Diffuse euthyroid goiter is not a specific disease, but includes a number of pathologies affecting the thyroid gland. The disease is often the result of a lack of iodine, is visible to the naked eye and is easily palpated upon palpation. The diffuse euthyroid goiter code according to ICD-10 has E 04.0. A disease can take several different forms:
- non-toxic goiter with one pathological node;
- multinodal non-toxic goiter ;
- goiter diffuse nontoxic euthyroid;
- unspecified non-toxic goiter;
- other specified varieties of non-toxic goiter.
The disease requires an accurate diagnosis by examination, testing and other necessary manipulations.
What kind of illness is this?
Diffuse non-toxic euthyroid goiter is a pathological enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is easily palpated, visible to the naked eye and has a non-toxic origin. At the same time, the function of the organ does not change significantly, the amount of hormones produced remains at the same level and the external form of the gland is adaptive.
If a nodal variety of the disease is diagnosed, then this means that nodes in a single or multiple quantity appeared on the gland. It is depending on their growth that the final diagnosis is made.
Often the patient goes to the doctor because of a cosmetic defect, which is quite difficult to hide even under clothes. Also, a person may be disturbed by a feeling of squeezing and heaviness in the neck. The specialist makes the final diagnosis based on the collected history, laboratory examinations and external examination.
Causes of the disease
Diffuse euthyroid goiter is a consequence of iodine deficiency. It is proved that for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland per day, an adult should consume at least 150 micrograms of this microelement. The main route of intake of the substance is considered to be food, and also a certain amount enters the body with water and air. Therefore, in places of residence where a deficiency of iodine is detected in water and the surrounding air, a disease more often occurs, which is called diffuse euthyroid goiter. Sometimes the starting point for the development of pathology are thiocyanates and flavonoids.
In all other cases, the diagnosed goiter is considered to be sporadic, but the causes of its occurrence have not yet been fully determined by specialists. However, there is a fairly plausible version that most doctors adhere to. It is believed that sporadic goiter is most likely to occur due to a lack of enzymes involved in the formation of thyroid hormones, which is caused by a birth defect.
Provocative factors
Diffuse euthyroid goiter, of course, is the result of a lack of iodine in the body. However, the factors that provoke the onset of the disease may be the following:
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- prolonged use of various drugs;
- work requiring contact with harmful substances (chemical industry, X-ray rooms);
- excess in the body of calcium and malfunctions of the parathyroid glands;
- pregnancy.
Nodular euthyroid diffuse goiter can develop against the background of frequent inflammation of the thyroid gland tissues. Such a pathology appears as a result of proliferation of cells in the affected organ. The reasons may also be:
- Autoimmune reactions that occur in the patient’s body.
- Cervical osteochondrosis, which causes difficulty in the outflow of lymph.
Many experts believe that age-related changes can also cause overgrowth of nodes.
Goiter classification
Symptoms of the disease will vary, depending on the nature of the pathology and its progression. Judging by the WHO classification, the following degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- 0 degree. The size of the organ is within normal limits, there are no clinical data indicating the presence of pathology, but changes have already begun to occur inside the body that require adjustment.
- Diffuse euthyroid goiter of 1 degree. The doctor can already detect a slight increase in palpation of the thyroid gland . Also, only some parts of the organ can undergo a change in size. However, with the usual anatomical position, the goiter is difficult to suspect.
- Diffuse euthyroid goiter 2 degrees. Changes in the thyroid gland are already visible to the naked eye and with the standard position of the neck.
We will consider the symptoms of the disease further, because the clinical picture in each case will be different.
Pathology of the first degree
Diffuse euthyroid goiter of the 1st degree is manifested by rather meager symptoms, because there is no lack of hormones characteristic of a healthy gland. However, patients may complain of some enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is sometimes noticeable with a thorough examination of the neck. At the same time, patients rarely feel real discomfort.
