The human legs, especially the small joints of the feet, experience considerable loads every day, supporting the body weight, often overweight. If concomitant diseases of the musculoskeletal system join in, then the cartilage of the joints wears out and leads to deforming arthrosis of the feet. Chronic destruction of the cartilage of the legs more often occurs in men and women over the age of forty. This disease is systemic. To some extent, all joints of the body suffer, but changes undergo those that are subjected to maximum load. It all depends on lifestyle, professional activity, genetic predisposition and some provoking factors. This article will describe the causes, manifestations of foot arthrosis, symptoms and treatment of the disease.
General information
All joints of the foot are susceptible to the disease, but the ankle and metatarsophalangeal of the big toe are more often affected. The disease manifests itself not only in people after forty years, but also at a young age. Athletes involved in gymnastics, jumping, boxing, wrestling often experience symptoms of this disease.
A chronic disease called osteoarthrosis is associated with damage to the joints, cartilage and inflammatory processes in the periarticular tissues, which disrupt their metabolism and blood microcirculation. As a result of this, sharp painful sensations appear, fingers are bent, and in places of heavy load corns appear. Each movement is accompanied by pain. Trying not to disturb the affected joint, the person transfers the load to the outer edge of the foot. As a result, the gait changes, fatigue sets in, activity and ability to work decrease.
Causes of the disease
Many believe that the main cause of osteoarthritis is the physiological aging of the body and increased wear of the cartilage as a result of great physical exertion and a number of factors contributing to their degeneration. The main circumstances leading to the development of foot arthrosis:
- congenital structural features of the foot - flat feet, improperly formed joints, one limb longer than the other, wide foot;
- incorrect posture;
- joint overload - sports, prolonged stay on the legs;
- overweight;
- injured feet - dislocations, sprains;
- constant wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine system diseases;
- constant subcooling;
- inflammatory processes in the joints.
All of these factors contribute to the development of pathology.
Symptoms of foot arthrosis
Signs of the disease appear depending on abnormal changes in the joints of the foot. The disease has a long course, it takes several years to develop it. For help, a doctor is consulted when severe pain occurs or fingers are deformed. The disease proceeds, passing through three degrees of development, with various symptoms:
- First one. There are no distinct signs. Patients complain of leg fatigue after prolonged walking. Pain is rare and after rest completely disappears. Many consider this symptom to be overwork and do not pay any attention to it. In addition, a crunch appears in the joints of the foot, but this is not a characteristic sign of the disease.
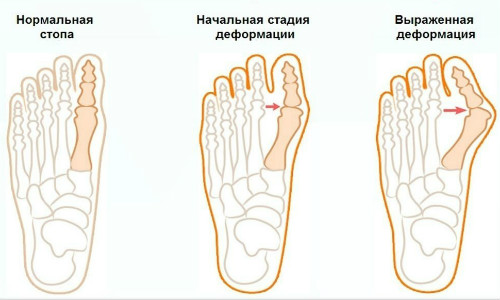
- The second one. Symptoms of foot arthrosis are aggravated. Intense pains begin to appear, disturbing with small loads and not passing after a long rest. There is a thickening of the heads of bones and proliferation of connective tissue around the affected joints. As a result, you have to buy shoes a size larger. The big toe deviates to the outside of the foot, forming a protruding bone.
- The third. The pain becomes constant, taking analgesics does not always help. The deformity of the fingers is joined by poor mobility of the joints of the foot. The gait is changing, the person is shifting from side to side. As a result, the spine and other joints suffer.
Late access to a doctor leads to the progression of the disease, and the treatment of symptoms of foot arthrosis is significantly complicated, which subsequently becomes the cause of disability.
Diagnostics
The following measures are taken to make a diagnosis:
- a conversation with the patient, during which complaints are heard, an anamnesis is collected;
- visual inspection;
- general analysis of blood and urine;
- conventional radiography - X-rays are passed through the foot, and an image is obtained in which the doctor can clearly examine the bone structures and all existing formations;
- nuclear magnetic resonance makes it possible to study soft tissue;
- computed tomography is performed in the initial stages of the disease;
- ultrasound - for diagnosis is rarely used, but is used to monitor the condition of cartilage and joint;
- bone scintigraphy can distinguish arthrosis from other pathologies;
- puncture - a fluid is taken from the joint, and a laboratory study is done to exclude gout and infectious diseases.
All of these methods examine the articular region, allowing you to find out the full picture of the condition of the pathology and determine the stage of arthrosis. After the final diagnosis is made, the doctor prescribes the treatment of arthrosis of the foot.
