The drug belongs to the therapeutic group of steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To use the solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration, there is a wide range of medical indications.
The medicine is produced in several dosage forms. What indications does Prednisone have intravenously?
Structure
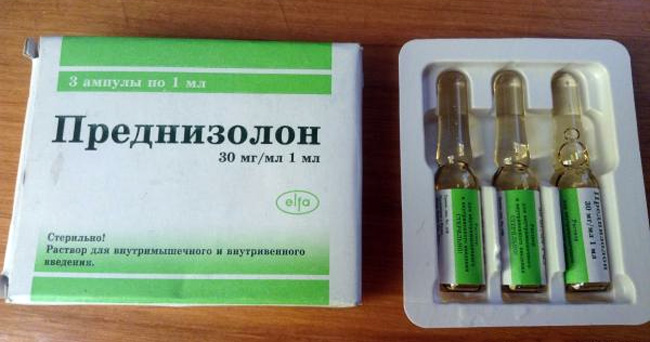
The main active component of the drug is the substance of the same name, its concentration in 1 milliliter of the solution is 30 mg. In addition, the structure of the medication includes additional components:
- pyrosulphuric acid salt;
- caustic soda;
- nicotinic acid amide;
- disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid;
- water.
The solution for parenteral use is contained in 1 ml glass ampoules. Ampoules are placed in plastic packages of 3 pieces.
Pharmacological properties
"Prednisolone" is considered a synthetic substitute for the natural hormone, which refers to glucocorticosteroids. After the injection, the active substance has several positive effects:
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- immunosuppressive effect.
In addition, the active component of the solution for reduces the synthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone in the pituitary gland, helps to increase the rate of protein breakdown in the body.
After using the drug, the active component accumulates in the blood and spreads evenly in the tissues, where it has therapeutic effects.
In what cases is prescribed an injection of prednisone intravenously or intramuscularly
There are a number of medical indications in which the solution is used as an emergency therapy drug, they include:
- Shock conditions, which is accompanied by a critical decrease in systemic blood pressure.
- Anaphylactic shock (an allergic reaction, a state of increased sensitivity of the body).
- Bronchial asthma (chronic inflammation of the respiratory system, which is characterized by asthma attacks).
- Asthmatic status (a severe, life-threatening complication of bronchial asthma, usually resulting from a prolonged non-stopping attack).
- Cerebral edema after injury.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (damage to the connective tissue, which is caused by a common immunocomplex lesion of the connective tissue and its derivatives).
- Rheumatism (a systemic inflammatory disease of the connective tissue with the primary localization of the pathological process in the membranes of the heart).
- Rheumatoid arthritis (autoimmune progressive lesion of connective tissue of inflammatory origin with joint damage).
- Acute hepatitis (inflammatory damage to the liver of various origins with the death of a large number of liver cells and the occurrence of functional organ failure, up to the hepatic coma).
- Thyrotoxic crisis (the most serious, life-threatening complication of diffuse toxic goiter).
In addition, the prednisolone solution is used to reduce the intensity of inflammation and cicatricial changes in tissues after a burn with acids and alkalis.
Limitations
If it is necessary to use the solution for parenteral administration according to indications, individual intolerance to substances is considered a significant contraindication to its use.
From the instructions for use with Prednisone, it is known intravenously that in other situations, several pathological conditions of the body are distinguished in which the medication is not used:
- Peptic ulcer disease (a chronic disease for which a characteristic feature is the presence of periods of remission (a period of time during which the disease does not appear) and exacerbations; and is accompanied by the formation of an ulcer (damage to the mucous membrane) in the stomach or duodenum).
- Gastritis with increased acidity (inflammation of the mucous membrane (inner) of the wall of the stomach).
- Diverticulitis (a bowel disease characterized by inflammation of the blindly ending protrusion of its wall).
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis (a type of chronic inflammatory disease of the large intestine of unknown etiology).
- Herpetic infection (a chronic infectious disease that is provoked by the herpes simplex virus and is characterized by damage to the integumentary tissues and nerve cells).
- Herpes zoster (a disease caused by the herpes virus).
- Chickenpox (an infectious disease with an airborne transmission, characterized by fever, as well as rashes on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of small vesicles with transparent contents).
- Amoebiasis (anthroponous invasion with fecal-oral transmission mechanism, which is characterized by chronic recurrent colitis with extraintestinal manifestations).
- Measles (acute illness, which manifests itself with a temperature of more than 39 degrees, as well as severe intoxication, cough and rash).
- Strongyloidosis (parasitic, chronically proceeding, anthroponous infection).
- Systemic mycosis (a number of severe diseases caused by a fungus).
- HIV (a slowly progressive disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus).
