The aorta is the largest unpaired artery. It belongs to a large circle of blood circulation and nourishes all the organs of our body with blood. The aorta is divided into 3 departments and 2 parts - the abdominal and thoracic. Most often (in 95% of cases), an abdominal aortic aneurysm occurs, which we will talk about today.
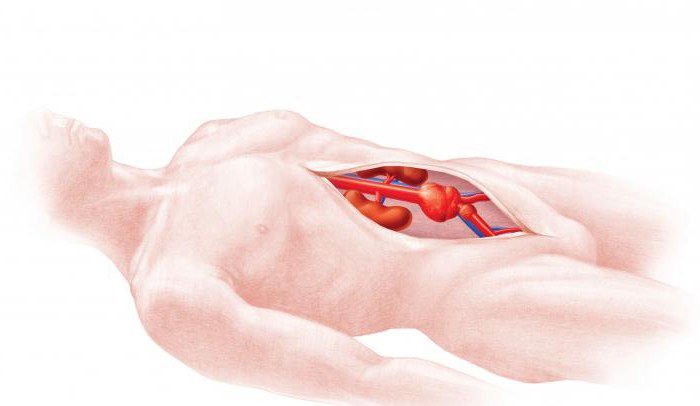
Aneurysm is the expansion or protrusion of the aorta. This disease is still the basis of many discussions, because doctors cannot agree unanimously on what degree of expansion of the vascular wall can be diagnosed as an aneurysm. Earlier, the diagnosis was confirmed when the aorta was enlarged by 2 times or when its diameter expanded by more than 3 cm. But taking into account the fact that the aorta has a diameter of 15 to 32 cm, the concept of “more than 3 cm” is clearly vague. Therefore, in 1991, thanks to a study of American scientists, an aneurysm began to be considered a pathological expansion of the aortic lumen 50% more than its normal diameter. But this definition remains quite conditional.
This issue becomes especially important when choosing the tactics of surgical intervention, however, alas, it still remains open. Meanwhile, about 15,000 Americans die annually from aneurysm. In most cases, they simply do not have time to diagnose it.
Which doctor treats aneurysms?
This disease is treated by a vascular surgeon, since the main treatment for the problem is surgical. If the operation is not indicated, the patient should be observed by a therapist, cardiologist or internist (specialist in internal medicine), carefully monitor his condition. Aneurysm is quite insidious, it can begin to grow suddenly, increasing the risk of its most serious complication - rupture.
Who is at risk?
Aneurysm is diagnosed both in men and in women (in the latter, however, much less often). However, it is noted that in men over 65, it occurs more often. This is largely due to the passion of many for smoking, which is especially detrimental in old age.
So, the risk group includes:
- people suffering from arterial hypertension;
- smokers
- persons whose family has already been diagnosed with aneurysm of the abdominal aorta or other cardiovascular diseases and / or pathologies of peripheral circulation;
- overweight and sedentary people.
Attention! As studies prove, many aneurysms are inherited from their ancestors.
Types of abdominal aortic aneurysms: classification
Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta is divided into several types, depending on its shape, localization and pathological features:
- Sack-shaped (resembles a sac, which is connected through the neck to the lumen of the aorta).
- Spindle-shaped. It resembles a spindle in shape, which connects through the hole to the aortic lumen. The most common form of aneurysm.
According to pathological features, the following types of aneurysms are distinguished:
- True. The wall of its vessel is dilated, as it is formed of many layers of the aorta.
- Pseudo-aneurysm. Appears after an injury due to the development of a pulsating hematoma.
- Exfoliating. That is, its walls are stratified, and the cavities are filled with an intramural hematoma, which connects through the wall of the damaged vascular tissue to the lumen of the aorta.
Distinguish it by localization:
- Aneurysm of the infrarenal section of the abdominal aorta is located above / below the branch of the renal arteries.
- Suprarenal is located above the branching of arteries
- Total aneurysm spreads along the entire length of the vessel.
What are the causes of aneurysm?
- Atherosclerosis, in which the vascular wall becomes thick and loses elasticity, and fat forms in the form of atherosclerotic plaques on its walls. The composition of the plaques includes bad cholesterol and other fats. While doctors have not yet fully determined how exactly atherosclerosis affects the development of aneurysm, it is assumed that as a result of this disease, circulatory disorders in the vessel appear and the supply of nutrients stops. As a result, vascular tissue is damaged, followed by its splitting. As a result, a diagnosis of "abdominal aortic aneurysm" is made.
