According to ICD-10, erysipelas is encoded as A46. The name of the disease received from the Polish word róża. Belongs to the number of infectious, affects mucous membranes, skin integuments. Currently, the prevalence of pathology is quite large. Among other infectious skin lesions in terms of the frequency of occurrence in the world of erysipelas, it occupies the fourth place, which makes it an extremely urgent medical problem. One of the forms of streptococcus can provoke the disease. You can get infected from both the patient and the carrier. Pathology manifests itself in a febrile state, inflamed areas of red on the skin, mucous membranes.
general information
Coded as A46 in ICD-10, erysipelas may develop in a simple or complicated form. The second option is a severe pathology that affects soft tissues. Usually, the disease begins quickly, progresses at a high speed, while there is a strong intoxication of the body. The patient, as a rule, is infectious to a small degree. Pathologies are more susceptible to women, especially in the period shortly before menopause. Every third patient in the future faces relapses. Pathology itself has been known to mankind for a very long time, and descriptions of symptoms are present in the works of ancient authors. In 1882, for the first time, it was possible to isolate the pathogen in pure form in laboratory conditions. Among the scientists who have studied the source of erysipelas by their efforts, Cherkasov and Halperin deserve special attention.
Currently, medicine knows about two dozen types of streptococci. Among them, the categories A to G are most often found and most dangerous for humans. It is the beta-hemolytic forms that belong to the first group that can provoke erysipelas in children and adults. They also cause other pathologies - pustular skin diseases, soft tissue lesions, phlegmon. Streptococcus can cause osteomyelitis, provoke the appearance of a boil or cause an abscess. Against the background of infection of the body, angina, bronchitis or scarlet fever is possible. Streptococcus beta-hemolytic type can cause toxic shock, cause rheumatism, pharyngitis. Any form of streptococcus classified as category A can cause erysipelas.
Pathogen: know the enemy in person
Bacteria that provoke erysipelas are round in shape, arranged in chains, in rare cases - in pairs. The bacterium can be divided into two parts - it is precisely by this mechanism that the colony multiplies. In pus, sputum, and other substances in the external environment, streptococcus is able to live for months. The causative agent does not die at low temperatures, is resistant to freezing. Only some disinfectants, heat and direct sunlight inhibit the vital functions of bacteria.
Causing erysipelas, streptococci are sensitive to antimicrobial agents. Such bacteria get antibiotic resistance, but slowly enough. In the process of life, microorganisms generate exo-, endotoxins, enzyme compounds that adversely affect the human body. If a bacterial colony grows in a highly nutritious environment, the microorganisms are drop-shaped and shine. Matte colonies are possible with uneven edges and gray shades. There are also transparent, convex forms of life.
Where the trouble came from
Erysipelas is a disease that is easiest to catch from an already sick person or carrier of infection. It is such people who belong to the category of "reservoirs" - as it is called in the medical literature. The bacterium can penetrate the skin from an external source, an infectious focus. Long-term use of steroid hormones, as statistics show, creates the conditions for rapid infection and active development of a streptococcus colony. It is known that the risk of erysipelas is higher if a person is sick with tonsillitis in a chronic form, if the teeth are affected by caries or diseases of the ENT organs are observed. An open path to the body for infection is skin injuries, cracks, abrasions, wounds. Similar damage to the mucous membranes is another option for the penetration of streptococcus. Damage to the nasal cavity, genitals - all this provokes the risk of erysipelas. Pathology is more often transmitted by contact or by airborne droplets.
It is known that the causative agent of erysipelas is found on the skin, mucous membranes of many healthy people, while the disease does not start. Such people in medicine are called carriers of bacteria. The tendency to relapse in erysipelas is presumably due to a hereditary factor. Higher risk of inflammatory processes for women during a period when reproductive function gradually fades away. The danger is increased if a person is sick with venous insufficiency, a variety of edema, lymphostasis have been identified. The likelihood of infection is greater if there are fungal colonies on the feet, as well as in the case of trophic ulcers.
