Digestive disorders and diseases accompany pain or discomfort in the abdomen, nausea and belching, vomiting, an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, or a violation of swallowing. Some of these symptoms result from errors in the diet, while others are signs of the disease. To understand the meaning of the symptoms and tactics of the patient who has experienced them, this publication will help.
Message to Patients
A high-quality, objective and honest history is the main component of an accurate diagnosis. Diagnosis of diseases of the digestive system and dyspepsia requires an adequate assessment of symptoms. It is unacceptable to go to a specialist and simply complain about any violation, forcing the doctor to extract the remaining characteristics of the symptoms from the patient with ticks. And even worse, when patients, because of their reluctance to understand and because of the opportunity to shift this task to the doctor, do not bother to note the circumstances of their complaints. All these points impede the work of the doctor and delay the cure of the patient.
Terminology
To differentiate diseases of the digestive system and interpret the meaning of nausea and belching, you need to give a clear understanding of these terms. Nausea is a feeling of heaviness in the pit of the stomach and chest, discomfort in the mouth and throat with a feeling of crushing from the bottom up and rolling in the upper abdomen, sometimes accompanied by severe salivation, belching and hiccups, often preceded by vomiting.
Belching - a state of separation of gas or a small portion of gastric contents from the oral cavity, accompanied by an unpleasant aftertaste.
Vomiting is the active separation of the contents of the stomach or duodenum into the esophagus and oral cavity as a result of reverse peristalsis.
Dysphagia - disorders when swallowing or swallowing food, a feeling of difficulty passing food in the throat or chest, the appearance of pain, burning, hiccups or nausea when swallowing.
Objectification of symptoms
Feeling of nausea and belching, vomiting, dysphagia or abdominal pain do not bother constantly, but appear in certain conditions. They need to be clearly specified when contacting a doctor, but, more importantly, they need to be tracked before a visit to a specialist. Otherwise, remembering and trying to think out the circumstances of the occurrence of symptoms, you can mislead the doctor and send him on a false trail. Therefore, situations in which symptoms such as nausea and burping occur should be monitored by the patient.
It is necessary to pay attention to the time of the appearance of the complaint: before eating in a condition of hunger, during eating, or after some time after eating. The nature of the symptom is important, that is, it is permanent or paroxysmal, manifests itself in some position or does not depend on the position of the body, passes on its own, or requires the adoption of any measures. If we are talking about vomiting, it is important to notice what color the vomit is, how many times it happens and how much secretion appears with each episode.
Belching, like all other symptoms, also requires deep detail. It is necessary to monitor the conditions under which it develops; this happens with normal filling of the stomach while maintaining a feeling of incomplete saturation or when it is full. It should be noted whether belching is accompanied by hiccups and abdominal pains, a sensation of a taste in the mouth, or throwing contents into the oral cavity, at what interval from eating this occurs.
The origin of burping air
Symptoms such as nausea and belching of air often accompany each other, although the patient is more often worried about burping. But many do not turn to a specialist just because of belching, even if it brings discomfort. The reason is that this symptom often manifests itself after alcohol intoxication, and such a contingent of patients, because of their special attitude to health, for this reason will never consult a doctor. Even the systematic appearance of vomiting does not alarm them, since they get used to it and even often cause it artificially to consume more alcohol.
The second common reason for mild burping of air is eating in a hurry and during a lively conversation, consuming carbonated drinks, and overeating with overflowing stomach. Also, often ingestion of air is observed when eating, which is facilitated by the presence of damaged or lost teeth, when chewing is carried out mainly on one side, and a portion of air is sucked into the oral cavity through the corner of the mouth. Mixing with a food lump, it is swallowed with food, and when the chyme is expanded in the stomach, it is released, causing belching.
Cardia insufficiency
The cause of nausea and burping air may be the failure of the cardiac sphincter of the esophagus. This is a condition of incomplete closure of the annular muscle, delimiting the esophagus from the stomach, which can lead to the development of reflux disease. Cardia insufficiency requires maintaining an upright body position for 1 hour after eating. It is necessary to exclude physical labor and leaning forward immediately after eating. This is only necessary to prevent GERD, although burping itself does not help. Refusing to talk about food, swallowing carefully chewed food in small portions, and prosthetics will help get rid of it or reduce discomfort.
Burping content
The cause of burping content also lies in the insufficiency of the cardiac opening. However, in this case, not only air is separated, but also a certain amount of the contents of the stomach or duodenum. Detachable, usually liquid or gruel, enters the esophagus and oral cavity without an attack of nausea. This happens after hiccups or leaning forward, pressing on the stomach after eating. The discharge has an unpleasant taste, which depends on the type of food eaten the day before and on the time of eating.
If belching with the contents appears during a meal or 5-15 minutes after it, then it may not have a taste. Sometimes belching of the air and nausea after taking alcohol can be observed, however, this is a sign of episodic dyspepsia, and not a disease. The acidic taste of the discharge is observed after its treatment with gastric juice. It is thrown into the esophagus and oral cavity after eating with cardia insufficiency. This symptom needs to be corrected, as the result is a high risk of developing GERD and esophagitis.
