Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex is a wide variety of hereditary diseases that arise as a result of defects in protein transit compounds. In this article we will talk about what these diseases are, as well as methods for their diagnosis and treatment.
A few words about the disease itself
The adrenal glands secrete a special kind of hormones that are actively involved in the development and growth of the whole organism. In other words, congenital adrenal cortical dysfunction is referred to as adrenogenital syndrome or adrenal cortical hyperplasia.
So, the appearance of adrenal gland pathologies of this group is usually associated with a decrease in cortisol production. And this, in turn, is the cause of increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone. Thus, patients develop significant thickenings of the adrenal cortex.
The problem of the disease in the modern world
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex is a hereditary disease. In this case, this pathology is observed with the same frequency in both female and male individuals. There are several clinical varieties of each ailment, and almost every one of them is incompatible with life. That is why babies with this disease very often die at birth.
According to medical statistics, congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex most often occurs as a result of the detection of defects of the twenty-first hydroxylase. Also, the prevalence of this disease depends on race. For example, if we take the representatives of the white race, then this disease will be seen in one baby out of 14 thousand. While the Eskimos will be sick every two hundred and eighty babies.
Fortunately, today the problem of combating these ailments is completely solvable, but only in the most developed countries of the world. If this pathology is detected even in infancy, health workers conduct special studies that help identify a congenital disease as early as possible. Thus, it is possible to start correctly selected hormonal treatment before the first symptoms of adrenal insufficiency appear.
Risk Factors
Most often, congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex occurs if this disease was discovered in at least one of the parents, or if the parents are direct carriers of the gene responsible for the transit of proteins that are needed to produce hormones in the adrenal cortex. If such a gene was found in both parents, then there is a probability of twenty-five percent that this pathology will be detected in the baby.
What leads to the development of dysfunction
It is very important to understand how exactly the mechanism of development of adrenal cortical dysfunction passes. It is worth considering that as a result of improper protein transfer, the amount of aldosterone and cortisol in the adrenal glands will decrease. And this is the reason for the increase in the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone by the pituitary gland. This hormone is responsible for regulating the proper functioning of the adrenal glands themselves.
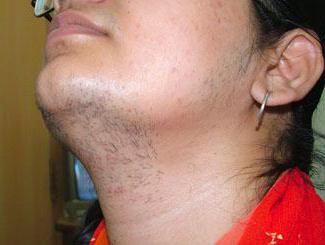
If adrenocorticotropic hormones are produced in excessively large quantities, then this leads to the phenomenon of hyperplasia. An increased secretion of male hormones will also be noticed. A high concentration of androgens leads to deformations of the genital organs, as well as to excessive growth of hair on the face and throughout the body.
Forms of the disease
In medical practice, there are three forms of this disease:
- Uncomplicated, or viril form. This form usually occurs with a slight protein deficiency of the twenty-first hydroxylase.
- The salt-forming form of congenital adrenal cortex dysfunction is characterized by a deeper deficiency of this enzyme.
- The hypertonic variety results from a significant lack of the 11b-hydrolactase enzyme.
Symptoms of the disease
The first form is usually accompanied by the presence of symptoms such as a penis-shaped clitoris, large scrotal labia, or urogenital sinus in girls. In individuals, both male and female, a very rapid development is observed not only of the physical plane, but also of the sexual one. At the same time, an isosexual type of development is observed in boys, and heterosexual in girls.
A salt-in form of congenital adrenal cortex dysfunction is usually observed in children. In addition to the symptoms listed above, the first serious violations of the adrenal cortex itself are also added. In this case, appetite, electrolyte metabolism is significantly impaired, and body weight does not increase. In addition, hypotension very often develops and dehydration of the body occurs. If the signs could not be recognized even in the first stages of the disease, then there is a huge risk of death in the presence of collapse phenomena. If, from the very beginning, the correct treatment was chosen, then with age such phenomena can be completely excluded.