Features of the onset of the disease
Usually erysipelatous inflammation of the skin is noted on the legs, face. More rarely, the disease affects the hands, body, genitals and their skin, mucous membranes close to them. Inflammation is localized in the dermis, that is, the main skin layer responsible for the correct trophism, as well as bearing a supporting function. Derma is rich in fibers, capillaries, which provides harmful microorganisms with everything necessary for active life. The inflammatory process during infection is both infectious and allergic. Substances that produce colonies quickly lead to intoxication of the body, which gives rise to fever.
Erysipelas begins due to aggressive toxic effects on organic tissues of enzymes, compounds, antigens secreted by streptococci, active substances produced by colonies. At the same time, small arteries are harmed, vessels that provide lymph flow, veins suffer. Usually, inflammation is either serous or serous-hemorrhagic. Human skin antigens are to some extent similar to streptococcus polysaccharides, which causes an autoimmune reaction - body antibodies attack their own tissues. All this becomes a cause of damage to the vascular tissue, skin, blood begins to coagulate inside the vessels, the capillary walls are destroyed, hemorrhagic syndrome is observed in the damaged area. Vasodilatation leads to hyperemia of the skin, serous, hemorrhagic vesicles are formed.
Lesions: Numerous
Erysipelas of the skin is accompanied by the release into the bloodstream of substances produced by colonies of microorganisms, as well as other active compounds, including histamine. This contributes to the flow of the form of the disease into hemorrhagic. At the same time, there is a lack of lymphatic current, which causes swelling of the legs. Without adequate treatment, the vessels are replaced by fibrin, and this is the foundation for the appearance of elephantiasis. An infectious allergic focus actively consumes glucocorticoids, against the background of which adrenal insufficiency is possible. This leads to improper protein metabolism, water-salt reactions.
Symptoms of erysipelas are more likely to manifest if genetic characteristics cause low resistance to the disease. In some people, the body is characterized by hypersensitivity to substances that produce staphilo-, streptococci. The risk of getting erysipelas increases if the immune system weakens. This is observed against a background of various factors. It is necessary to take into account the decrease in all forms of natural defense - local, cellular, as well as humoral factor and non-specific. The risk group for erysipelas includes those suffering from metabolic disorders, the balance of active biological compounds, as well as patients who have identified malfunctioning of the neuroendocrine system.
Disease: what happens
Before starting treatment for erysipelas, you should understand what class the pathology belongs to. Modern doctors distinguish seven forms of the disease:
The specified classification is based on the characteristics of the affected areas.
Based on the severity, we can talk about a mild disease, moderate and severe. Also, erysipelas is primary, repeated, relapse. Forms can be localized strictly in one place, widespread, focal migration, metastases are possible. The common form begins with a localized, but gradually the focus spreads beyond the primary region. Migration is expressed by the formation of new affected areas in the vicinity of existing ones, and there are connecting elements between them. Erysipelas metastases are called new areas of inflammation formed far from the primary. The causative agent of the disease provokes just such a form if it spreads through the body with blood flow. This form is the most severe and dangerous, high probability of blood poisoning.
Terminology Dedicated
If the symptoms of erysipelas are worried for the first time, they talk about the primary disease. When a situation repeats in the same area, a second is diagnosed. At the same time, it is taken into account that at least two years have passed between cases. Repeated erysipelas can be established if the time period is less than two years, but the area of localization is different. Relapses are an option when repeatedly inflammatory processes appear in the same area.
With mild erysipelas, the patient is disturbed by a fever, but rather short-term. Poisoning of the body manifests itself in mild symptoms. More often this is observed if the disease has developed in an erythematous form. If the fever lasts up to five days, they speak of an average level of severity. The patient suffers from severe symptoms of poisoning. So the erythematic, erythematous-bullous varieties can manifest themselves. If complications of erysipelas are observed (for example, sepsis), and the disease itself is diagnosed in a hemorrhagic form, the pathology is difficult to tolerate. The temperature often rises to 40 degrees, poisoning manifests itself as very vivid symptoms. There is a chance of toxic shock.
