Lymph nodes are a structural component of the human lymphatic system, and their inflammation leads to a variety of body dysfunctions. There are cervical, intrathoracic, femoral, submandibular, supraclavicular, popliteal, inguinal and axillary lymph nodes, which largely determine the functionality of all internal systems. If there is inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck in an adult or child, that is, they are enlarged, this is considered a dangerous symptom.
About diseases of the lymphatic system
A number of diseases are known to medicine, the development of which can be accompanied by acute lesions of the structures of the lymphatic system. They occur not only in adults, children can also become a victim of this dangerous symptomatology. Each disease is always combined with an inflammatory process, it requires diagnosis and history data collection.
Types of pathologies
The main ailments are:
- Regional lymphadenitis, which may be the result of trauma or excessive activity of pathogenic microorganisms. With inflammation, the lymph nodes increase in size, begin to hurt, and accumulate pus. In this situation, surgical intervention is required.
- Lymphangitis is a disease that is characterized by inflammation of the vessels of the lymphatic system, often spreading to the lower body. There is severe pain, severe swelling is observed, the usual functionality of the limbs is disrupted.
- Angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy is a dangerous pathology that is preceded by infections and viruses. This inflammatory process proceeds with complications that can lead to the development of cancer.
Lymphadenitis: a brief description of the pathology
Lymphadenitis (according to ICD-10 code L04) is a specific or non-specific inflammatory lesion of the lymph nodes. The disease is characterized by their soreness and increase, headache, weakness, malaise, fever. The inflammatory response in lymphadenitis is the barrier function of the lymphatic system, which limits the spread of infection throughout the body. Typically, lymph node disease occurs as a complication of inflammation of a certain location. Infectious pathogens enter the regional lymph nodes with lymph, which flows from the original purulent focus. In other cases, the disease occurs when the infection directly enters the lymphatic network through damaged mucous membranes or skin.
Causes of Lymphadenitis
The causative agent of this disease of the lymph nodes is the pyogenic flora - streptococci and staphylococci, as well as the toxins secreted by them. They penetrate the lymph nodes by hematogenous, lymphogenous or contact route. The initial focus may be purulent wounds, boils, panaritiums, carbuncles, erysipelas, phlegmon, trophic ulcers, caries, thrombophlebitis, osteomyelitis. Local inflammatory processes are often accompanied by a regional form.
What is the cause of lymph node disease in children? This disease is often associated with influenza, chronic tonsillitis, otitis media, childhood infections, and skin diseases. The cause of specific lymphadenitis are the causative agents of syphilis, tularemia, tuberculosis, gonorrhea, plague, actinomycosis, anthrax, etc.
What are the main symptoms of lymphadenitis?
An acute nonspecific process begins with soreness in the region of regional lymph nodes and their increase. With hyperplastic and catarrhal forms, enlarged nodes are easily palpated, their pain is insignificant, general disorders are weak.
When suppuration, the node becomes painful and dense, intoxication develops - loss of appetite, fever, headache, weakness. Local manifestations are growing - edema and hyperemia in the area of the affected node, its contours become fuzzy. If the formed abscess is not opened on time, pus may exit to the outside or to neighboring tissues.
Lymphadenitis (according to ICD-10 - L04) in children passes with high fever, loss of appetite, malaise, and sleep disturbance.
Treatment of a pathology such as lymphadenitis
Hyperplastic and catarrhal acute lymphadenitis is usually treated conservatively. Antibiotic therapy is carried out based on the sensitivity of the flora, vitamin and UHF therapy. With a purulent process, it carries out surgical intervention, during which pus is removed, sanitation and drainage of the lesion are performed. Active detoxification treatment is also prescribed. In chronic disease of the lymph nodes of a non-specific type, therapy of the underlying disease is required.
A disease of the lymphatic system called lymphangitis
Lymphangitis is an inflammation of the lymphatic capillaries and trunks of an acute or chronic nature that occurs a second time, with purulent or inflammatory processes in the body. Lymphangitis is accompanied by painful swelling and flushing along the inflamed vessels, regional lymphadenitis, edema, fever, chills, weakness. With this disease of the lymph nodes, lymph vessels of different depths of localization and caliber can be affected. Most often, lymphangitis of the extremities is observed, which is explained by their frequent microtrauma, a large number of microbial pathogens and features of lymph circulation.
Causes of lymphangitis
The disease occurs a second time, against the background of a deep or superficial purulent-inflammatory focus - a boil, an infected wound or abrasion, an abscess, phlegmon. The main pathogens in this case are beta-hemolytic streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, sometimes Proteus and Escherichia coli. Specific lymphangitis is caused by the presence of tuberculosis in the patient.
Microbial agents enter the interstitial space from the focus, then into the lymphatic capillaries, and through the lymphatic current to large lymph nodes and vessels. Reactive inflammation of the vascular walls is expressed in edema of the endothelium, an increase in its permeability, the occurrence of exudation, intravascular thrombosis, prolapse of fibrin clots. Such changes provoke lymphostasis - a disorder of local lymphatic circulation. With the progression of inflammation, purulent lymphangitis and thrombus melting occur.
Symptoms of a pathology called lymphangitis.
With this pathology, intoxication of the body is significantly pronounced, which usually accompanies a severe inflammatory process. The patient has fever, chills, sweating, headache, weakness. Reticular lymphangitis occurs with the appearance of severe hyperemia of the skin surface around the infectious focus (wounds, abscess) with a reinforced mesh pattern on the background of erythema. According to the clinical picture, lymphangitis resembles an erysipelas, but redness differs in vague borders, uncharacteristic of erysipelas.
A local sign of lymphangitis is the presence of red stripes on the skin along the lymph vessels passing to the regional lymph nodes. In this case, swelling, soreness and tightening of the cords, tension of the surrounding tissues quickly develop.
