According to average statistics, liver diseases associated with impaired fat metabolism are becoming more common. This is especially true for residents of America and Europe, who more often than others receive an ominous diagnosis of steatohepatitis. What is it and how to prevent this pathology? This is what will be discussed.
Fatty disease and steatohepatitis
Due to a violation of the metabolism of acylglycerols (fats) and unoxidized products in the gastrointestinal tract, the structure of the liver itself changes. But the most dangerous thing is that such changes are completely invisible, that is, this will not affect the well-being of a sick person. At least until the patient undergoes a medical examination. It is important to make a diagnosis on time and conduct competent therapy, since dying liver cells are replaced by connective tissue. Similar processes invariably threaten complications such as cirrhosis. It is important for a person with a similar ailment to adhere to a diet.
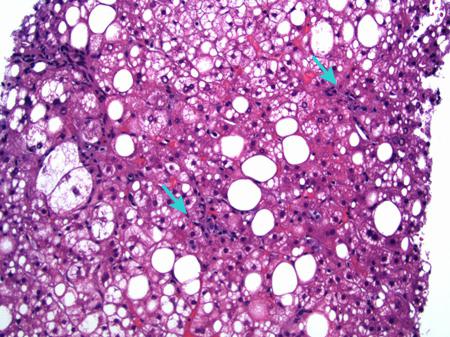
Steatohepatitis - what is it? The disease occurs against the background of fatty liver disease (fatty liver disease), which provokes a number of ailments: hypertension, obesity, chronic hyperglycemia syndrome, atherosclerosis, etc. As a result, liver cells are oversaturated with triglycerides (neutral fats), because of which its structure changes and fatty hepatosis develops. Over time, in hepatocytes, oxidative processes begin that destroy liver cells. As a result, inflammation develops, which provokes the manifestation of statohepatitis. There are three forms of the disease: alcoholic, nonalcoholic and medicinal.
Alcohol form
Most often, alcohol stetohepatitis occurs in people who suffer from a chronic form of alcoholism, which is about 35%. Because 95% of alcoholic beverages are destroyed only in the liver cells, which invariably affects its functioning. The toxic effect of ethyl alcohol on the liver invariably causes inflammatory organ damage.
This is manifested by pain in the ribs (on the right side), psychopathological disorders, dyspepsia and icteric symptoms. The liver enlarges and becomes harder, which is clearly palpable during palpation, which causes dull pain. In addition, the veins in the esophagus expand, which threatens internal bleeding.
Due to inflammatory processes, the activity of transaminases increases, the level of triglycerides in the blood increases. The indicators of bilirubin, lipophilic alcohol, alkaline phosphatase, etc. change upward. The most obvious symptom is a decrease in the activity of aminotransferases (liver enzymes) against the background of withdrawal symptoms.
You can diagnose chronic steatohepatitis only after a full examination: laboratory data, ultrasound, biopsy, palpation and communication with your doctor.
It is important to protect liver cells from destruction and eliminate, or at least minimize, inflammatory processes. Stop the growth of connective tissue in the organ and prevent the development of cirrhosis.
Alcohol is strictly prohibited! Otherwise, the treatment will be useless.
Non-alcoholic form
Metabolic steatohepatitis occurs due to oversaturation of liver cells with neutral fats - triglycerides. And as a result - oxidative and inflammatory processes, destruction of organ cells, proliferation of connective tissue and the development of cirrhosis. Recently, cases of non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis have become more frequent.
The disease occurs against the background of excess weight, pancreatic diseases, impaired fat metabolism, sudden weight loss. Also, the cause may be malnutrition, namely protein deficiency, decreased levels of antitrypsin, etc.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis can occur on its own or be a consequence of other diseases. Without a laboratory examination, a person may not notice his signs. Transaminases are activated, the size of the liver increases. Many are diagnosed with NASH when they go to the doctor with complaints of other diseases.
In order to cure or stop the development of the disease, it is necessary to normalize oxidative processes, accelerate the transportation of neutral fats from the liver, reduce the accumulation of fats in the cells of the body and the oxidative degradation of lipids. Oxidants damage the composition of membranes, nerve endings and break the structural unit of nucleic acids.
A mandatory component of treatment is a diet. You need to select a diet individually for each case, since the course of the disease in all patients is different. And thanks to well-chosen diet therapy, you can stop oxidative and inflammatory processes and stop the development of the disease.
It is strongly recommended that you undergo a mandatory medical examination every six months so that the ailment does not turn into a serious form.
Dosage form
Another form is medicinal steatohepatitis. What is it and why does it arise? One thing is certain: the reason is not the use of alcoholic beverages. As the name implies, this form of the disease occurs due to the use of drugs dangerous to the liver. These include tetracycline antibiotics, synthetic estrogens, Chloroquin, Delagil, drugs for the treatment of viral immunodeficiency, antifungal agents and others.