- Diabetes mellitus, which “loves” to infect the blood arteries. It is often accompanied by retinopathy, nephropathy, aneurysm.
- Genetics. In some congenital syndromes (Ehlers-Danlos, Marfan, cystic medionecrosis Erdheim, etc.), arteries, including the abdominal aorta, suffer. Often, the relationship between abdominal aortic aneurysm and genetic diseases can be traced.
- Infectious diseases. These include diseases that affect the inner layer of the heart (endocardium), - syphilis, ecdocarditis, salmonellosis, etc.
- Injuries to the abdomen. For example, with a strong blow to the chest or abdomen, the aorta may be affected.
- Inflammatory processes. Nonspecific aortoarteritis, for example, causes a weakening of the aortic wall. True, no specific information on this issue yet. But non-inflammatory diseases of the vascular wall often occur due to atherosclerotic plaques.
In general, smoking, lack of exercise, and age are most often the cause of aneurysm. It is imperative to diagnose it on time. Aneurysms of the thoracic and abdominal aorta have different symptoms, which we will now consider.
What are the symptoms of abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Most often, aneurysm does not make itself felt at all and is diagnosed completely by accident during the examination. Since it displaces organs, disrupting their vital functions, the diagnosis may be made incorrectly, therefore it is extremely important to conduct an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Doctors note that the thoracic aneurysm is especially “secretive”. It may not appear at all or cause chest pain, coughing and shortness of breath. If it increases, the aneurysm of the abdominal aorta becomes relevant.
Of the few symptoms of aneurysm, several are distinguished that occur together or separately:
- Heaviness in the abdomen, an unpleasant sensation of fullness and pulse, which resembles an increased heart rate.
- Abdominal pain, not acute, rather, aching, dull character. It is localized directly in the navel or to the left of it.
And by indirect signs the aneurysm of the abdominal aorta makes itself felt. Its symptoms are so varied that it is very difficult to suspect a true problem in them. This is due to the fact that a growing aneurysm can interfere with the functioning of different organs and systems. As a result, it can be confused with renal colic, pancreatitis, or radiculitis.
Coronary artery disease causes pain in the lower back (in particular, the lower back) and impaired sensation in the legs along with impaired movement.
Abdominal syndrome is manifested by vomiting, belching, diarrhea or constipation, as well as a lack of appetite, which entails weight loss.
Chronic ischemia of the legs is expressed in circulatory disorders (cold feet), muscle pain during walking and at rest, periodic lameness.
Urological cider reports itself with urination disorders, pain, a feeling of heaviness in the lower back, and even the appearance of red blood cells in the urine.
The rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm begins with increased pain in the abdomen, general weakness and dizziness. Sometimes the pain gives to the lower back, groin or perineum. In this case, the patient needs immediate medical attention, since the condition is fraught with death. Often an aneurysm breaks into the middle part of the small intestine, stomach or duodenum, less often - into the large stomach. When an abdominal aortic aneurysm ruptures, its symptoms may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. In the left
region of the abdomen, a formation is palpated, slowly increasing and with a strong pulsation. Its boundaries are not felt.
If the aneurysm ruptures, the symptoms are very vivid, but they can be easily confused with other health-hazardous conditions, so be sure to call an ambulance for any acute pain in your stomach or chest.
Diagnosis of the disease
The first diagnostic stage is an examination by a doctor who, upon palpation, feels a strong pulsation in the abdomen, this is an aneurysm of the abdominal aorta. Its diagnosis includes studies that allow you to visualize what is happening in the abdominal cavity. First of all, this is ultrasound, as well as computed tomography (CT) and multispiral computed tomography of the aorta (MSCT).
If an abdominal aortic aneurysm is suspected, an ultrasound scan makes it possible to confirm its presence with almost one hundred percent certainty. It shows the exact localization of the aneurysm, the state of the vascular wall, the place of rupture, if any.
A CT scan or MSCT is performed to detect calcification, stratification, intracellular thrombosis, a risk of rupture, or an existing rupture.
If the above diagnostic tests do not allow you to accurately diagnose (although this happens quite rarely), aortography is prescribed. The method allows you to examine the aorta and its branches in real time by introducing a special fluid into the vessel. It is indicated if there is a suspicion of damage to the visceral and renal arteries, the condition of the distal bloodstream is unknown.
Complications of abdominal aortic aneurysm
This condition is dangerous not only for health, but also for life. First of all, the aorta can cause embolism (blockage) of arteries, infectious complications, and heart failure.
