Anaphylactic shock is a rapidly developing reaction to an allergen, accompanied by circulatory disorders, spasms, oxygen deficiency. Shock can occur lightning fast, and can last several hours.
Its severity depends on the amount of allergen ingested. May arise under various circumstances:
- When bitten by poisonous insects, snakes. Bee sting.
- The use of drugs (first aid may be required in case of anaphylactic shock in dentistry with banal tooth treatment, in gynecology, urology, traumatology, when visiting a surgeon, during an injection).
- With vaccination.
- For food allergies. Seasonal hay fever can also result in dire consequences.
Manifestations of anaphylaxis
- A sharp deterioration in peripheral and central blood circulation, accompanied by a decrease in pressure in the arteries. At the same time, the victim feels headaches, nausea, clouding in the eyes, while pallor of the skin is observed, the pulse is threadlike.
- Shock (pain and toxic): a person experiences severe chest pain, suffocation.
The nature of the anaphylactic reaction, and therefore the provision of first aid for anaphylactic shock, depends on which organ is affected. From here, 4 types of anaphylaxis are distinguished:
- affecting the skin;
- nervous system (cerebral type);
- heart muscle (cardiogenic: heart attacks, myocarditis);
- respiratory system (asthmatic type).
Most often, allergic reactions of this type are recurrent. In order to provide first aid in time for anaphylactic shock, appropriate preparations are required at hand. Usually people prone to such reactions have these remedies. Also, each specialist providing medical care should have a special first-aid kit with him. Without a first-aid kit at hand, not a single doctor has the right to work.
First aid
First aid in case of anaphylactic shock consists in the following measures:
- Depending on the location of the victim, call an ambulance, doctor, resuscitation team.
- Rid the patient of the source of the allergic reaction, depending on the situation: remove the needle with the drug solution, rinse the stomach with allergenic food, take out the sting, try to squeeze out the poison, offer the patient an air-conditioned room, without access to harmful pollen, and so on.
- Lay the patient up with the legs up to the height of the pillow.
- Allow the victim to breathe fresh cool air (open the window, if it is an allergic reaction to some environmental factors, pollen should turn on the air conditioner).
- Make sure that the person is conscious (ask him about something, for example, with which he connects this reaction, to have a slight physical effect).
- To clear the respiratory system of mucus, vomit, if necessary.
- Put your head on your side.
- When providing first aid for anaphylactic shock, you may encounter respiratory arrest and circulatory arrest - urgent resuscitation measures are necessary. The basis of these activities is: indirect heart massage (30 presses) and artificial respiration (2 breaths).
- If two people help, you need to change every 2 minutes. Only indirect heart massage is allowed until the ambulance arrives if those providing first aid are not trained in the correct artificial respiration technique or there is a risk of infection.
- If such a condition arises in a person, it is also recommended, when the opportunity arises, to check his pulse and pressure. If the pressure is not detected, the shock develops rapidly, it is urgent to carry out resuscitation measures, apply drugs.
- As a first aid for anaphylactic shock, a tourniquet must be applied above the injection site with the allergen. Do not forget about the rules for applying a tourniquet. Be sure to put a note under it, with the number and time of overlay. The maximum overlay time in summer is 2 hours, in winter 1.5 hours. Optimal - every 30 minutes, loosen the tourniquet for 5 minutes, in order to avoid circulatory disorders in the limbs.
- It is necessary before the doctor arrives to be close to the patient, to control his consciousness, to provide all possible assistance. The arrived resuscitation team needs to know: how long the victim is in this condition, what the reaction to, information about the manipulations performed.