Disease treatment
Deforming arthrosis is treated on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is subject to patients with severe pain and requiring surgical intervention. When treating at home, the patient must comply with all the instructions of a doctor, which may be a therapist, rheumatologist, traumatologist or surgeon. The choice of a doctor depends on the disease, as a result of which the joint was damaged. A complex course of therapy is usually prescribed, consisting of:
- from conservative therapy;
- lifestyle changes;
- folk remedies;
- surgical intervention.
Lifestyle of a patient with arthrosis
To improve well-being, you should abandon the habits that lead to an aggravation of the disease. First of all, it is necessary to reduce the load on the damaged joint, for this:
- limit the duration of the walk;
- when moving, take five-minute breaks;
- long time not to stand in one place;
- limit ascents and descents of stairs;
- not tolerate severity;
- use a cane.
Equally important is weight loss:
- switch to a low-calorie diet;
- arrange fasting days;
- carry out body massage;
- engage in physiotherapy exercises.
Drug treatment
For the treatment of arthrosis of the foot, various groups of drugs are prescribed that fulfill a specific goal:
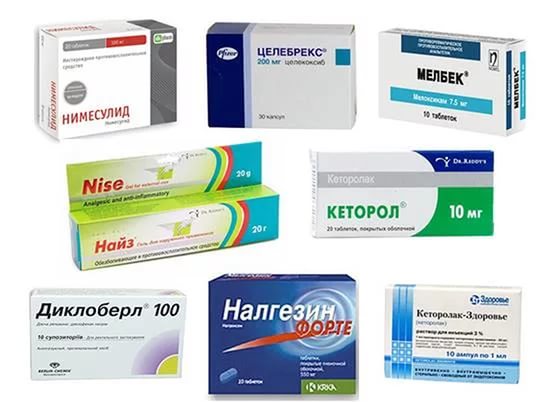
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain and inflammation. They serve to alleviate the symptoms of the disease. With a decrease in pain, muscle spasms are reflexively reduced. This leads to improved blood circulation, and the possibility of movement increases. They are taken no more than ten days, the most effective: Ortofen, Naklofen, Diklofenak, Ibuprofen, Nurofen.
- Chondroprotectors are agents for treating arthrosis of the joints of the foot, helping to improve tissue nutrition and restore cartilage that are difficult to regenerate. They have an effect when the disease is just starting to develop. Reception is conducted by long courses up to six months. And only 3-4 months after the start of treatment, there are signs of improvement. Effectively operates Structum, Arthra, and Don.
- Analgesics - with their help they block strong pain that appears in the second stage of the disease. To do this, prescribe ointment "Nikoflex", "Viprosal", "Apizartron."
- Minerals and vitamins normalize metabolic processes, support the immune system. It is recommended to take Vitrum, Oligovit.
In addition to systemic drugs that affect the whole body, for the treatment of foot arthrosis, local therapy is used using creams and ointments, for example, Fastum Gel, Finalgon. Some drugs are injected into the joint cavity, for example, “Hyalur”, “Ostenil”.
Non-drug therapy
Includes physiotherapy, massage and physiotherapy. With their help, a metered load is created on damaged joints, which helps restore functions. Exercises are selected together with the doctor depending on the condition of the joints. All measures should maintain and improve the functional mobility of the foot. When performing procedures, certain rules must be observed:
- classes begin with exercises for healthy joints, gradually connecting the affected;
- all movements should not be very intense and not cause pain and injury;
- increase the load gradually;
- classes to conduct systematically and for a long time.
From physiotherapy to treat arthrosis of the joints of the foot, apply:
- applications of coolants - use peat mud, ozokerite and paraffin (under the influence of heat, metabolic processes that contribute to the restoration of cartilage are improved);
- magnetotherapy - increased vascular permeability and the rate of enzymatic reactions;
- infrared rays help to anesthetize and stop inflammation;
- electrophoresis using "Analgin", "Sodium salicylate" and "Lidocaine" brings relief from pain;
- Ultraphonophoresis - “Analgin” and “Hydrocortisone” medications are introduced to prevent inflammation and pain under the influence of ultrasound.
In addition, a special diet with a high content of vitamins and minerals, wearing special orthopedic shoes and insoles is recommended.
Folk remedies
They are used for symptomatic treatment in order to stop the progression of the disease, until the changes in the cartilage and joints have occurred. Alternative treatment of foot arthrosis is used to reduce redness and swelling of the joints, relieve pain. The following drugs are prepared for treatment:
- Banana. Take the peel of five bananas, wipe and pour 0.5 liters of vodka. Insist for a month, apply for rubbing the foot.
