Unfortunately, many have no idea how easy it is to get syphilis. For this, it is not always necessary to enter into close physical contact or sexual relations with the patient. Syphilis of the throat can be easily infected by drinking water from one glass with the patient, eating from a common plate, using the same cutlery or cosmetic.
But how to recognize this disease? What causes her? How is it going? What are the implications? What is known about the modern diagnosis and treatment of this serious disease? We will reveal the answers to all questions below.
How is the disease transmitted?
Syphilis in the throat is a consequence of not only the sexual, but also the domestic way of transmitting the infection. It is important to remember that, regardless of form, it can be transmitted through infected blood from the expectant mother to the fetus. In this case, they speak of a congenital type of disease.
Can there be syphilis in the throat, larynx, tongue? Yes, and this form of the disease is relatively easy to get infected. Here are the main ways to transmit it:
- Unprotected oral sex (in this case, both partners become infected).
- Kiss (in particular, infection occurs when the tongue penetrates).
- Unfair treatment of medical instruments (in this way you can become infected with syphilis, for example, in questionable dental clinics).
- Use of common utensils, cutlery, hygiene items.
- Smoking one cigarette with an infected person.
Is transmission possible in the domestic way?
But it should be noted that syphilis of the throat through household contact is transmitted much less often than through sexual contact. Such infection through dishes, cigarettes, common spoons and forks is possible only if there are three factors:
- Damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, larynx, and throat.
- For some reason, weakened immunity.
- The presence of chronic serious illnesses.
Signs of Congenital Disease
Laryngeal syphilis can be congenital. In this case, the first symptoms may appear already on the 5-6th month of the baby's life. The disease is detected by the following signs:
- Chronic runny nose.
- The presence of damage to the mucous membrane of the pharynx.
- Cracks in the corners of the lips, which eventually change into scars.
These signs are characteristic of the second stage of acquired syphilis.
The congenital type of the disease begins to manifest itself more actively in adolescence and college age. These are symptoms characteristic of the third stage of acquired syphilis. To them are added chronic diseases of the nasal, oral cavity, pharynx, and eyes. In some cases, the functioning of the sensory organs may be impaired.
First common symptoms
Recognizing syphilis in the throat at the initial stage of the development of the disease is quite difficult. Basically, it is discovered purely by accident. The patient has the following:
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat.
- A hoarse, hoarse voice.
- Labored breathing.
- Pain in the ears.
- Double epiglottis.
- The appearance of wounds on the black-fold folds.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- The appearance of fistulas on the mucous membranes.
Secondary General Symptoms
Then the symptoms of syphilis in the throat begin to manifest themselves more clearly:
- The mucous membrane lining the throat becomes bright red, covered with white spots. The latter are distinguished by even outlines, somewhat rise above the mucosa itself.
- In rare cases, mucosal tissue defects are observed.
- Diagnosed with respiratory failure. In particular, due to the appearance of scars, ulcers with syphilis. Such symptoms may resolve themselves over time to relapse in the future.
- Red or cyanotic tissue seals are a mixture of mucosal cells secreted by lymph and blood. Appear both over the larynx and in the area of the respiratory passage.
- The appearance of the so-called syphilitic nodes, which are in the same form for months, after which they disintegrate, leaving scars on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Specific symptoms
Symptoms of syphilis in the throat may also vary slightly depending on the form of infection that struck the patient:
- Sore throat type. In this case, syphilis is manifested by symptoms of unilateral tonsillitis. The patient may complain of sore throat during swallowing, a slight increase in body temperature, the development of lymphadenitis.
- Erosive type. Ulcers with syphilis (another name - erosion) characteristically appear on one tonsil. They are distinguished by round edges, covered with gray matter. When probing, it seems that there is cartilage at the bottom of such an ulcer.
- Ulcerative type. This form of the disease is characterized by a large number of ulcers on the surface of the tonsils of the palate. They are also round, with a dirty gray tint to the bottom. Additionally, the patient may notice an increase in body temperature, sore throat - both spontaneous and only when swallowing. Symptomatically, this type of syphilis is similar to a peritonsillar abscess.
- Pseudoflegmonous type. It is noted that this kind of syphilis is difficult to diagnose, since the symptoms are almost identical to peritonsillar phlegmon. Syphilis begins to manifest itself only in the second stage. Trial autopsy, puncture of ulcers in the sky, in the mouth do not give any results. The patient's body temperature is kept steadily high.
- Gangrenous type. This type of disease mainly develops on the mucous membrane of the tonsils. Gangrene appears, less often - granulation growths. The patient's well-being quickly worsens: his body temperature rises sharply, he suffers from fever, and sweating increases. As for the tonsil and the areas of tissue around it, they undergo gangrenous decay.
- Erythematous-opalescent type. Hyperthermia of the mucous membranes of the pharynx, tonsils and palate is observed. The disease spreads, much like scarlet fever: only certain sections of the mucosa can be captured, sometimes a sore throat is felt at night. Syphilis can develop even without an increase in body temperature.
- Hypertrophic type. The spread of the disease goes to the lymphadenoid ring of the pharynx. Tonsils, lingual and palatine, suffer most. The patient complains of a cough that cannot be neutralized by usual means, hoarseness.
