In the middle of the last century, mankind has achieved some success in the fight against certain infections. But, as it turned out, it was too early to celebrate the final victory over such a misfortune as infectious diseases. Their list includes more than 1200 items, and is constantly updated with newly discovered diseases.
How infectious diseases were studied
Mass diseases have been known to man since ancient times. There is evidence that back in the 5th century BC philosophers and doctors were aware of the existence of some tiny, invisible to the eye living organisms that could cause diseases characterized by rapid spread and high mortality. During the Middle Ages, however, these materialistic views were forgotten, and the outbreaks of mass diseases were explained solely by God's punishment. But the fact that the sick must be isolated, as well as destroy infected things, buildings and corpses, knew even then.
Knowledge accumulated gradually, and the middle of the 19th century was marked by the emergence of a science such as microbiology. Then the causative agents of many diseases were discovered: anthrax, cholera, plague, tuberculosis and others. Infectious diseases have since been singled out as a separate group.
Terminology
The word "infection" in Latin means "pollution", "infection". As a biological concept, this term refers to the penetration of a microscopic pathogen into a more highly organized organism. It can be either a person or an animal, or a plant. Next, the interaction between the micro- and macroorganism systems begins, proceeding, of course, not in isolation, but under specific environmental conditions. This is a very complex biological process, and it is called infectious. As a result of this interaction, the macroorganism is either completely released from the pathogen or dies. The form in which the infectious process manifests itself is the specific infectious disease.
Common characteristics for infectious diseases
You can talk about the onset of an infectious disease if, after a meeting of a pathogen and a macroorganism, in particular a person, a violation of the vital functions of the latter occurs, symptoms of the disease appear, and an increase in antibody titer occurs in the blood. There are other forms of infectious processes: a healthy carrier of the virus in the presence of immunity or natural immunity to this disease, chronic infections, slow infections.
In addition to the fact that all infectious diseases begin with pathogenic microorganisms, pathogens, there are other characteristics common to them. Such diseases are contagious, that is, they can be transmitted from a sick person or animal to a healthy one. Under certain conditions, epidemics and pandemics may occur, that is, a massive spread of the disease, and this is already a very serious threat to society.
In addition, infectious diseases, a list of which can be found in any medical guide, always occur cyclically. This means that in the process of the disease, certain time intervals alternate in turn: the incubation period, the stage of the precursors of the disease, the period of the height of the disease, the period of decline and, finally, the recovery period.
The incubation period has no clinical manifestations yet. The shorter it is, the higher the pathogenicity of the pathogen and the greater its dose, and can be several hours, several months or even years. The precursors of the disease are the most common and rather vague symptoms, on the basis of which it is difficult to suspect a specific infectious disease. Typical clinical manifestations of it are maximum at the height of the disease. Further, the disease begins to fade, but relapses are characteristic of some infectious diseases.
Another specific characteristic of infectious diseases is the formation of immunity in the process of disease.
Pathogens of Infectious Diseases
The causative agents of infectious diseases are viruses, bacteria and fungi. For the introduction to be successful for a pathogenic microorganism, a single meeting of a macro- and microorganism is not enough. Certain conditions are required. Of great importance is the state of the macroorganism and its protective systems.
A lot depends on the pathogenicity of the pathogen itself. It is determined by the degree of virulence (toxicity) of the microorganism, its toxigenicity (otherwise - the ability to produce toxins) and aggressiveness. Environmental conditions also play a large role.
Classification of Infectious Diseases
First of all, infectious diseases can be systematized depending on the pathogen. In general, viral, bacterial and fungal infections are isolated. Chlamydial, mycoplasmal, rickettsial, spirochetal infections are distinguished separately, although chlamydia, mycoplasmas, and rickettsia, and spirochetes belong to the kingdom of bacteria. Viruses are perhaps the most common pathogens. However, bacteria can cause many ailments. Among the most famous - such as tonsillitis, meningitis, cholera, plague, bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, tetanus. To fungal infectious diseases, or mycoses, include candidiasis, dermatophytosis, onychomycosis, lichen.