If the disease gives metastases or proceeds in a migrating form, it is characterized by a severe course. With proper therapy, started in a timely manner, it is possible to develop an erased form that is interrupted. Both options are found in practice at a low frequency.
First manifestations
The incubation period of streptococcus is up to five days. Usually the disease has an acute onset, you can accurately indicate at what time the first symptoms appeared. The patient complains of a headache, fever is observed, the patient weakens, muscles and joints ache, chills, feels sick and vomits. Perhaps a convulsive state, in some - disorders of consciousness. When toxins produced by streptococcus colonies enter the circulatory system, poisoning of the body develops. In parallel, local signs of the disease gradually appear. In some cases, their development takes up to ten hours. As a rule, with erysipelas, swelling is one of the typical symptoms indicating a lesion by bacteria.
A distinctive feature of the agent is its excellent survival in lymphatic flow. It is here that the conditions for the propagation of colonies are optimal, which leads to an almost instant spread of pathological microorganisms into the lymph nodes on the periphery. This causes an increase in inflammatory foci. Symptoms of poisoning the body worry about a week, the whole period of the patient is in fever. In rare cases, symptoms last longer. Any of the forms is associated with inflammatory processes in the lymphatic system, nodes and blood vessels suffer.
Some features
Most often, doctors diagnose erysipelatous inflammation of the legs, although lesions of the hands and face are possible. Markedly less frequently, foci form on the body, mucous membranes, and in the genital area. There is a chance of breast damage. In the lower limbs, the disease is due to a violation of the integrity of the skin. Usually this is provoked by a bruise, an injury. Often the disease is observed against the background of fungal infection of the nails, feet. The risk of getting sick is higher if there is poor blood circulation in the legs , diabetes mellitus, and excess weight have been diagnosed. More often erysipelas bother smokers and those suffering from varicose veins. Chronic infectious foci in various tissues and organs can cause the disease.
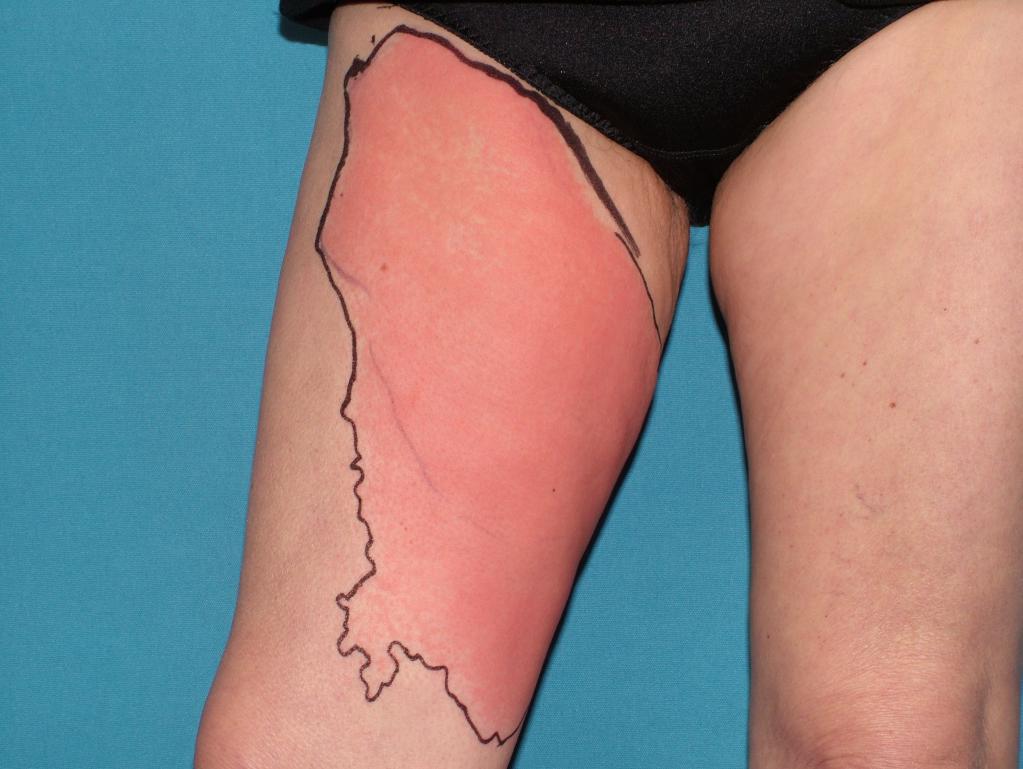
Erysipelas of the leg manifests itself as pain in the affected area. Patients describe him as bursting. It burns in the leg, the limb swells, the skin turns red. Already by these signs, you can suspect a mug and urgently consult a doctor. In most cases, the disease is prone to relapse, the risk of this form is especially high if the pathology is not properly treated. In an increased danger, people suffering from infectious inflammatory processes in the tissues of the body, especially if they occur in a chronic form. If relapses are frequent, over time the skin changes, the structure of the fiber is disrupted, which leads to elephantiasis, lymphostasis.