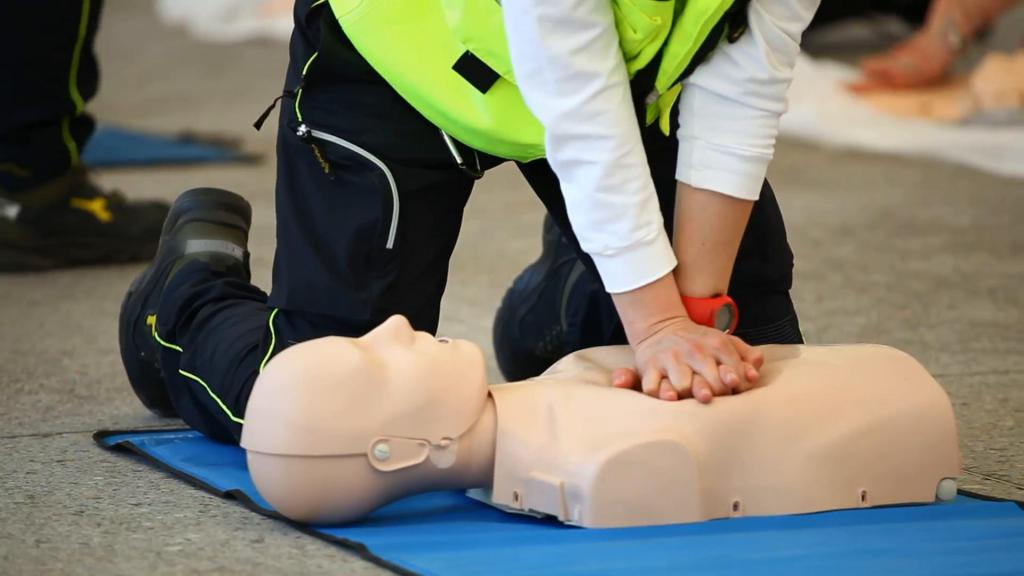
First aid for anaphylactic shock is a very serious undertaking, timely delivery of it will help to avoid a fatal outcome.
Every mid-level and high-level medical professional should know the rules for providing this care. Always when carrying out manipulations that may entail an allergic reaction, specialists should carry the drugs used to relieve the attack. There is a special list of medicines for first aid for anaphylactic shock.
This list includes
- Adrenaline 0.1%, in ampoules of one milliliter. There are also special EpiPen syringe pens that contain a single dose of adrenaline.
- Norepinephrine 0.2% in ampoules of 1 milliliter.
- Antiallergic drugs (Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Loratadine, Zirtek).
- Corticosteroids (prednisone in ampoules of 30 milligrams, hydrocortisone in ampoules of 4 milligrams).
- Pressure boosters (Ephedrine 5% in ampoules, Mesaton 1%).
- Bronchodilators (relieving bronchospasm) - "Eufillin" 2.4% in ampoules.
- Cardiac glycosides (Strofantin 0.05%, Korglikon 0.06% in ampoules).
- Tonic agents (caffeine 10%).
- Stimulants of respiratory activity ("Cordiamin").
- For intravenous (i / v), intramuscular (i / m) infusions of drugs, physical. solution, glucose solution 5%, infusion systems. Also, alcohol, gloves, sterile syringes, wipes, fixing adhesive plaster are needed.
Nursing care
A nurse who injects patients always carries medications for emergency care in shock. It takes into account the possibility that anaphylactic shock will occur. Nurse's first aid: the algorithm is clear and coherent:
- The nurse should stop, do not administer the drug anymore.
- Urgently call a doctor.
- Place a tourniquet on the extremity into which the injection was made, above the injection site.
- Give the patient an appropriate posture (lying down, put legs on a pillow).
- Lay the patient’s head on one side, pull out the dentures, and lower the lower jaw forward, releasing the airways.
- If necessary, start mechanical ventilation, cardiac massage (indirect).
Anaphylactic shock is a deadly condition. For first aid, a nurse can use:
- A solution of adrenaline 0.1%: subcutaneously inject half a milliliter. The introduction into the gluteal or femoral muscle is allowed. Also urgently needed to prick the injection site with the allergen with the following composition: dilute a half milliliter of adrenaline 0.1% in a syringe with 5 milliliters physical. solution, in about five to six places. Here also make ice.
- Quick access to the patient's veins is very important in case of anaphylactic shock. First aid: the algorithm of the nurse’s actions also includes intravenous infusion. The nurse must provide quick access to the patient's vessels. To do this, she catheterizes a vein and injects saline. Introduces a solution of prednisolone, 60-150 milligrams in 20 milliliters of saline intravenously (calculated at 1-2 mg per kg of weight of the victim). (It is allowed to use dexamethasone 8-32 milligrams, 100-300 milligrams of hydrocortisone in muscle or vein).
- It is advisable to inject 5 milliliters of 1% Diphenhydramine into a muscle, 2 milliliters of Suprastin 2%.
Medical assistance
- It is necessary to carry out infusion into a venous catheter: physical. a solution with a total volume of at least 1 liter, if possible - enter 0.5 l of physical. solution and 0.5 l of "Reftan HES".
- If hypotension persists, it is necessary to re-inject 0.5-1.0 milliliters of 0.1% adrenaline into the muscle, 15-20 minutes later, after the first injection. This can be done every 15-20 minutes.