Most often, infectious diseases are classified according to the location of pathogens, taking into account the mechanism of their transmission, but this applies to those diseases that spread from person to person. Accordingly, intestinal infectious diseases transmitted by the fecal-oral route (astrovirus infection, polio, cholera, typhoid fever) are isolated. There are infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract. The method of infection with them is called airborne droplets (SARS, diphtheria, scarlet fever, flu). Infectious diseases are still able to localize in the blood and be transmitted through insect bites and medical manipulations. It is about injections and blood transfusions. These include hepatitis B, plague, and typhus. There are also external infections that affect the skin and mucous membrane and are transmitted by contact.
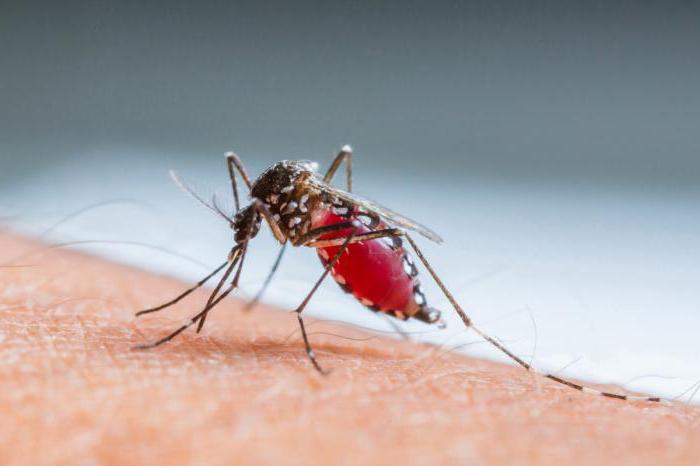
In the process of evolution, each type of pathogen of an infectious disease has its own entrance gate to infection. So, a number of microorganisms penetrate through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, others through the digestive tract, genital tract. It happens, however, that the same pathogen is able to enter the human body simultaneously in different ways. For example, hepatitis B is transmitted through the blood, from mother to child and through contact.
As for the sources of infection, anthroponoses are distinguished if the disease comes from a person, and zoonoses if the animals are infected. I must say that the causative agents of zoonoses when they enter the human body in the future are no longer released into the environment, so the intensity of the spread of zoonoses is an order of magnitude lower than anthroponoses. Zoonoses include brucellosis, botulism, plague, tularemia, rabies, anthrax, foot and mouth disease, tetanus. For zoonoses, as a rule, several transmission mechanisms are characteristic .
There are three main habitats for infectious agents. This is a human body, an animal organism and an inanimate environment - soil and water bodies.
Symptoms of Infectious Diseases
Common symptoms of infectious diseases include malaise, headache, pallor, chills, aching muscles, fever, and sometimes nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea. In addition to general symptoms, there are symptoms that are characteristic of only one disease. For example, a rash with meningococcal infection is very specific.
Diagnostics
As for the diagnosis, it should be based on a comprehensive and comprehensive study of the patient. The study includes a detailed and thorough survey, an examination of organs and systems, and a mandatory analysis of the results of laboratory tests. Early diagnosis of infectious diseases presents certain difficulties, but is of great importance both for timely adequate treatment of the patient, and for the organization of preventive measures.
Treatment
In the treatment of such ailments as infectious diseases, the list of which is so frighteningly extensive, there are several directions. First of all, these are measures aimed at reducing the activity of a pathogenic microorganism and neutralizing its toxins. For this, antibacterial drugs, bacteriophages, interferons and other drugs are used.
Secondly, it is necessary to activate the body's defenses by using immunomodulatory drugs and vitamins. Treatment must be comprehensive. It is important to normalize the functions of organs and systems disturbed by the disease. In any case, the approach to treatment should take into account all the individual characteristics of the patient and the course of his disease.
Prevention
In order to maximally protect yourself and your loved ones from such a threat as infectious diseases, the list of which includes diseases of a viral, bacterial and fungal nature, it is necessary to remember quarantine measures, vaccinations, and strengthening immunity. And sometimes, in order to be saved from infection, it is enough to observe basic rules of personal hygiene.