If you take medications from a risk group for a long time, then the functionality of the liver may be impaired. This means a violation of the oxidative processes of triglycerides, which most often forms LSH (drug steatohepatitis), the symptoms of which are rather unpleasant and noticeable. And therefore, you must strictly adhere to the course of treatment, as complications may occur. The most dangerous pathology is the necrosis of liver cells of various degrees of severity.
At risk are people who have already observed impaired liver function. You can take such medications only on the recommendation of the attending physician and under his close supervision. It is strongly recommended that hepatoprotectors be taken at the same time as dangerous drugs.
Degree of defeat
The histological picture and the percentage of cellular liver damage shows at what stage of development the disease is.
Steatohepatitis of a minimal degree of activity occurs against the background of metabolic disorders and is characterized by mild inflammatory processes. About 35% of the cells are susceptible to damage. Detecting the disease at an early stage guarantees a more effective treatment.
This can not be said about the serious form of the disease: fatty vesicles were detected in 70% of the cells, and all this happens against the background of a general severe inflammatory process.
Steatohepatitis of moderate activity is provoked by other diseases and is characterized by damage to about 68% of cells, the inflammatory reaction is not too intense, but already more noticeable than in the first stage.
Causes
The root cause of this ailment is a metabolic disorder, the result of which may be the appearance of excess weight or, conversely, sudden weight loss. A strict diet or overeating can also trigger liver steatohepatitis.
The main causes of the development of the disease:
This includes overweight or sudden weight loss as a result of malnutrition. Endocrine diseases, disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, resulting in a sharp increase in blood sugar. The ratio of lipids (fat-like substances) in the blood changes. The introduction of glucose into the blood by the intravenous method. Switching to a completely prenatal diet.
Some medications can cause fatty hepatosis, which results in oversaturation of liver cells with fats. Such a reaction can cause steroid hormones, drugs that inhibit or completely suppress cell division. As well as antibiotics, intended for the treatment of infectious diseases, and some anti-inflammatory drugs that lower fever and anesthetize.
- Gastrointestinal surgery.
- Intestinal diverticulosis (saccular protrusion of the intestinal wall).
- Hepatocerebral dystrophy. This is a hereditary disease that is characterized by impaired copper metabolism in the body.
Symptomatology
As already noted, depending on the causes that cause inflammatory processes in the liver cells, three types of the disease are distinguished: alcoholic, medicinal, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Symptoms, causes of the development of the disease and treatment methods in each case are different.
The alcoholic form of the disease has the following symptoms:
- The size of the liver increases, it becomes denser, which is noticeable during palpation.
- Pain in the ribs (on the right side).
- Digestive disorders, meaning diarrhea or constipation.
- The patient sweats a lot and is constantly thirsty.
- Feeling of exhaustion and weakness.
- Appetite is lost, a person is losing weight dramatically.
- The patient is constantly sick, vomiting is often manifested.
- The skin and sclera of the eyes become yellow.
Signs of the dosage form of the disease:
- Systematic pain (acute pain) of the liver.
- Violation of the secretion of bile.
- The skin is painted in a characteristic yellow hue.
- Skin irritation appears.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis symptoms have the following:
- Frequent painful sensations of the liver.
- The patient feels a constant heaviness in the abdomen.
- Exhaustion and weakness.
- Thirst and excessive sweating.
Diagnosis
The danger is that most often the disease is slow and does not have obvious symptoms. The main danger signal is pain in the liver, its increase and compaction.
Modern medicine has many ways to diagnose various forms of this disease. Recently, it is alcoholic steatohepatitis most often registered, the treatment of which is a very complex and difficult process. That is why the first and foremost is an alcohol history.
Survey Stages:
- Ultrasound of the liver for its increase and external changes.
- Laboratory tests to detect cholesterol, hydrolysis enzyme, globular protein, bile pigment, neutral fats, etc. These data will help to identify at what stage of development the disease is.
If you diagnose moderate steatohepatitis in time, then the chance of a speedy recovery increases.
If, according to the results of the examination, no signs of alcoholic hepatosis were detected, then a study is conducted on a non-alcoholic form of the disease:
- A biopsy, which involves intravital sampling of liver cells from the patient’s body.
- Ultrasound to detect excess weight or endocrine diseases. This study is done if a biopsy is not possible.
The dosage form of the disease can be identified by the attending physician, who prescribed drugs to the patient at risk. Methods of determination: ultrasound examination, examination on a computed tomography scanner, laboratory tests or diagnostics using a biopsy.
The ideal option is a method of complex functional diagnostics.
Treatment and complications
It is important to exclude toxic effects on the liver, increase the sensitivity of the body to the action of insulin. And also to normalize the metabolism of fats in cells and restore immunity. These are the main tasks for the attending physician and his patient. Steatohepatitis with a minimal degree of activity is best treated.
In this case, the patient must follow the recommendations of a specialist. It is important to exclude excessive physical activity. You need to engage in sports, but in moderation: swimming, Pilates and walking are acceptable. This is especially true for overweight people.
