Often with diseases of the cardiovascular system, circulatory hypoxia develops as a result of a decrease in cardiac output and circulatory disorders. With the development of shock or collapse, the reason for the violation of the supply of oxygen to the tissues is a decrease in the amount of circulating blood. At the same time, hemoglobin values remain within normal limits, and a high oxygen content in arterial blood is also observed.
Description of the problem
Circulatory hypoxia is a pathological disease characterized by a violation of the transport of oxygen to organs and tissues as a result of a temporary slowdown or cessation of blood flow in tissue capillaries with the development of stagnant phenomena in them. This pathology is observed with a violation of the cardiovascular system, the development of a shock condition, heart defects, hypertension, acute and chronic inflammation in various organs and tissues of the body. The disease is characterized by a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in venous blood, while in arterial blood its rate is within normal limits.
Characteristic
Insufficient blood supply leads to the accumulation in the tissues of various unoxidized products. Therefore, they increase the need for oxygen. Thus, the following characteristics are inherent in the disease:
- slowing blood flow;
- local stasis;
- ischemia;
- stagnation phenomena.
Types of Hypoxia
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish several varieties of this disease. So, there are the following types of hypoxia:
- Local, which is characterized by local circulatory disorders and the penetration of oxygen into the tissue from the blood. Pathology occurs in the area of thrombosis, ischemia, embolism, hyperemia in certain organs and tissues of the body.
- Systemic, which develops as a result of heart failure, a decrease in total peripheral vascular resistance, as well as the amount of circulating blood, dehydration, DIC, and other phenomena. If blood flow disorders are observed in a large circle of blood circulation, the flow of oxygen into the blood of the lungs remains within normal limits, but its transportation to the tissues is disturbed. With circulatory disorders in a small circle, oxygen saturation of arterial blood is disturbed.
- Regional hypoxia develops due to the fact that in the blood the pH decreases and gas composition is disturbed, the coefficient of the difference in oxygen in the venous and arterial blood increases. This phenomenon can be observed with pulmonary edema, an excessive amount of water inside the cells.

Other types of pathology
Also exist:
- Congestive cardiovascular hypoxia, which is caused by absolute circulatory failure with its general disorders (heart failure, shock).
- Ischemic hypoxia, which occurs with local blood flow disorders (venous stasis of ischemia, arterial spasm).
Causes of the disease
Consider the factors that lead to a similar ailment. Hypoxia is an insufficient blood supply to organs and tissues of the body. This condition is quite dangerous for human health. The causes of hypoxia include:
- decrease in the amount of circulating blood;
- decrease in minute volume of blood circulation in violation of vascular tone, heart failure;
- microcirculation disturbance;
- disorder of the penetration of oxygen through the vascular walls during their inflammation.
Thus, circulating hypoxia, the causes of which are described above, develops as a result of impaired transportation of arterial blood saturated with oxygen to tissues. This phenomenon is quite common in diseases of the cardiac and vascular systems.
Symptoms and signs of hypoxia
The severity of the disease is determined by a decrease in local blood flow, as well as a decrease in its overall speed. Violation of blood circulation as a result of spasm of blood vessels or their sclerotic changes, the formation of blood clots can provoke the development of severe complications from the brain. In this case, signs of hypoxia are manifested in dizziness, nausea, impaired coordination of movements, impaired activity of the higher parts of the brain. In severe cases, loss of consciousness, paresis and paralysis can be observed.