- If there is no effect, dopamine is administered. For 400 milliliters of saline, 200 milligrams of dopamine is injected intravenously, very slowly (2-11 drops per minute), until the systolic pressure reaches 90 millimeters of mercury.
- With the development of heart failure, cardiac glycosides (strophanthin 0.05% 1 milliliter or corglycon 0.06% 1 milliliter) are used intravenously on physical. solution.
- If bradycardia develops (heart rate is less than 55 per min), first aid for anaphylactic shock involves subcutaneous administration of half a milliliter of 0.1% atropine. If the condition persists, repeat in the same amount in five to ten minutes.
- For breathing problems, inject 10 milliliters of Eufillin 2.4% saline into the vein, or 24% solution into the muscle.
- Keep pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate under constant control.
- Ensure the delivery of the victim to intensive care.
Anaphylactic shock in children
It is the most severe acute form of an allergic disease in which there is a direct threat to the life of the child. Anaphylactic shock is dangerous with severe disorders in the cardiac, vascular, respiratory and nervous systems.
An allergic reaction of this type can cause foods, drugs, insect bites, and more.
Symptomatology
The child begins dizziness, headaches, weakness, cold sweat. Children in this period experience fear, become pale. The picture of the further development of anaphylaxis is similar to that of adults: hypotension develops, suffocation, the child loses consciousness, the pulse is threadlike. The process may be accompanied by convulsions.
Sometimes the course of shock is different. In this case, redness of the skin can be observed, the child sneezes, coughs, says that it is hot, hard to breathe. Abdominal pain may appear.
So, in pediatrics, the following forms of anaphylaxis can be distinguished:
- Typical - low blood pressure, the appearance of respiratory failure, impaired consciousness, seizures, skin reactions.
- Asphyxia - the prevalence of respiratory failure due to edema of the respiratory system, the development of bronchospasm.
- Hemodynamic - heart rhythm disturbances are observed, accompanied by painful sensations, heart sounds are deaf, pressure drops, the pulse becomes threadlike.
- Cerebral - the child loses consciousness, the respiratory rhythm goes astray, cerebral edema, convulsions occur.
- Abdominal - symptoms of an acute abdomen, which is why errors in diagnosis are possible with this form.
Treatment
First aid for anaphylactic shock in children includes mandatory activities that are part of international standards. The goal of treatment is to restore blood circulation, saturate the body with oxygen. An important task is also the removal of spasms from smooth muscles in order to avoid late complications.
When carrying out medical care, a child must take into account the age and weight of the small patient. First aid for anaphylactic shock - an algorithm of actions in pediatric practice:
- Stop penetration of the allergen into the body. Chop adrenaline 0.1% from 0.3 to half a milliliter injection site.
- Apply a tourniquet to the affected limb, above the injection site with the allergen that caused the reaction.
- Put the baby, turn your head on its side.
- In the muscle, make an injection of adrenaline at the rate of 0.01 milliliter per 1 kilogram (not more than 0.5 milliliter).
- In the gluteus muscle, make an injection of Diphenhydramine 1% per 1 milligram per 1 kg. It is allowed to use "Tavegil" or "Suprastin" according to the instructions on age dosages.
Pipolfen should not be used in pediatrics, as it is a hypotensive drug.
Further, the use of corticosteroids (dexamethasone 0.3-0.6 milligrams per kg, hydrocortisone 4-8 milligrams per kilogram, prednisone 2-4 milligrams per kg is necessary.
Further, providing venous access, enter the above funds in appropriate quantities intravenously. The rate of intravenous administration of drugs, as well as the amount of fluid injected, depends on the pressure of the small patient.
The fight against bronchospasm
First aid for anaphylactic shock - an algorithm of actions to combat bronchospasm:
- Oxygen therapy.
- Intravenous use of Eufillina solution, at the rate of 3-5 milligrams per kilogram of a child.
- Inhalation with Salbutamol, Berotek.
If the child experiences seizures, Sibazon, Diazepam, Droperidol are used.
A clear control of blood pressure, respiratory rate, and cardiac activity is constantly needed.
Resuscitation in pediatrics
If necessary, an indirect heart massage is performed along with artificial respiration. The frequency of pressing the area of the chest of the child:
- up to a year - more than 120 times per minute, combined 1 breath - 5 clicks;
- from a year to seven years - 100-200 times per minute, combined 1 breath - 5 clicks;
- over seven years old - 80-100 times per minute, combined 2 breaths - 15 clicks.