- Garlic. Grind a few cloves into the pulp, add vegetable oil. The mixture is applied to the affected joint under a bandage.
- Hops and St. John's wort. Grind 10 grams of dry grass into powder, add 50 g of petroleum jelly, mix. Lubricate diseased joints with the obtained ointment twice a day.
- How to treat foot arthrosis using honey, alcohol, salt? Equal amounts of ingredients are mixed until sour cream. From the resulting mass, make a compress over the damaged joint overnight. As a result, the pain will lessen.
- Bath with sea salt. Dissolve 250 grams of sea salt in two liters of warm water, mix. Keep feet for 30 minutes. After the procedure, wear woolen socks.
All recipes can also be used as preventative measures: athletes, the elderly, patients with ankle fractures and sprain.
Surgery
The chronic course of foot arthrosis, prone to progression, often leads to the final destruction of cartilage. The patient is tormented by severe pain, the joint is completely immobilized. In this case, only the operation will help:
- Arthroscopy of the joint. Used in the second stage of the disease in young patients, but gives a temporary effect. A special apparatus, an arthroscope, removes blood clots and small pieces of the damaged joint. The pain eventually decreases significantly.
- Endoprosthetics. The operation is performed with complete destruction of the joint and terrible pain. The joint is replaced with an artificial one with a service life of up to 15 years. At the same time, all the functions of the foot are preserved, the pain disappears. Patients who underwent joint replacement leave mostly positive reviews: the arthrosis of the foot is completely cured, the pain is gone, the normal work of the foot is completely preserved. The postoperative period is complex and long, but the resulting effect is worth the effort. A positive attitude helps faster recovery.
Toe Arthrosis Treatment
With this disease, cartilage is destroyed and the inflammatory process of the soft tissue surrounding the joint occurs. This happens as a result of metabolic and circulatory disorders in the tissues of the cartilage. The disease can affect either one thumb, or several or all together. This is manifested by joint pain, redness and slight swelling. Movement becomes difficult, a person begins to limp. Painful sensations with arthrosis of the joints of the toes and stiffness are more often felt in the evening and in the morning. The disease is detected by x-ray examination. Next, the causes are established and treatment is prescribed. The patient should change his lifestyle by reducing physical activity on his legs and food, adding more foods containing vitamins and minerals to the diet. The specific treatment technique is selected by the attending physician. It is primarily aimed at the treatment of the disease, as a result of which the ailment arose. Comprehensive treatment for arthrosis of the toes consists of the use of folk remedies, physiotherapeutic procedures, therapeutic exercises and drug treatment. The following drugs are mainly prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory - "Indomethacin", "Ketonal";
- painkillers - "Spazmalgon", "Analgin";
- chondroprotectors - restore and slow down the destruction of the joint: "Arthra", "Chondroitin sulfate";
- for injection into the joint - "Fermatron", "Synvisc."
In advanced cases, surgery is performed.
The difference between arthrosis and arthritis
Both diseases are associated with damage to the joints of the foot. With arthrosis, articular cartilage and bone tissue are affected. With mechanical stress, this leads to a slow destruction of the joint. There are many different reasons that contribute to the occurrence of osteoarthrosis. Of great importance are great physical exertion and ankle injuries. Arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease. It arises as a result of inflammatory processes that occur in other organs of the person or when bacteria multiply, which are constantly in the body and are activated when the immune system is weakened. Arthritis is characterized by an acute course of the disease with fever and severe pain in the affected joints. Then the disease recedes, but the changes that have occurred in the joint remain, and subsequently arthrosis may develop. Anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat foot arthritis, while arthrosis develops slowly and does not have an effective treatment.
Arthrosis Prevention
For the prevention of the disease, it is recommended:
- Proper nutrition. Eat more plant foods, reduce the volume of fatty, smoked, spicy foods. Introduce fish oil into the diet.
- Comfortable shoes. Choose with flexible soles, wide toes and comfortable heels, use orthopedic insoles.
- Watch your own weight.
- With a heavy load on the feet, use bandages.
- Limit mechanical stress on the legs.
- In the summer, walk barefoot.
Arthrosis of the foot affects not only the elderly, but also people of middle and young age. All risk factors for the disease are distinguished by internal and external. Internal include genetic abnormalities and physiological characteristics of a person: congenital pathologies of joints, flat feet. The external ones consist of a lifestyle and environmental influences: wearing uncomfortable shoes, playing sports, a lot of physical load on the legs associated with work. Knowing these features, you should carefully monitor your feet and consult a doctor in time when the first signs of the disease appear.