With deep lymphangitis, hyperemia is not observed, but pain and swelling in the limbs quickly increase. A sharp pain is also noted, lymphedema develops.
The symptomatology of chronic lymphangitis is usually erased and is characterized by persistent edema due to blockage of deep lymphatic vessels and lymphostasis.
How to treat enlarged lymph nodes in this case?
What is the treatment for lymphangitis?
With acute lymphangitis, the elimination of the main focus is necessary, through which inflammation is maintained in the lymphatic vessels. The treatment of wounds, the opening of phlegmon, abscesses, panaritiums, their rehabilitation and drainage are carried out. The affected limb is fixed in an elevated position. With lymphangitis, you can not massage and warm the inflamed area. Rubbing various ointments is also contraindicated. Drug therapy includes the use of antibiotics (cephalosporins, semi-synthetic penicillins, lincosamides, aminoglycosides), antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs, carrying out infusion treatment, ultraviolet irradiation of blood.
With sluggish chronic lymphangitis, local dressings with ointments, compresses with dimethyl sulfoxide or half-alcohol, UFO, mud therapy are prescribed.
What diseases are lymph nodes enlarged for?
What is dangerous lymphadenopathy?
Angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy is a specific lesion that currently does not have a specific place in the classification of lymphatic tissue diseases. This syndrome in the fast progressing course and clinical picture resembles lymphosarcoma and lymphogranulomatosis. However, on the basis of histological studies of tissue and the study of biopsy material, signs of a malignant process do not occur. Many researchers point out that morphological changes have common features with transplant versus host reactions, and angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy is regarded as an immunoproliferative or hyperergic reaction to an endogenous or exogenous antigen. Based on these data, etiological factors of the onset of this disease are distinguished in a number of patients.
The main causes of lymphadenopathy
It has been established that this pathology arises as a result of prolonged use of drugs such as aspirin, oletetrin, ampicillin, penicillin, psychotropic drugs, and also after vaccination against smallpox. Prolonged sensitization leads to an immunoproliferative reaction. However, in most patients it is not possible to identify the etiological factors of the disease.
To date, in the medical literature there are indications of the transition of this disease to the immunoblastic true form of lymphosarcoma. Due to the fact that angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy very often passes into lymphosarcoma, many medical specialists consider this pathology as a stage preceding the development of a malignant tumor.
This disease of the lymphatic system is mainly affected by older people, however, cases of pathology in children are also known.
What are the symptoms of lymphadenopathy?
As a rule, the pathological process occurs acutely, which is accompanied by a worsening of the condition. The patient has a sharp lethargy, weakness, headache, the temperature rises to 38-39 ° C. The febrile state is permanent, less commonly observed subfebrile condition. Against this background, the vast majority of patients have enlarged lymph nodes. Generalized enlargement of the nodes is more characteristic, but peripheral local lymphadenopathy is possible, which is asymptomatic for a long time. The mediastinal and peripheral lymph nodes, as well as those located in the abdominal cavity, are involved in the pathological process. They are not fused with neighboring tissues, mobile, have no tendency to suppuration.
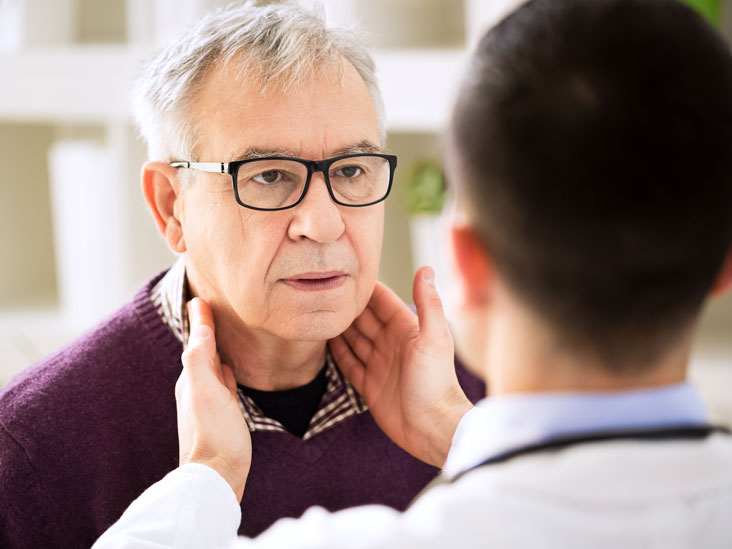
Many patients have a skin rash like urticaria, which is accompanied by periodic itching. The skin is moderately hyperemic, there are small papular elements and combs. Sometimes there may be an increase in the spleen and liver, which reach large sizes. Damage to the lung tissue is extremely rare. They are mainly caused by various infectious factors. At the peak of the disease, severe intoxication symptoms appear. The cardiovascular system suffers - the patient develops tachycardia, systolic murmur in the heart, and muffling of tones. Patients often lack appetite, they are concerned about profuse night sweat. Increased susceptibility to infectious diseases, which often act as a cause of death. Angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy is characterized by an aggressive acute course, and in the bulk, patients die within 1-2 years. But the cause of death is mainly infectious complications.
Lymphadenopathy treatment
People suffering from this disease are prescribed corticosteroid drugs. In the absence of positive results from hormonal therapy, cytostatic medications are prescribed - “Chlorbutin”, “Cyclophosphamide”, “Vinblastin” - or intensive chemotherapy is carried out according to the schemes of TsOPP, VAMP, TsVPP. An important role is played by measures aimed at preventing the development of infectious complications. In this case, conditions of maximum sterility are created, treatment of the mucous membranes and skin with bactericidal solutions. If infectious complications occur, antibiotics are prescribed.
We examined the names of diseases with inflammation of the lymph nodes.