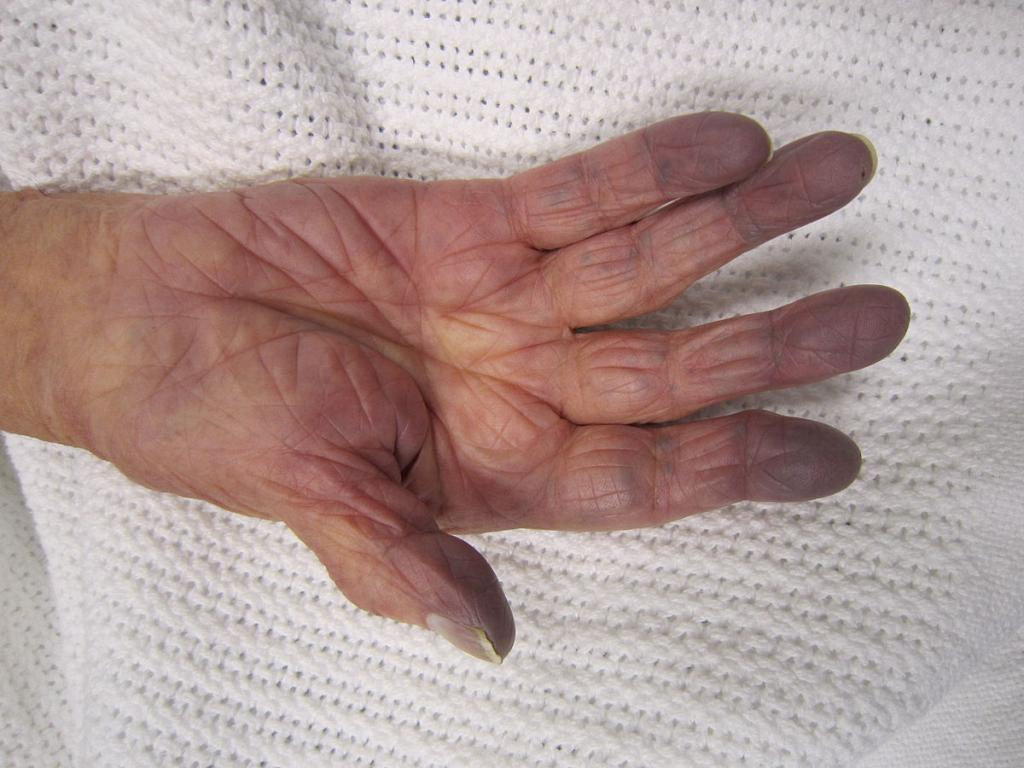
With a local blood flow disorder, necrosis of the areas of the skin is observed, accompanied by pain. Also in this case, the occurrence of heart attacks in the lungs, liver and kidneys is possible. Violation of blood circulation in the vessels of the heart leads to the development of ischemia, myocardial infarction. With the cessation of blood flow to the muscles of the extremities, necrosis of some areas occurs, which leads to the appearance of gangrene.
With a decrease in the rate of total blood flow, gas exchange processes in the lungs deteriorate, so arterial blood does not receive enough oxygen, resulting in arterial hypoxemia. Lightning acute circulatory hypoxia leads to loss of consciousness, stopping the functioning of the body and its death. Chronic pathology is accompanied by adaptation of the body to the disease.
Adaptation to the disease
There are two forms of adaptation to hypoxia:
1. Emergency, which provides activation of the mechanism of oxygen transport to cells. Such mechanisms exist in every organism and are activated immediately with the development of pathology. In this case, there is an increase in alveolar ventilation, respiratory rate, cardiac output and heart rate, redistribution of blood flow, a change in the diameter of blood vessels in the brain and heart, and oxygen capacity in the blood also increases.

2. Long-term adaptation occurs at all levels of the body, including cellular metabolism. These mechanisms develop gradually, they provide optimal conditions for the life of the organism in extreme conditions of its existence. First of all, the efficiency of biological oxidation in cells increases, the degree of incorporation of oxygen into the blood of the lungs, the number of mitochondria increases, the lungs, myocardium, cardiac output increase, the blood supply to the heart tissues increases, and arterial hyperemia develops. As a result, the efficiency of the functioning of organs and tissues increases, the efficiency of metabolism increases.
Therapy
Typically, circulatory hypoxia involves etiotropic treatment, which is aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease. For this, pathology is eliminated by restoring oxygen pressure in the air. To do this, the room is ventilated or air is supplied into it with a normal oxygen concentration. In the presence of diseases of organs and systems, they are treated. During therapy, the patient should observe bed rest and rest.
Symptomatic treatment is carried out in order to eliminate the pathological conditions of the patient, as well as complications of the disease. To this end, the doctor prescribes anesthetics, analgesics, cardiological medicines and tranquilizers.
In acute disease, direct-acting antihypoxants are used. They are considered as first aid, usually synthetic drugs are prescribed. In a chronic disease, herbal preparations are often used. In most cases, this treatment is indicated for older people. In this case, preference must be given to the remedy, which, in addition to eliminating hypoxia, has a therapeutic effect on the pathology of the organ that caused the development of this disease.