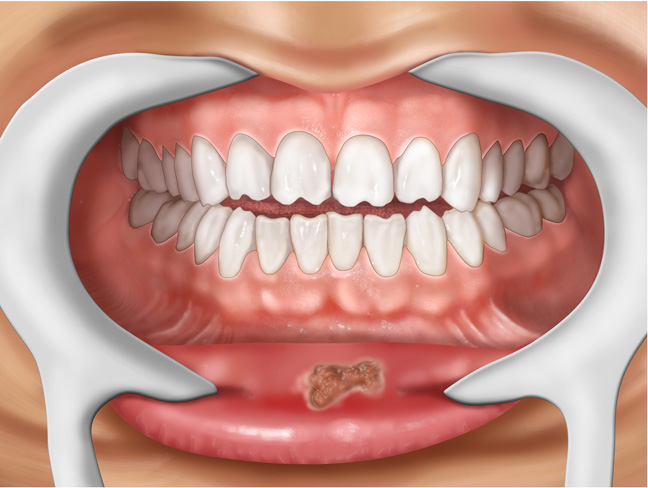
First stage
Ulcers in the sky, in the mouth can not always speak precisely about syphilis. These are signs of a different kind of disease. Let's look at how syphilis manifests itself in the initial stage.
The penetration of pale treponema (syphilitic pathogen) is accompanied by the appearance of hard chancres in the mouth - seals of white or pinkish color with erosion in the center, which can be up to 2 mm in diameter. In addition to this patient, nothing bothers.
Then, such seals spread to the lips, gums, palate, tongue, and inside of the cheeks. As for ulcers under the tongue, they look more like narrow alkalis - due to the formation of folds on the mucous membrane. If they are somewhat stretched, then the formation will take a round ulcer.
Several or just one chancre can form. Then, among the signs of the disease, a new one appears - enlarged lymph nodes.
Second stage
Here, in addition to ulcers in the tongue (the causes and treatment of which may be different than syphilis), chancres in the palate and gums in some cases also show characteristic skin rashes. In place of the chancres, roseola is formed - painless pink-colored spots that grow over time, merge, transforming into edematous stomatitis. In these roseola treponems, the causative agents of syphilis, are also “stored”.
After a while, they disappear. However, if you do not turn to proper therapy, the disease returns again with a vengeance. Papules (dense nodes of tissues) appear, which merge, turn into plaques.
Such nodules peel off at their edges and externally have an indefinite shape. They can merge into chains and patterns on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. The location is asymmetrical. In addition to papules, purulent vesicles called pustules also appear.
At this stage, the patient becomes dangerous to others. He is urgently placed in a hospital where a comprehensive treatment is carried out. If the disease is not treated, syphilis from the throat flows into the larynx, into the upper respiratory tract.
Tertiary stage
It develops several years after infection. Dense nodes and tubercles form in the mouth. They form within 3-5 months. In the sky, the patient’s tongue, seals are noticeable, which are destroyed, turning into ulcers. The wounds are then drawn into star-shaped scars.
As a result, the oral cavity is strongly deformed. A gap may occur between the mouth and nasal cavity, maxillary sinuses. At this stage, the patient’s tongue becomes numb and stops moving. Accordingly, a person can no longer speak normally. This defect is not eliminated even with a complete cure for syphilis. To return the possibility of speech, you need to either have plastic surgery or insert a prosthesis.
Diagnostics at the first stage
The most successful option will be the timely detection by the doctor of a hard chancre in the patient's mouth. However, many doctors lack experience in recognizing syphilis. Often they are confused with tuberculous ulcers, various peptic ulcers affecting the tonsils. As a result, the wrong treatment is prescribed. Therefore, not only a narrow specialist, but also a therapist should know what syphilis looks like in the throat.
To identify the disease at the initial stage, the patient undergoes a test for a serological reaction. He is prescribed tests for the presence of pale treponemas in the oral cavity.
Diagnostics in the second stage
It is also not easy to detect syphilis of the throat in the second stage of the disease. It is highly likely to confuse its manifestations with the symptoms of any type of tonsillitis, herpes, leukopathy, tuberculosis, and malignant tumors in the oral cavity.
For an accurate diagnosis of syphilis, the patient needs to undergo a test for a serological reaction.
Diagnostics in the third stage
Here again, the diagnosis of syphilis is complicated by the similarity of the signs of this disease with others: tuberculosis, oncological pathologies. To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is sent for a biopsy and radiography of the lungs.
Directions of treatment
It should be noted that syphilis is difficult to treat. Therefore, treatment at home is not allowed - constant monitoring by the attending physician is necessary.
The main direction of therapy is to resist the destruction of the larynx. For this, both intravenous and intramuscular antibiotics are prescribed, as well as such additional therapy as inhalations, rinses, immunomodulators, physiotherapeutic measures.
The choice of the main antibacterial agent in relation to a particular patient is individual. It depends on the cause of the disease, and the characteristics of its course. To eliminate treponema, use penicillin, macrolides, cephalosporin. If the disease is launched to the last stage, bismuth preparations are prescribed.
If the effect of treponem has already been transferred to the nasal cavity and pharynx, then patients are prescribed solutions of potassium permanganate or sodium bicarbonate. With their help, do washing, facilitating the condition.
They also turn to the local treatment of the throat with an alkaline-oily mixture that eliminates dryness and discomfort. It is used for inhalation. An additional remedy is a penicillin solution in the form of a spray.
Symptomatic therapy includes the use of antipyretic drugs, probiotics, drugs to stimulate the work of the immune forces.
The main direction of prevention of any form of syphilis is the exclusion of accidental unprotected sexual intercourse. With any type of sexual contact, it is necessary to use barrier contraceptives. Also, with responsibility, approach the choice of medical clinics, especially dental ones. Make a habit of using only your dishes, hygiene products.