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex in women leads to a change in the structure of the external genital organs. At the same time, the huge amount of male androgen hormones released does not affect the differentiation of the internal female genital organs. Usually, the development of the ovaries and uterus is completely normal. The external genitalia have an irregular shape already at the birth of a girl. In medical practice, there were many cases when, at the birth of a girl, she was assigned a masculine gender.
Due to the negative effects of androgens, patients begin to grow very quickly from birth. Very early, they develop secondary sexual characteristics. In addition, all patients have short stature and a rather disproportionate physique. The pelvis remains very narrow and the shoulders excessively wide. At the same time, in mammals, the mammary glands do not begin to grow, and menstruation does not appear. At the same time, the external genitalia are modified, the hairline appears throughout the body, and the voice is getting lower.
Male patients develop according to the isosexual type. Already in infancy, you can notice hypertrophy of the genital organ, and the testes are usually small in size. In adolescence, patients often have tumorous formations on the testicles. Very often, men with this pathology suffer from infertility.
The hypertensive form of this disease is also characterized by all the symptoms listed above, but is also accompanied by high blood pressure. When conducting special examinations, doctors notice such indicators: the presence of protein in the urine, the borders of the heart are dilated, and the vessels of the fundus are changed.
Nonclassical form of the disease
The non-classical form of congenital adrenal cortical dysfunction is considered the simplest and easiest form of the course of this disease. In this case, 21-hydroxylase is produced in a volume slightly less than normal. In this case, usually the genitals of both men and women develop correctly, and the first signs of the disease can be noticeable only after the teenage period. Most often, the non-classical form of congenital adrenal cortex dysfunction is seen in women who are concerned about such problems:
- persistent irregularities in the cycle of menstruation;
- moderate or severe acne;
- can't get pregnant;
- some areas on the body acquire a male-type hairline.
Most often, the deviations are insignificant, therefore, they have no effect on the function of childbearing. Women discover when they become pregnant that they have the disease "congenital adrenal cortex dysfunction." The non-classical form, the treatment of which is carried out only in women, in males usually does not cause serious unrest. Therefore, treatment is impractical.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is very important in childhood to determine the presence of a disease such as congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. Diagnosis allows you to determine the form of the disease, and helps to deal with further treatment.
For all babies born with noticeable abnormalities in the structure of the external genitalia, doctors carry out special diagnostics that can determine sex chromatin, as well as determine the karyotype. Most often, with a congenital form of this pathology in young patients, an excessively large amount of male hormone is observed in the blood. To determine its level, you need to conduct a screening test. Typically, such testing shows that the concentration of this hormone in the blood is exceeded several times.
As you know, congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex in children is accompanied by a very rapid growth of bone tissue. In order to study its structure and structure, doctors use the method of instrumental diagnostics. In this case, an x-ray is taken, and already from the pictures you can determine the bone age of the patient. If pathologies are present, then usually the condition of all joints and bones is significantly older than the patient's age.
If at birth the girls showed signs of hermaphroditism, then doctors conduct an ultrasound of the female genital organs. In this case, their structure is usually no different from the norm.
Also, in the first year of life of babies, doctors conduct differential diagnosis. It allows us to determine whether hermaphroditism is false or true. In this case, the diagnostic method is karyotyping. And, of course, the level of the male hormone androgen is definitely determined.
In addition to the methods listed above, an anamnestic data analysis is also carried out. The main and most important criterion can be called the level of 17-hydroxyprogesterone.
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex in children can be detected already on the fourth or fifth day after birth by using a procedure such as neonatal screening. This test involves checking 17-hydroxyprogesterone in blood taken from the heel. Such an analysis will help to find out about the presence of pathology in the first days of life. This will help start treatment in a timely manner.
Treatment methods
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex, the symptoms of which are described above, due to the congenital nature, should be treated with the help of continuous replacement therapy with a drug such as Prednisolone, as well as all kinds of analogues. The constant intake of glucocorticoids in the body has the most positive effect on it. On the one hand, these substances are able to eliminate adrenal insufficiency of congenital origin. On the other hand, preparations containing hormones are able to suppress the excessive secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone. In addition, the feedback mechanism begins to be regulated, which means that the level of hydrogeneration is minimized.