Diet therapy is prescribed for each patient individually. It is highly recommended to refuse spicy and fatty foods, smoked products, various marinades and caffeine. Regardless of the results of treatment, the diet will have to be kept constantly. It is strictly forbidden to drink (even in small quantities) alcoholic beverages, as the disease will begin to develop even more actively.
Depending on the type of disease (alcoholic drug and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis), treatment is carried out by different methods, different medications are prescribed.
But we can distinguish medications that fight the main symptoms of this ailment:
- Hypoglycemic agents to increase insulin sensitivity.
- Bile acid drugs that lower transaminase activity and protect liver cells.
- Hepatoprotectors (Essential Forte) in the form of capsules or ampoules. Their action is to eliminate an insufficient amount of phospholipids in the patient's body.
- Hyploidymic drugs (statins) that lower blood cholesterol.
- Any form of the disease, even steatohepatitis of minimal activity, requires inpatient treatment under the constant supervision of specialists. Since illiterate therapy provokes the risk of developing cirrhosis, liver fibrosis, and even liver failure.
Diet
Most people with fatty hepatosis have problems with being overweight, and therefore sports and a low-calorie diet are a chance for recovery. After all, in order to minimize inflammation in the liver, you need to lose weight. A serious illness that disciplines you is all steatohepatitis. Diet is a very important factor in the healing process. The list of products that you can and should even be consumed: chicken (skin cannot be eaten), meat of calf, rabbit, boiled fish (river), protein, dairy products of minimal fat content. The animal proteins that are contained in these products stop the fatty degeneration of liver cells. This is not the case with animal fats: lamb, pork, beef, fat cream, etc. Instead of these products, it is better to use vegetable or olive oil.
Complex carbohydrates, such as white cereals, flour and sweets, should be excluded from the diet. Eating vegetables, berries, herbs, fruits, cereals and bran helps lower blood cholesterol.
It does not matter what form of the disease a person has: alcoholic, medicinal or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, a diet is a prerequisite!
Prevention
To prevent an ailment, it is extremely important to focus on the treatment of the main pathologies that can provoke it: overweight, endocrine diseases, etc. Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating the reasons that provoke it:
- Alcoholic beverages should be consumed in moderation.
- A balanced diet.
- It is necessary to cure diseases that contribute to the development of fatty hepatosis as soon as possible.
- Careful use of drugs that are dangerous for the liver. Along with them, you need to take hepatoprotectors.
It does not matter what form of the disease is found in the patient: diet is a prerequisite. And this means a ban on fried, fatty, spicy, smoked and various pickles. Only protein foods, vegetable fats, vegetables and fruits.
It is also important to lead an active lifestyle: the correct schedule of the day, normal sleep (at least 7 hours), personal hygiene and, of course, physical exercise. Subject to these rules, obesity is definitely not threatening you. In addition, immunity increases, metabolism normalizes, and in general the body functions normally.
People with chronic fatty hepatosis should undergo treatment every year. Thus, they will be able to avoid possible complications.
Treatment with folk remedies
A serious disease that threatens with dangerous complications is steatohepatitis. The treatment of this ailment can be supported by alternative medicines. In addition, complex therapy is approved by modern doctors.
One of the traditional medicines is milk thistle grass, which restores liver cells and thereby stabilizes its functionality. Many effective natural preparations aimed at treating fatty hepatosis contain milk thistle seed extract.
How to Make Milk Thistle Powder Against Steatohepatitis
To prepare the potion, you will need fruit (35 g). Grind the seeds in a blender until a powder is formed and consume 1 teaspoon 6 times a day with a glass of warm boiled water.
35 grams of milk thistle powder is the daily requirement for restoring liver function. The course of treatment should last at least 40 days, after which you will notice how you feel better. The liver decreases to normal size, the unnatural compaction disappears for it, fat metabolism improves, etc.
Doctors themselves prescribe such medicines, since they are more natural and do not contain hazardous toxic components. Maybe they do not show such a quick result, but they are absolutely safe for the body.
Naturally, taking the initiative without the approval of your doctor is strictly prohibited! Since complex treatment can only be prescribed by a qualified specialist after a full examination and observation of the course of the disease.
To reduce the inflammatory processes in the liver, you can try such means:
- Almond or apricot oil.
- Herbal tea from St. John's wort, calendula, chicory and immortelle.
- Infusion of sage, knotweed, repeshka and horsetail.
- The fruits of viburnum and cranberries.
All these drugs have a positive effect on the functioning of the liver, especially in the initial stages of the disease. But for the treatment of more advanced forms, they are used only in combination with traditional medications. And then only after the approval of the attending physician.
Steatohepatitis - what is it? This disease has many names: "pathology of a civilized society", "silent killer", obesity of the liver, etc. But no matter how you call it, it is a serious disease that must be fought systematically, constantly and hard. Do not do without patience, willpower and discipline. Yes, it may be hard, but life is more expensive and worth it. The main thing is to follow the doctor's recommendations and constantly follow his instructions. Only in this case, you can overcome this terrible disease!