The worst pandemic of the 21st century was Ebola raging on the African continent. A fatal disease in just one year claimed the lives of more than seven thousand people. At the moment, a truly proven cure for this ailment does not exist. How is Ebola prevention worldwide? How to recognize the most dangerous virus and protect yourself and your loved ones from its terrible effects? We will try to find answers to these questions.
What is a virus?
Ebola disease is one of the most dangerous for human life in our time. A powerful virus that infects humans, monkeys, and a number of small mammals is almost invulnerable to treatment. Its destructive effect is transmitted to all parts of the body, from the internal organs to the skin and brain. The deadly process begins with the fact that the blood becomes more viscous, the formation of clots begins, which clog the capillaries throughout the body. The result of all this is the necrosis of cells and the decomposition of organs. Cracks form on the skin from which blood oozes, the insides decompose, paralysis occurs, and in the worst case, death.
Varieties of the virus and their brief description
The official name for the disease is Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Infection occurs under the influence of an infection belonging to the group of filoviruses. The main features of GLE are high mortality, the speed of spread, as well as the severe course of the disease. There is a fairly simple answer to the question of how Ebola manifests itself. Even during human life, the virus leads to the fact that its organs die and begin to decompose.
Ebola disease is divided into five main varieties, each of which has certain characteristics. So, it is customary to distinguish:
- Zaire type. It was first recorded in 1976 in the locality of the same name (Zaire, the Ebola River), due to which it got its name, and also gave the name to the fever itself. This type of disease is considered the main and most severe. This statement was fully confirmed by the epidemic that began in 2013.
- Sudanese type. It is less dangerous, however, mortality from it is still at a very high level. The first time was celebrated in Sudan. The name of the disease also received on a geographical basis.
- Cote d'Ivoire, or Thai Forest, type. An epidemic of this variety has not been registered in official medicine. The disease was discovered in 2004, she fell ill with a researcher at one of the organizations conducting the study of chimpanzee corpses. This type is considered the easiest.
- Bundibugio, or Bundibugio type. The disease was reported in Uganda in 2007. The outbreak of the virus was rather small, however, it could not do without human casualties.
The Reston Ebola subtype can be distinguished into a separate category. The specified form differs from all of the above in that it is absolutely not dangerous for people, only monkeys are ill with it. However, it is worth noting that studies on the spread of the disease were carried out only in relation to fully healthy males. In this regard, science does not have accurate data on how the infection will develop with weakened human immunity.
Area of occurrence of viral infection
The most common Ebola in Africa. In all cases, the first outbreaks of disease were noted on this continent. Most often, the virus is rampant in countries located in the immediate vicinity of the equator. Isolated cases of fever were noted in a number of states located far from Africa (USA, Germany). However, it is assumed that the disease was introduced into them by people from the outside. At one time, diseases began in such countries as Congo, Sudan, Ugadan, Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone.
Methods for spreading fever
How does the Ebola virus spread? Infection most often occurs as a result of contact with secretions (urine, feces, sperm, sweat) or the blood of a sick person or animal (not only living, but also dead). Infection is also transmitted through unprotected intercourse. It is necessary to be afraid of common household items (for example, bedding), blood transfusion, the use of non-disposable syringes. In very rare cases, infection is possible by airborne droplets (inhalation of part of the sputum of an infected person). Ebola in Africa is often transmitted during ritual funeral rites during which relatives touch the corpse. Performing such actions is strongly discouraged.
These methods of spreading the infection are mostly secondary. It is not currently possible to determine the initial cause of the onset of the disease. According to one of the most popular versions, for the first time the virus was detected in bats (“flying dogs”). It is also believed that the main distributors can be small rodents living in the immediate vicinity of human habitation. You can get infected by contact with the skin of a deceased animal. Perhaps most of the fevers began in this way (hunters felt the corpses of dead animals).
New outbreak
The Ebola outbreak in 2014 was the most powerful of all known manifestations of the disease. To date, more than 7,000 people have died. In 1976, the world first learned of such a thing as Ebola. At that time, treatment, prevention and protective measures were not known, therefore almost 40 years ago, the virus claimed the lives of 280 people (38 of those who became ill recovered).
The first cases of a new epidemic appeared in December 2013 in Guinea. Subsequently, the virus spread to Nigeria, Liberia and several other countries. Medical staff from international organizations providing assistance to patients on the ground were in a zone of significant risk. Many of them became ill and were taken home for treatment. A similar situation provoked a real panic around the globe.
How is the fight against this dangerous disease going on these days? How to stop its spread? Ebola, like any other acute viral infection with the possibility of death, requires clear, organizational measures on the part of state authorities and medical personnel. So, first of all, it is carried out:
- Hospitalization of the patient in special boxes (protective measures can be compared with those used in case of plague);
- Marking of household items and treatment of an infected person, their constant disinfection and separate storage, and subsequently destruction;
- Disposal of items in contact with the patient through treatment with phenol solution and then burning;
- Isolation of persons who are possible carriers of infection on the same grounds as patients.
The characteristic signs of a terrible fever
What are the signs of Ebola? Symptoms of the disease are quite simple, however, at first, fever can be confused with classic respiratory disease (ARVI) or tonsillitis. At the very beginning, patients note the following changes in health status:
- severe headache;
- general muscle weakness;
- sore throat;
- increased body temperature (38 degrees and above);
- upset stool.