What diseases are still forbidden to use the drug? From the instructions for use with Prednisoloneum, it is known intravenously that the solution is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- AIDS (late manifestation of infection of the body with the human immunodeficiency virus).
- Time before vaccination.
- Myocardial infarction (one of the clinical forms of cardiac ischemia, proceeding with the development of ischemic necrosis (local tissue death) of the myocardium (the muscle middle layer of the heart, which makes up the bulk of its mass), due to the absolute or relative insufficiency of its blood supply).
- Hypertension (a chronic ailment characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure to high numbers due to a violation of the regulation of blood circulation in the human body).
- Hypertriglyceridemia (a disease in which the level of triglycerides in the blood rises).
- Diabetes mellitus (a thyroid disease characterized by absolute or relative insufficiency in the body of insulin - the hormone of the pancreas, resulting in hyperglycemia).
- Thyrotoxicosis (a process that occurs in the human body due to a persistent increase in the number of thyroid hormones).
- Hypothyroidism (a syndrome that develops with a low concentration of thyroid hormones, is one of the most common diseases).
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease (a disease in which there is an increased content of glucocorticoid hormones in the blood of the adrenal cortex).
- Pregnancy.
- Osteoporosis (a progressive disease of the skeleton with a decrease in bone density and an increased risk of fractures).
- Myasthenia gravis (a neuromuscular lesion that is caused by pathological fatigue of the striated muscles).
- Poliomyelitis (an infectious disease characterized by damage to the gray matter of the spinal cord by poliovirus and pathology of the nervous system).
Before using the solution, the doctor should make sure that there are no contraindications. How to administer prednisone intravenously?
How to use the drug
The solution is intended for parenteral administration, it can be administered intramuscularly or intravenously drip in compliance with the rules of antiseptics, which are aimed at eliminating the infection. The dosage regimen of the drug depends on the indications.
How to administer prednisone intravenously? In shock conditions, the medication is injected jet to normalize the level of systemic blood pressure. Then, a maintenance concentration is applied intravenously drip.
In the absence of positive dynamics, the solution can be reused jet. A single concentration ranges from 40 to 400 milligrams.
In acute insufficiency of the adrenal glands, 100-200 milligrams are prescribed, the duration of treatment can be 15 days.
In acute thyrotoxicosis, it is recommended to take from 200 to 300 mg of the drug for 2-3 applications, the duration of treatment is about 6 days.
With asthmatic status, on the first day, up to 1000 mg of Prednisolone is used, then the dosage is regularly reduced to maintenance.
In acute liver and kidney disease, the daily dosage is 25-75 milligrams. The maximum dosage of Prednisoloneum intravenously can reach 1000 mg per day.
In acute hepatitis, chemical burns after the use of aggressive compounds, the daily oral concentration depends on the severity of the pathology, it varies from 75 to 100 milligrams of the drug, the duration of treatment varies from 15 to 18 days.
In addition, it is known that with bronchial asthma, "Prednisolone" is prescribed intravenously from 60 mg, do not mix with saline, the duration of therapy is from 3 to 16 days.
After the end of the emergency treatment, if possible, they switch to the oral use of the drug in the form of tablets. Abrupt abolition of the use of the drug is excluded, the dosage is reduced gradually.
"Eufillin" and "Prednisone" are used intravenously for asthma. The proportions of the drugs, the volume of saline and the dosage are determined by the doctor.
In many situations, the concentration and mode of use is determined by the doctor individually.
Side effects
When using the solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration of the drug, the appearance of negative reactions to Prednisolone intravenously from various organs and systems is likely:
- Vomiting.
- Pancreatitis (a group of diseases and syndromes in which damage to the pancreas is observed).
- Loss of appetite.
- Arrhythmia (one of the most common cardiological diseases, in which the heart rhythm increases or decreases under the influence of external factors).
- Bradycardia (a decrease in heart rate (slowing the pulse) of less than 60 beats per minute in adults at rest).
- Arterial hypertension (a disease in which there is a steady increase in blood pressure).
- Hypercoagulation (a condition in which the activity of the coagulating blood system is increased).
- Thrombosis (the formation of blood clots inside the blood vessels that interferes with the free flow of blood through the circulatory system).
- Delirium (a mental disorder that occurs with confusion, impaired attention, perception, thinking and emotions).
- Hallucinations.
- The development of euphoria.
- Depressive disorders.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Insomnia (disruption of the onset and maintenance of sleep).
- Steroid diabetes mellitus (an endocrine disease that occurs subsequently with an increased concentration of hormones in the blood of the adrenal cortex and impaired suppression of their hormones.
What other adverse reactions can the drug cause?
Side effects of Prednisone intravenously are as follows:
- Delayed sexual development.