Age and disease
In the elderly, treatment of erysipelas is often required on the face. The disease manifests itself as a severe pain syndrome, accompanied by a risk of gangrene. Pathology regresses very slowly, it is characterized by a protracted course. But in childhood, the disease is rare and usually easy. Pathology can occur in various areas of the body, but the prognosis is almost always favorable. More often diagnosed with erythematic erysipelas. The disease is somewhat more severe at one year of age or younger. Inflammation is often localized on the face, in areas of diaper rash, but can spread to other parts of the body. If the form is phlegmonous, sepsis is highly likely. If a person is affected, there is a risk of meningitis.
Streptococcus can get into the umbilical wound of an infant. This erysipelas is characterized by the severity of the course, quickly covers the back, arms, legs, buttocks, accompanied by a pronounced general poisoning of the body. The child has a fever, possibly a convulsive state, blood poisoning. It is among newborns that the probability of a fatal outcome is especially high.
Doctor, why am I sick?
Before starting treatment, a diagnosis should be made. Erysipelas are established by analyzing the patient's complaints, medical history and the results of various studies. Do not underestimate the importance of professional diagnosis, as the symptoms of erysipelas are similar to some other skin pathologists. In the general case, differential diagnostics are done, but sometimes bacteriological analyzes are necessary. Usually these are prescribed if the doctor doubts the diagnosis.
The highest likelihood of confusing erysipelas and dermatitis, erythema, lichen. It can be assumed that it is erysipelas, if the disease begins acutely, the lymph nodes are enlarged, and the pain syndrome weakens at rest. Laboratory studies show streptococcus, allow you to determine which antimicrobial compounds it is sensitive to. Correctly performed diagnosis helps to choose the optimal treatment program, although the method is not always effective. True, it is worthwhile to understand that it is undesirable to use folk remedies for erysipelas. The disease can cause serious complications and even death if you do not start the right treatment, including antimicrobial drugs of your choice. There is currently no specific technique for detecting erysipelas in laboratory conditions, but it is known that with a disease in the blood, the concentration of leukocytes increases and ESR increases.
What to do?
Normally, with erysipelas, antibiotic treatment is practiced. The patient undergoes a course at home, regularly visiting a doctor to monitor the results of the selected program. If the disease is severe, relapse, complications, concomitant pathologies are observed, it is possible to place the patient in a hospital. It is recommended to undergo inpatient treatment if the erysipelas affects a child or an elderly person. The mode is chosen, focusing on the localization of the disease. Special nutrition is not required. The doctor prescribes antibiotics - this is the main group of drugs against erysipelas. Penicillins of natural and artificial origin show the best results. Well established "Amoxicillin", "Oxacillin." Doctors often advise staying on Ampicillin or Benzylpenicillin.
, , (, ). , , , . – .