Second degree goiter
Diffuse-nodal euthyroid goiter of the 2nd degree can already be manifested in violations of the function of swallowing and breathing. This situation occurs due to compression of the expanding gland of the trachea and esophagus. At the same time, the patient's quality of life drops sharply. A cosmetic defect is also present in a rather pronounced degree.
With a disease of the second degree, complications often occur, expressed in the proliferation of the superior vena cava and hemorrhage in the tissue of the affected organ. Euthyroid goiter of the 1st degree, if untreated, quickly proceeds to the next stage, while the disease will progress if the therapy is not competent, and will be transformed into a nodular variety or toxic.
Symptoms of the disease in the first degree
The disease may be accompanied by the appearance of hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. In this case, the signs of diffuse-nodal euthyroid goiter can be as follows:
- apathy, depression, lethargy and lack of exercise;
- increased susceptibility to infectious pathologies;
- nausea and disturbances in appetite;
- decrease in normal body temperature;
- dry skin
- in children, growth retardation;
- hair loss;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- decreased libido and complete impotence.
However, the disease can be expressed in different ways, depending on how the gland behaves. In this case, symptoms are considered with a decrease in its function. If the body begins to pathologically actively produce hormones, then the following symptoms are possible in the patient:
- insomnia and irritability;
- increase in normal body temperature;
- exophthalmos;
- heart palpitations;
- weight loss with increased appetite.
Signs of a second degree disease
If, in the first degree of euthyroid goiter of the thyroid gland, symptoms are expressed only in general health and a change in the body, then in the second, mechanical signs of pathology are added. Iron expands and begins to squeeze the esophagus. The patient complains of a sensation of a lump in the throat that does not go away and leads to malfunctioning in swallowing. The respiratory organs, in particular the trachea, are also involved in the process. The result is:
- characteristic husky voice;
- frequent persistent cough;
- shortness of breath, which progresses as the disease develops;
- asthma attacks.
Sore throat also appears, because the nodes on the thyroid gland grow rapidly. At the same time, they begin to become inflamed, which threatens hemorrhages. In the absence of nodes, palpation is usually not painful.
If the euthyroid goiter of the thyroid gland flows with the formation of nodes, then they are visible during examination and look like cones on the base of the neck. A diagnosis of “mixed goiter” can also be made when the size of the organ is significantly increased and there are areas of swelling.
Diagnostic Methods
To make a diagnosis, the endocrinologist will perform the following manipulations:
- Palpation of the affected organ. Thus, the doctor will be able to assess the extent of the problem, to understand what is the real increase in the gland. It can be local, relating only to its individual sections, and general, affecting the entire body as a whole.
- After a digital examination and the obtained data, the patient receives a referral for ultrasound. As a result, a more accurate visualization of the detected pathology can be obtained. The ICD-10 diagnosis of "diffuse euthyroid goiter" is made when an organ enlargement is detected in men up to 25 mm and in women up to 18 mm. If formations are detected, even less than 1 cm in a circle, then a diagnosis of “multinodular” or “nodular goiter” is made, depending on their number.
- If the ultrasound data showed the presence of formations more than 1 cm in a circle, as well as with a diffuse goiter of any nodes, then an aspiration fine-needle biopsy is prescribed. Such manipulation is necessary to exclude the cancerous nature of the disease.