- Cataract (a pathological condition characterized by clouding of the lens of the eye and provoking various degrees of vision damage until it is completely lost. Clouding of the lens is caused by denaturation of the protein that is part of it).
- An increase in intraocular pressure with a violation of the optic disc.
- Corneal hypotrophy (a general definition of a group of diseases characterized by changes in the structure of the cornea, which is accompanied by a progressive decrease in visual acuity).
- Exophthalmos (a disease that is caused by a pathological protrusion of one or both eyes, and the size of the eyeball remains the same).
- When using the drug in the tissue of the eye, head or neck, it is possible to deposit crystals of the active component in the structures of the eye.
- Weight gain.
- Hypocalcemia (a condition that develops in the human body due to a violation of the electrophysiological process).
- Loss of potassium salts with the development of arrhythmia.
- Osteoporosis (a progressive disease of the skeleton with a decrease in bone density and an increased risk of fractures).
- Pathological ruptures of tendons and muscles.
- Deterioration of the healing of the epidermis in case of its violations.
- Petechiae (point rashes on the skin, which are no more than three millimeters, hemorrhagic in nature, and having a circle shape).
- Steroid acne (the appearance of acne on the skin indicates a malfunction of the sebaceous glandular apparatus).
- Thinning of the skin.
- Dryness.
- Rashes on the skin.
- Itching
- Urticaria (a disease manifested by a rash, the main element of which is a blister, i.e. a clearly limited area of skin edema).
- Quincke's angioedema (a reaction to the effects of various biological and chemical factors, often of an allergic nature).
- Anaphylactic shock (an acute allergic process that develops in a sensitized body in response to repeated contact with an allergen and is accompanied by a violation of hemodynamics).
In the field of application of the drug, it may appear to decrease the sensitivity of the skin, the development of tingling, burning, and hyperemia of the tissues.
The severity and nature of the negative effects depends on the concentration and duration of use of the solution for parenteral use. "Prednisolone" with glucose is not used intravenously, since the drug itself is made ready-to-use.
Features
Before starting Prednisolone therapy for parenteral administration, the doctor must make sure that there are no restrictions, and also draws attention to several nuances, which include:
- With prolonged treatment with a medication, an optometrist should be consulted, and laboratory monitoring of peripheral blood status should be regularly carried out.
- To reduce the likelihood of adverse reactions, potassium medications and antacids are prescribed in parallel.
- In people with a pronounced violation of the functional activity of the liver with cirrhosis, with hypothyroidism, the pharmacological effect of the drug is likely to increase.
- When treating in a situation of exposure to stress, dose adjustment of the solution is required.
- After myocardial infarction, Prednisolone can be used with extreme caution, since a violation of the connective tissue scar of the heart is possible.
- When using the medication, vaccination is not carried out.
- Mental disorders are considered the basis for regular medical supervision when using the medicine.
- When therapy is discontinued, especially in situations of increased pharmacological dosages, withdrawal syndrome may occur, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, lethargy, as well as lethargy, skeletal muscle stenosis, as well as an increase in the manifestations of the pathological process.
- When prescribing Prednisolone for infectious diseases, etiotropic treatment must be carried out, which is aimed at eliminating the source of the pathogen.
- The use of the drug in children requires regular monitoring of growth and physical development.
- The drug is not recommended for use by pregnant women.
- The active substance of the prednisolone solution can be combined with a large number of drugs of other pharmacological groups.
- You can not carry out work that requires increased attention when using.
How to replace Prednisolone tablets with injections? If the doctor prescribed a specific dosage form according to indications and contraindications, then it cannot be replaced.
In pharmacies, the solution "Prednisolone" for parenteral use is available only by prescription. It is forbidden to use it independently without appropriate medical prescription.
How to breed Prednisoloneum intravenously? The medication is a ready-made solution. You can not mix it with any injection solutions.
Generics
Similar substitutes in structure and pharmacological action are:
- Decortin.
- Prednisone
- Medopred.
- Betamethasone.
- Hydrocortisone.
- Dexason.
- Dexamed.
- Kenalog.
- Lemod.
- Medrol.
- Metipred.
- "Flosterone."
Before changing the medicine, you need to consult a specialist. What price does Prednisone have?
How to store the drug
The shelf life of the drug is 3 years. Prednisone should be kept in its original packaging.
Far from children, at a temperature of no higher than + 25 ° C. The price of Prednisolone varies from 30 to 120 rubles.
Opinions
Responses to the drug "Prednisolone" in injections are contradictory. On the one hand, many patients distinguish the drug as quite effective, on the other, they note that it has an extensive spectrum of adverse reactions and with prolonged use it provokes withdrawal syndrome.
In addition, some patients note that the injection is painful. Nevertheless, it is injections for children and adults that often very quickly neutralize the pathology.