Exfoliating aneurysm of the abdominal aorta is a dangerous complication, which consists in its rupture and blood entering the layers of the vascular body. If all 3 layers are stratified and the aorta breaks completely, intense blood loss occurs.
But, of course, the worst complication of aneurysm is its rupture. Many patients with untreated aneurysm die within 5 years. Before rupture, a person feels severe pain in the lower abdomen and in the lower back. If the abdominal aortic aneurysm is torn, the course of the disease is characterized by profuse bleeding, which leads to shock and death. Therefore, with acute pain in the abdomen and chest, be sure to call an ambulance, since it is dangerous to delay. According to statistics, only 3% of patients die immediately after aortic rupture, while others live from 6 hours to 3 months. In most cases, they die within a day. How is aneurysm treated? Consider below.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Treatment
Many people mistakenly believe that with a diagnosis of "abdominal aortic aneurysm," treatment can only be surgical. In fact, everything is individual here.
If the aneurysm does not reach a diameter of 4.5 cm, then the operation is not indicated, because it itself can carry a greater risk to life than the vessel itself, which has increased in size. Typically, this trend is observed in older men who suffer from concomitant diseases and, in addition, do not stop smoking (and with a similar diagnosis, it is simply necessary to stop smoking!). Expectant tactics are preferable for them, because the risk of aortic rupture with this diameter is only about 3% per year. In this case, once every six months the patient is forced to do an ultrasound in order to find out the size of the aorta. If the vascular wall gradually expands, then this is the main indication for the operation, because the probability of its rupture increases by 50%.
Elderly people who have aneurysm of the abdominal aorta, it is advisable to carry out treatment using the endovascular, minimally invasive method. During the operation, a catheter is inserted into the artery through the stent. Once in the aorta, it opens and embraces the artery, thereby replacing the affected area of its body. The advantages of the operation include easier tolerance and a short recovery period - only a few days. But this method also has its own nuances, therefore not everyone is carried out. The main disadvantage of this operation is that in 10% of cases there is distal migration of the installed stand.
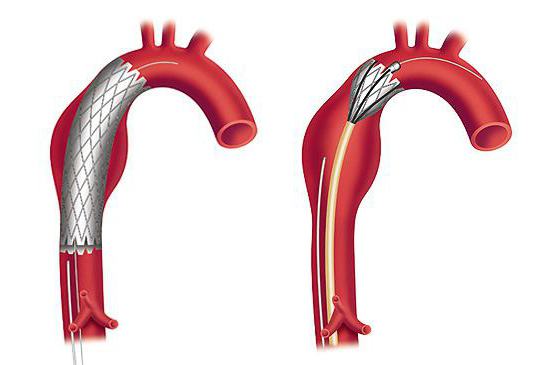
If diagnosed with "abdominal aortic aneurysm," the operation is often open. During its implementation, the affected area of the aorta is removed and replaced with a prosthesis made of dacron (synthetic fabric based on polyester). In order to provide access to the aorta, median laparatomy is used. The duration of the operation is usually about 2-3 hours. After surgery, a noticeable scar remains.
The patient recovers about two weeks. The resumption of work in some cases is possible only after 4-10 weeks. Exercise is strictly forbidden to the patient, rest and walks are shown.
Contraindications for open surgery
Surgical intervention is prohibited in the following conditions:
- Recently suffered a heart attack (at least a month).
- Heart and pulmonary failure.
- Renal failure.
- Affected iliac and femoral arteries.
Rehabilitation period after surgery
Of course, the presence of complications after surgery is affected by the age and associated diseases of the patient. Also, the patient's condition may worsen if his body is already weakened (HIV, onco, diabetes), obesity and heart disease occur. Moreover, a pre-planned operation gives the patient more chances to survive and recover than emergency intervention in case of rupture of the aortic aneurysm.
Complications can occur as a reaction to general anesthesia, which not everyone can tolerate, the development of infection, damage to internal organs and bleeding. In a very small number of cases, the operation ends in death.
If the operation is planned, doctors recommend a week before its completion to stop taking blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin, etc.). Be sure to inform your doctor about which medications you are currently taking before surgery.
The risk of relapse is extremely small, but if a person suddenly begins to worry about pain in the back or abdomen, nausea, vomiting, numbness of the legs or general poor health, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Aneurysm Prevention
Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta is less likely to occur if you give up (and ideally do not get this habit at all) from smoking, control your pressure and your weight. It is also important to lead an active and healthy lifestyle. Be healthy!