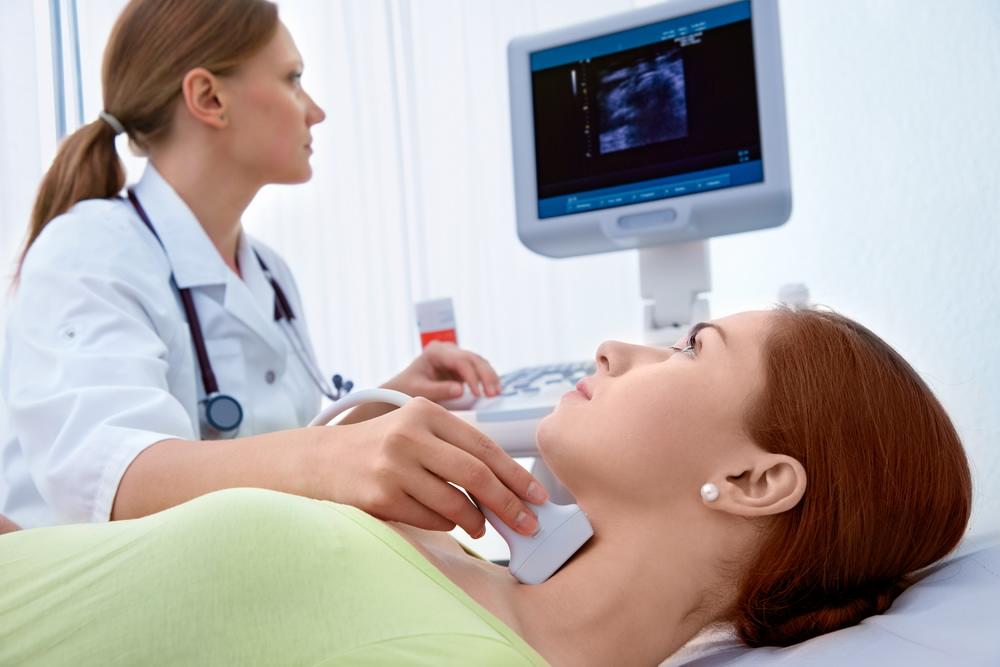
Sometimes scintigraphy may be indicated. The procedure is important for making an accurate diagnosis, but is not always required. With its help, it is possible to determine the nature of the pathology.
The procedure is as follows:
- they drive an iodine isotope intravenously;
- with its uniform distribution, a diffuse increase in the thyroid gland is placed;
- if cold, hot or warm areas are detected, this indicates nodular formations;
- if the node exhibits excessive activity, then the zone is hot (treatment is required immediately);
- a warm node indicates optimal hormonal activity and characterizes the presence of nodular euthyroid goiter.
Laboratory blood tests can also be used. If hormone levels are normal and there is an increase in thyroglobulin production, then this indicates a lack of iodine. Additionally, X-ray and tomography are used for suspected goiter of the second degree.
How is the disease treated?
Treatment of diffuse euthyroid goiter involves the use of drug therapy, the use of radioactive iodine and surgical intervention. Of course, any competent doctor will always try to do with conservative methods. It should be understood that only strict indications lead to surgical intervention and an operation is never performed without proof.
Medicines used
The disease requires treatment by an endocrinologist. In this case, the doctor can go in different ways:
- use suppressive therapy:
- apply iodine therapy;
- prescribe a combination treatment.
If iodine preparations are used, then the maximum duration of treatment cannot last more than six months. It is noted that after this the size of the affected organ is reduced by no less than a third. Sometimes a complete cure is fixed and a normal size is achieved. The daily dosage of iodine medications is usually from 100 to 200 mcg. The treatment regimen is selected based on the collected history and age of the patient.
Monotherapy using iodine preparations does not require the calculation of an individual dosage and does not cause side effects. However, the effect of such therapy is somewhat weaker than when prescribing a suppressive technique. It is more suitable as a preventative measure after surgery to avoid relapse. In addition, monotherapy gives the greatest effect in the treatment of patients not older than 40 years. Then the degree of effectiveness decreases according to an increase in age.
Suppressive method
If, against the background of using only iodine preparations, there are no improvements or the patient is age-related, then the use of a suppressive technique will be most optimal. A synthetic analogue of the hormone that is produced by the thyroid gland, sodium levothyroxine, is used. Its advantage is the quickly achieved effect. However, with cancellation in almost 100% of cases, relapse is diagnosed.