Reflux disease
Nausea and belching with bitterness is a specific symptom that has an interesting mechanism of appearance. It develops due to the casting of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach, and from it into the esophagus and oral cavity. The feeling of bitterness in the mouth develops due to bile, which is thrown up in a minimum amount, first due to duodenogastric reflux, and then gastroesophageal. Nausea in this case is observed due to irritation of the stomach by the components of the contents of the duodenum 12. This is treated by reducing the intervals between meals up to 4-6 hours. Eating in small portions 6-8 times a day.
Pyloric stenosis
In the diseases described above, the main symptom is nausea and belching after eating, the treatment of which requires not medication and surgery, but a discipline of nutrition. Among the diseases that can cause the appearance of these symptoms, it should be noted reflux diseases, insufficiency of cardia and GERD, gastritis. Moreover, vomiting is observed quite rarely and is not constant after each meal.
Against this background, pyloric stenosis is a serious pathology. It develops due to the narrowing of the output section of the stomach and the limitation of its throughput. This is observed in postoperative patients or as a result of a pyloric ulcer. Cicatricial narrowing of a duodenal ulcer of a bulb can give similar symptoms. With these diseases, constant nausea and belching, hiccups and vomiting are disturbing.
Characterization of pyloric stenosis symptoms
With stenosis of the pyloric stomach, ingestion of food into the duodenum 12 is difficult due to cicatricial narrowing. As a result, the contents processed by the gastric juice are delayed and are often thrown back into the esophagus. This can happen at different times from a meal. And the later from him, the more pronounced the symptom. For example, belching with rotten eggs and nausea with vomiting are a common sign of pyloric stenosis.
With the first degree of stenosis, belching and discomfort in the abdomen during the first few hours from eating are observed. These signs are less pronounced or almost absent with frequent meals in small portions. In the second degree of stenosis, when food lingers in the stomach longer, heaviness in the stomach, discomfort, and sometimes nausea and hiccups are observed along with belching with air and acid. Vomiting is rare, although it may occur with overeating.
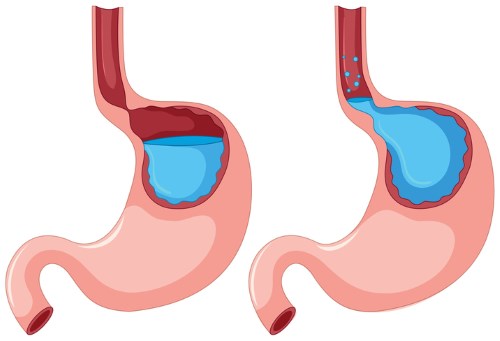
With the third degree of stenosis, the delay time of food in the stomach already leaves 6-8 hours, and during this period of time its decay can occur. Among complaints, patients often indicate nausea and belching with rotten smell air, belching with contents with putrid smack. There is almost constant repeated vomiting: it develops after each meal after 4-8 hours from a meal. In vomit, processed food with a putrefactive and sometimes fecal odor. The fourth degree of pyloric stenosis in symptoms is almost the same as the third. Treatment requires surgical intervention, and in the first and often second degree for the correction of a fairly frequent fractional nutrition in small portions.
Dysphagia
Esophageal or oropharyngeal dysphagia is a group of disorders of swallowing food, in which it is difficult to pass only solid or any food through the esophagus and pharynx. This develops due to neurological pathologies, for example, after a cerebral infarction with a loss of swallowing function. As a reason, stenosis of the esophagus after surgery, a chemical burn or growth of a neoplasm should be indicated.
In all these cases, burping food and nausea are observed, although the latter symptom is rare. As a rule, nausea does not have time to develop, as hiccups and vomiting appear when chewed food enters the esophagus or throat. Drinking water or chopping food with liquids helps to facilitate nutrition. It should be swallowed in small portions.
Esophageal dysphagia
With severe stenosis of the esophagus, the patient refuses food due to nausea and burping when swallowing. Only a small portion of the food that he will be able to swallow will reach the stomach and digest. In this regard, one of the main symptoms is rapid weight loss due to the inability of adequate nutrition. Very often, in the presence of a tumor narrowing of the esophagus, blood may be present in the vomit due to mechanical trauma to the neoplasm.
Persistent nausea and belching after eating, associated with the inability to swallow or difficulty in passing food into the stomach, are serious symptoms that cannot be ignored due to the rapid growth of epithelial tumors. This can lead to a situation where a correctly diagnosed disease cannot be cured due to late treatment.
Recommendations
Each of the above symptoms requires attention from the patient and then the doctor. And it is especially important to pay attention to them during their systematic repetition. Vomiting after eating or nausea after eating are symptoms that potentially characterize a tumor in the pharynx, esophagus, or stomach. And although they are not basic, it is unacceptable to constantly put up with vomiting and get used to it, not knowing its origin. To find out the cause of the appearance of these symptoms will allow endoscopic examination of the stomach with a biopsy of the mucous membrane. Its diagnostic benefit is extremely high, therefore, FEGDS should be performed as soon as possible.