If the disease is in salt form, that is, it is also characterized by a deficiency of mineralocorticoids, then salt solutions and deoxycorticosterone acetate are also added to the treatment. In addition, all girls also need surgical intervention, with which you can remove the hypertrophic clitoris.
Conservative treatment method
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex, the treatment of which can really cope with this pathology, must be started in childhood. This should be done immediately after the disease has been identified.
Most often, with the purpose of substitution therapy, doctors advise using the drug “Prednisolone”. It has all the necessary properties for the treatment of this disease, and with a correctly selected dosage will not have a negative effect on the human body.
The treatment process itself must begin with a diagnostic test. In this case, doctors prescribe this drug for a week at 15-20 mg per day, or two to four milligrams of "Dexamethasone", which should be taken for two to three days. If this test showed good results, then you can begin ongoing treatment with Prednisolone. Most often, the daily dosage is about 10-15 mg per day. However, each case is completely individual, so only general recommendations are indicated in the article. It depends on the age of the child, as well as on the level of hormones in the blood and on the degree of virilization.
Over time, the dose gradually decreases. This is done at 2-2.5 mg per week. The final dosage can be determined only one to two months after the start of treatment. According to experts, the daily dosage for children under the age of one year should be selected only individually, while focusing on clinical data more than hormonal indicators. In fact, it is quite difficult to choose the optimal dose for the baby. It is necessary to conduct continuous testing in order to eliminate the risk of overdose. The minimum daily requirement is only 2.5 mg, while the maximum is 15 mg.
Note that you need to take these drugs constantly. This is best done in the morning and afternoon, after eating. If you had a need to change the drug, then you must definitely take into account its physiological activity.
In some cases, the drug "Cortisone" is used to treat this disease. However, it is able to exert a weaker and shorter-term effect on suppressing the production of adrenocorticotropic hormones. This drug is weaker than Prednisolone more than five times, therefore, requires a sufficiently large dosage. For infants, such drugs are most often administered intramuscularly in the morning.
One of the most effective glucocorticoids is Dexamethasone. It is able to suppress the production of adrenocorticotropic hormones ten times more effective than Prednisolone does. But it is worth considering that it practically does not affect salt metabolism, and very often contributes to an overdose. The daily rate of this substance is usually 0.25-0.5 mg.
All of the above drugs will have a negative effect on the body only if the wrong dosage is selected. This suggests that taking the drug in a larger amount than required by the body will have a detrimental effect on it. With excessive use of any of these drugs, the patient will experience hyperemia and rounding of the face, increased appetite, and sometimes a suspension of growth and development. However, all the effects of an overdose will disappear very quickly if it is slightly reduced, or if you switch to a weaker medication.
Surgical treatment method
Usually, congenital adrenal cortical dysfunction is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. In this case, it does not matter what form this disease has.
One of the stages of proper treatment for girls is plastic surgery. Most often, surgery is performed to form the correct shape of the labia minora, resection of the clitoris and opening of the urogenital sinus. Such an operation is mandatory, as it helps to restore all the correct physiological functions of the girl’s body, and also has a socio-psychological value. Thus, the baby does not feel its inferiority, so it can be sent to a kindergarten or sports section. However, note that the operation must be performed at least one year after the start of treatment with hormonal drugs.
It is very important to study all aspects of a disease such as congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. ICD 10 is an international classification of diseases in which this ailment has an E.25.0 code
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex and pregnancy
If the patient has a post-pubertal form of this disease, then there is a high probability of fetal undevelopment, miscarriage, miscarriage and medical abortion. Very often, pregnant women complain of poor vitality and an absolute loss of appetite. Violations of electrolyte balance are not excluded. Typically, from the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy, the patient's condition improves significantly. , . .
– , . " ", . .
Future forecasts
, . , .
. . , , .
, .
, , , . - , , . . Be healthy.