
Unlike benign formations, malignant ones pose a serious threat to humans. Deformed cells completely lose the properties inherent in healthy ones. Naturally, they are not even able to partially fulfill their functions. Due to this transformation, cells begin to grow uncontrollably. The formation penetrates the lymphatic and blood vessels, as well as in the tissues located nearby. It develops quite rapidly, prone to metastasis.
In most cases, even after successful treatment, relapses occur. However, it should be noted that the treatment of malignant tumors is quite difficult. A favorable prognosis of surgical treatment is possible only in the early stages, until the formation began to grow into neighboring tissues. In the event that this has already happened and there is a defeat with metastases, the tumor is inoperable.
Pituitary tumor: symptoms in women and men
Different symptoms indicate the presence of a tumor. Most of them are rather unpleasant and do not allow a person to live fully. Above, a little has been said about the signs that manifest adenomas of various types. However, it is necessary to highlight the most common of them. The insidiousness of this disease lies in the fact that sometimes the pathology is asymptomatic - in approximately 20% of cases. With this course of the disease, diagnosing it is quite problematic. In other situations, the symptoms are pronounced. So, that indicates the presence of a tumor:
- severe hair loss;
- decreased vision;
- the girls have a menstrual cycle;
- a significant increase in the feet and hands;
- in men, female sexual characteristics are manifested;
- chronic runny nose;
- rapid increase / decrease in weight;
- drowsiness, weakness, decreased activity, headache, double vision;
- nervous disorders, tics, cramps, dementia, fainting;
- binge eating;
- puffiness, face change (teeth diverge, nose grows, bite changes).
These symptoms cannot be called specific. Some of them appear with other diseases. However, they should not be ignored, since the pituitary tumor can grow rapidly, and this, accordingly, will lead to serious consequences.
General diagnostics
In some cases, the symptoms of this disease, as they say, are obvious. For example, a doctor can only make a diagnosis when examined without additional examination if certain parts of the body are significantly enlarged (acromegaly). Itsenko - Cushing's disease also indicates the presence of a neoplasm. People suffering from it are characterized by characteristic changes in appearance. Also, the diagnosis of the pituitary tumor is carried out by external signs in children suffering from gigantism.
If the doctor suspected the presence of education, the patient is prescribed an examination. It includes:
- the passage of computed tomography, radiography (effective in case of a large tumor), MRI and angiography;
- screening for hormones - a blood and urine test;
- ophthalmic examination;
- cerebrospinal fluid biopsy.
The most effective diagnosis is tomography. Such a study allows to determine the location of the tumor and its size without error.
Pituitary tumor treatment
Given that this education can be of different types, treatment is selected depending on them. Also, when choosing a therapy, the doctor pays attention to the stage of the disease, as well as the size of the tumor. In the aggregate of these factors, surgical, drug or radiation treatment is prescribed. In some cases, complex therapy is used.
It is important to remember that with a tumor in no case should you rely on your strength. Diagnosis and treatment should only be carried out by a qualified doctor. The final decision is made at the consultation, where neurosurgeons, endocrinologists and neurologists are necessarily present.
Drug Administration
Drug treatment is used only if the pituitary tumor is benign. Before choosing drugs, its growth rate and participation in the synthesis of hormones are determined. If pathology is inactive according to the last criterion, dopamine agonists are prescribed, for example, Cabergoline or Bromocriptine. These drugs are able to regulate the production of hormones, to reduce the tumor in size. Such cases are known that the formation completely disappeared without surgical intervention.
Medicines are selected depending on the type of hormone, which is in excess in the body. For example, Sandostatin and Pegvisomant block the effects of growth hormone, and Cyproheptadine reduces the amount of corticosteroids.
Radiation therapy
If surgical treatment is contraindicated for some reason, patients are prescribed radiation therapy. This method consists in irradiating the tumor. The doctor selects the dose based on the size of the formation and its type. The positive effect does not occur quickly. Sometimes treatment lasts several years. Its advantage is that the tumor is irradiated from all sides, due to which it is reduced in size. During the procedures, the patient's condition is monitored by the attending physician. Computed tomography is done regularly to see how the neoplasm responds to therapy.
It is important to know that exposure has a number of side effects. And also it can not be used if the tumor is localized very close to the optic nerves.
Surgical intervention
Surgical removal of the pituitary tumor is the most effective treatment. Before planning the operation, the doctor determines the location and size of the neoplasm. As a rule, they remove it through the sphenoid cranial bone or frontally, using a special optical device.
Currently, most surgeons prefer to use endoscopic transsphenoid surgery to remove the tumor. It is carried out through the nasal passage. This type of intervention is as safe as possible, since it does not require incisions. And this reduces the risk of developing various complications. The operation through the nasal entrance is carried out using an endoscopic probe and special tools.
Often after surgery, patients are prescribed medication and radiation treatment.
Forecast
With a pituitary tumor, the prognosis depends on several factors. Of great importance are the timing of diagnosis, hormonal activity and the size of the formation. It is difficult to treat somatotropinomas and prolactinomas. Only 25% of patients were completely cured. The chances of a full recovery in patients with other types of adenomas are high - 80%. It is possible to restore the functionality of the optic nerves only if the disease was diagnosed at the initial stage of development. In the later stages, pathological processes are already irreversible.