Many of us associate the concept of "herpes" with a rash on the lips and do not attach much importance to it. However, the family of these viruses is quite numerous and insidious. To date, scientists have identified about a hundred types of herpes parasitizing in living organisms. The man "got" eight of them, including herpes type 6. This virus is present for life in 9 out of 10 people on our planet, but it manifests itself mainly in children.
The Human Herpes Virus Family
All eight herpes viruses are unusually similar in appearance. Sometimes, even under a microscope, they are difficult to distinguish. It is possible to distinguish them into separate groups only by reaction to certain antigens of their virion proteins, by the so-called antigenic properties of proteins, and also by the degree of homology (similarity) of their DNA. Some researchers distinguish
groups of herpes
viruses by the presence or absence of a large envelope. However, this method is not absolutely accurate.
Human herpes virus type 6, among other things, has 2 subtypes, A and B. Since their DNA is 95% similar, they were previously defined as varieties of the same type, but in 2012 they were isolated. In addition to 5% dissimilarity in DNA, they have other differences, in particular, clinical manifestations. However, in laboratories it is difficult to accurately identify them.
Type A
To date, it is known that type 6 herpes is considered more neurovirulent, that is, it is more often manifested in those who have diseases of nerve fibers, for example, multiple sclerosis. This ailment is absolutely not related to a person’s age. It occurs with equal frequency in both the elderly and young. There are cases of detection of multiple sclerosis even in infants. One of the causes of the disease is called infection with the herpes virus 6A of the nerve tissues of the brain and spinal cord. However, there are other reasons not related to herpes. The clinical manifestations of the disease depend on the site of infection, the stage of the disease, and many other factors. In addition, it is believed that the herpes 6A virus is more common in people with HIV. In laboratory conditions, it was found that in the bodies of macaques it dramatically enhances the development of AIDS. HIV viruses cannot penetrate into healthy cells until herpes viruses of type 6A have settled in them and conditions have been prepared for them. This feature has been adopted by scientists developing AIDS treatment methods.
Type B

Herpes type 6 B has been studied more widely. According to the results of numerous studies, it was found that it is the cause of a disease such as baby roseola. It is also called the sixth disease, pseudo-rubella or exanthema. This ailment occurs exclusively in children, and most often in babies up to two years of age. In adults, the body develops immunity to viruses. In the human body, viruses begin to react with immune factors, and when they get into the skin with blood, they damage tissues. The main symptom of the disease is a fever without any symptoms of a cold. In some children, it reaches 40 degrees and above. Sometimes the patient has an increase in lymph nodes. On the 3rd or 4th day, a rash of red or pink color appears on the back, abdomen and chest, turning pale with pressure. Within a short time, the rash spreads to the rest of the body. There is no itching and pain, the temperature drops. After a day, less often after a couple of hours, the rash passes without leaving any traces.
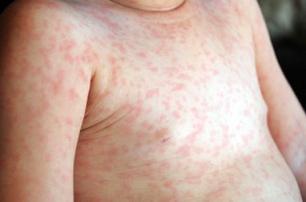
Herpes type 6 in adults
Most often, infection with the herpes 6B virus occurs in childhood. In adults, it is present in an inactive state, but under certain conditions its activity may resume. In particular, after organ transplantation, a number of patients may experience complications in the form of encephalitis or pneumonitis. Encephalitis is an inflammation of parts of the brain. Pneumonitis - damage to the walls of the alveoli in the lungs, which makes breathing difficult. Some researchers have linked bone marrow suppression with the 6B virus, leading to shortness of breath, anemia, and more serious consequences. In addition, they believe that this virus is responsible for the occurrence of chronic fatigue, manifested in fatigue, apathy, and depression. Herpes type 6 is associated with hepatitis diseases, with high sensitivity to antibiotics, with cancerous tumors and many others. However, all this has not yet been conclusively proven.
The mechanism of action of the virus
Herpes simplex virus type 6 has a dense membrane with receptors. The main component for them is the CD46 protein, which is located on the surface of almost all cells. Therefore, the virus so quickly and so easily "settles down" in the body. Once in the human body, he tries to penetrate into CD4 + cells, which differentiate into T-lymphocytes. The latter are able to suppress the immune response. Viruses, using this property, induce the phenotype of T-lymphocytes and bind to the protein CD46. Since this protein works in all cells except red blood cells, it is easy to imagine the possibilities of this herpes virus in our body. It was first discovered in 1986 in adult HIV patients. After a couple of years, it was isolated from infants with roseola. After a series of studies, the herpes simplex virus type 6 was found in people on all continents in almost every country.
Infection pathways
Since herpes type 6 is present in the vast majority of the world's population, it is very easy for an uninfected to get it. Most often this happens in infancy (from about the 3rd month of life), when maternal antibodies stop functioning in the child’s body. A small percentage of children become infected at birth if the mother of the newborn has caught this virus in the last months of pregnancy. If the child's parents have herpes, they can infect the baby through direct contact with him. Herpes 6 is known to be present in saliva. Therefore, the easiest way to get infected is by airborne droplets. You can infect a baby by kissing him or talking to him, bending over his face. Transmission of the virus with breast milk is not possible.
In addition, herpes 6 can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person directly with blood. There have been cases when the infection occurred through injections or when the patient was examined with non-sterile instruments.
Virus diagnosis
Unfortunately, with a primary infection, it is difficult to detect and accurately recognize the virus of this group. It is even more difficult to identify it during the inactive stage. It is determined by laboratory means. There are several methods for determining, depending on the manifestation of the infection. All of them boil down to immunological, biochemical and microbiological studies.
For example, they are used for myocarditis, which can be fatal. It has been found that herpes virus type 6 also causes it. Symptoms are absent, in contrast to myocarditis caused by other causes. In this disease, the virus is identified in a biopsy taken from the heart muscle, or in the blood. In case of doubtful results, additional studies are carried out. With pneumonitis, the virus is determined in sputum and blood serum, and chest x-ray data can serve as a reason for suggesting its presence. With hepatitis caused by the virus, liver and blood serum biopsy tests are performed . For various tumors and enlarged lymph nodes, special monitoring and serological tests are performed, as well as blood PCR. This test is widely used in the reactivation of the virus and in its inactive form.
Treatment
It is impossible to completely get rid of the herpes virus of any kind. The same can be said about herpes type 6. The treatment in this case consists in preventing the occurrence of relapses and maintaining the virus in an inactive state. The course and methods of treatment depend on the clinical manifestations of the disease. If it is a baby roseola, then special antiviral drugs are not prescribed. If the child has a strong fever, he is given antipyretic drugs such as ibuprofen or paracetamol and a heavy drink. Children with suppressed immunity are sometimes prescribed Foscarnet or Acyclovir. The last drug is currently considered not quite effective, so they began to replace it with "Ganciclovir." A very big minus of children's roseola is that it is often confused with ordinary rubella and the appropriate drugs are prescribed, although they are absolutely not needed.
Prevention
As you can see, the herpes virus is quite unpleasant. However, there is one positive point - the human body is able to develop immunity against it. Antibodies to this virus are produced during the first few days after infection. In the future, their number changes, but they are constantly present in the body. They are able to restrain herpes type 6. Symptoms of reactivation of the virus occur when a person has problems with the immune system or the body weakens other diseases. Therefore, the main preventive measure is all kinds of strengthening immunity. This includes physical activity, and the right way of life, and a balanced diet, and vitamin complexes. Another important point of prevention is personal hygiene.