Combination treatment
To avoid relapse when using only levothyroxine sodium, the doctor often resortes to a combined method of treatment. Only in this way can we quickly achieve results and avoid a repetition of the situation with the growth of the thyroid gland.
Surgical intervention
There are absolute indications for surgery and relative. If you are diagnosed with nodular goiter, then, of course, it is necessary to decide on an intervention for:
- pronounced nodes that are easy to remove surgically;
- formations that squeeze the trachea and larynx and create risks of suffocation;
- detection of hemorrhages in the nodes;
- tumor degeneration of formations.
If the nodes are small enough in size, do not cause inconvenience or there are a lot of them, then the indications for surgery are considered relative. In this case, there are risks of an early relapse after surgery and incomplete removal of all nodes. The specialist usually prefers to wait until the nodes grow to such a size that they are easy to visualize and remove.
It should be understood that the disease itself does not imply a mandatory surgical intervention. The operation is necessary only in emergency cases, when the growths begin to compress the respiratory system, which leads to a life threat. Usually, the intervention is carried out urgently, and the operation involves the removal of not only the nodes themselves, but also that part of the thyroid gland that compresses the trachea and esophagus.
How is the operation?
Surgical intervention consists in resection of the organ, and a total technique or subtotal can be used. The surgeon leaves the organ only if there is a good chance of recovery. Otherwise, there is no point in saving surgery, because relapses are most often recorded with incomplete removal of nodes, which is possible with a sufficient number of nodes.
According to the same indications as surgery, undergoing treatment with radioactive iodine. However, this technique does not always allow to achieve complete destruction of the node. As practice shows, under favorable conditions, education can decrease in size by only 80%. The essence of therapy is that under the influence of iodine, the tissue of the node and the thyroid gland itself are destroyed. Moreover, the effect can be seen only after 3-5 months of treatment. Often the method is used to avoid relapse after surgery, as well as in case of detection of thyroid cancer. However, absolute contraindications to the use of radioactive iodine should also be taken into account. These include pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Alternative medicine
Diffuse euthyroid goiter has indications for alternative treatment. However, it must be understood that therapy with folk remedies in no case can replace the prescribed medications or help avoid surgery. But we can safely say that using an alternative technique, you can significantly increase the effect of the prescribed treatment.
Herbal infusions
With goiter, the following decoctions perfectly help to reduce the size of the gland and stabilize its function:
- of calendula flowers (half a glass up to 4 times a day):
- from the leaves of wild strawberries (in a glass 3 times a day);
- from the root of wild mallow (you need to drink 500 ml of infusion during the day);
- from Scutellaria baicalensis (a tablespoon 3 times a day).
Before using any decoction, it is important to obtain the approval of a specialist.
What is the forecast?
Diffuse non-toxic euthyroid goiter with correctly prescribed treatment has a very encouraging prognosis. And it does not matter, nodular pathology or diffuse. A lethal outcome is recorded in very rare cases, and the cause of death is not the goiter itself, but compression of neighboring organs and asphyxiation. The quality of life of patients who are observed by a doctor and receive appropriate treatment does not significantly change.
Drug therapy helps to adjust the size of the gland. If a diffuse goiter without nodes is diagnosed, then almost 100% can cure the disease using only medications. Of course, in some patients, the formation of nodes is fixed, which require different treatment tactics and additional monitoring by a specialist.
Diffuse euthyroid goiter 2 degrees and the army
If a goiter is found in the conscript, the medical commission will send him for surgical treatment. However, this does not mean that an operation must be performed. This decision is discussed with the attending physician. In the future, events can develop in different ways.
If the operation did not help or the conscript refuses it, then it becomes unsuitable for military service. If clinical manifestations are absent, then a call is possible. Everything is decided individually and only on the basis of the conclusion of the commission. At the time of treatment, a delay is always given. Also, a person can receive a category that exempts from military service in peacetime, but does not serve as a basis for exemption from military service.