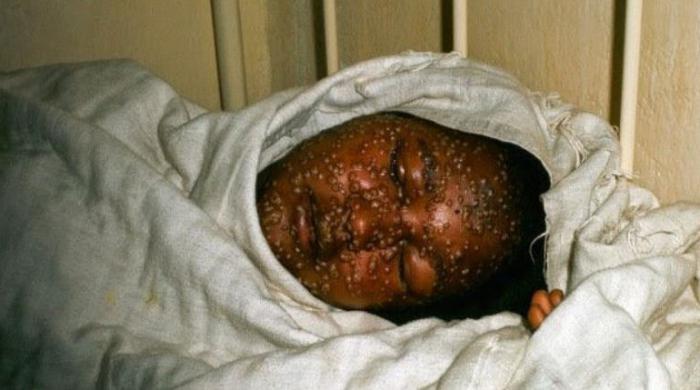
Over time, after 2-3 days, the virus progresses, and a person begins to overcome a dry cough, a rash (dots appear throughout the body of a red or crimson color), unpleasant sensations in the chest area are noted.
The second and often last week of the course of the disease is characterized by the most serious condition. Damage to the brain, internal organs and epidermis occurs, gums, liver, spleen and cracks in the skin begin to bleed. Internal organs begin to decompose during human life. In most cases, the disease ends in death 10-14 days after its onset.
Signs of Ebola by which doctors identify the disease
For an ordinary person, it will be enough to know the external signs of Ebola. Symptoms that a specialist will need for an accurate diagnosis are detected only by conducting special analyzes and tests. General specific prerequisites are considered:
- short incubation period, rapid development of the disease;
- bleeding disorder;
- global intoxication and dehydration;
- increase in white blood cells in the blood;
- decrease in platelet and hemoglobin levels.
There are many special laboratory tests to detect the Ebola virus. Symptoms of an external nature can be deceiving and be the result of diseases similar to fever, for example, Marburg disease. Most often, for accurate diagnosis, a test is performed to identify antigens.
Little known facts
Modern media outlets cover a disease such as Ebola. Symptoms, prevention and precautions are known to almost all people living in the potential risk zone. Unfortunately, many facts about the disease are still unknown to a wide range of people. These include the following data:
- The virus affects all people without exception, however, children suffer from it much less often. Scientists cannot explain this trend until now;
- The incubation period most often equals the interval of 4 to 7 days, however, in some cases it can reach 3 weeks;
- People who have had Ebola are discharged for 21 days;
- There are cases when the same person could get a viral infection several times;
- There are people with antibodies to fever. This means that they can carry the disease in a mild form and be carriers of infection.
- The fever virus persists in the sperm of a recovered man up to 7 weeks;
- Ebola virus has been studied by scientists only half, part of its protein molecules still remains a mystery to humanity;
- Ebola fever is much worse than AIDS, it destroys the human immune system not in 10 years, but in two weeks;
- The virus is quite resistant to high temperatures, dies in the blood while maintaining an indicator of 60 degrees for at least 30 minutes;
- The virus easily tolerates even severe cold;
- Folic acid deficiency and poor nutrition increase the risk of infection.
Basic preventive measures
If you live in a risk zone or have direct contact with citizens who have visited areas where this virus is rampant, the following rules should be followed. So, the prevention of Ebola comes down to such simple measures as:
- regular sterilization of premises, household items, equipment;
- wearing a protective set of clothing that excludes contact with infected people;
- complete exclusion of any contact with virus carriers.
Only the rapid detection and complete isolation of sick people can fully prevent the spread of the disease. If you do not live in a risk zone, try not to panic, exclude possible trips to countries where the epidemic is raging, and also refuse contact with citizens of these countries.
Persons working in African countries need to know how Ebola manifests, and in case of contact with infected people, ensure their protection by wearing a special suit and mask. This will help minimize the risk of infection.
Ebola spreads spontaneously, and in some cases, a person simply does not have the opportunity to conduct preliminary training. Significantly reduce the risk of the disease can also measures such as:
- restriction of contact with animals that may be potential carriers of the virus;
- to exclude interaction with decomposing corpses of animals;
- thoroughly wash with soap and water the exposed parts of the body, hands and face after walking along the street or visiting a public institution (especially a hospital);
- When eating animal products, subject them to initial heat treatment.
Treatments for fever
To date, the prevention of Ebola is the only real measure of protection against this dangerous disease. There is no special treatment as such. It is under development and has not passed all the necessary medical checks. Experimental methods today are used in European countries and in the United States, however, they cannot provide a 100% recovery of patients. In addition, a fever vaccine has not yet been developed.
What is Ebola treated today? Symptoms of the disease must be eliminated without fail. Since there is no special treatment, you need to be guided by the situation. Intensive therapy, restoration of blood and fluid loss (electrolyte preparations) is vital for a sick person. The fatal outcome of the disease is largely determined by the individual structure of the body. It is generally accepted that a person who has undergone Ebola receives the strongest immunity for life, however, cases of reinfection are known.
Ebola Prevention is the only way to stop a deadly disease today. Everyone should think about personal protective measures for themselves and their loved ones. Remember that a dangerous disease in most cases ends in death, develops very quickly and is characterized by a severe course. What else you need to know about such a dangerous disease as Ebola. Symptoms, prevention, treatment methods, all this, of course, is extremely important, however, quarantine is the main measure of protection for the population.