What is chronic bronchitis? This is a very common inflammatory disease, accompanied by prolonged cough with sputum production. You can talk about the chronic course of bronchitis if the cough lasts more than three months a year for two or more years. It is necessary to treat bronchitis of any stages and forms in a comprehensive and timely manner, because the inflammatory process not only negatively affects the quality of life, but also threatens with serious complications.
How bronchitis becomes chronic
The diagnosis of chronic bronchitis does not arise from nowhere. The disease begins gradually. Damaged mucous membranes produce more sputum, which is worse excreted. This causes a cough, attacks are mainly observed in the morning. Over time, the cough persists day and night, intensifies in wet and cold weather, and over the years becomes constant. With bronchitis, an increased amount of transparent sputum is odorless, during periods of exacerbation, sputum is greenish or yellowish purulent or mucopurulent, more thick and cloudy, with an unpleasant odor.

As the disease progresses, the bronchi narrow, letting in less air. Periodically, shortness of breath appears with a violation of exhalation (up to asthma attacks). In this case, doctors talk about the transition of bronchitis into chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Previously, doctors called this condition chronic obstructive bronchitis, but the name adopted today more accurately reflects the essence of the disease - not only the bronchi, but also the lungs suffer. In severe cases, the development of emphysema is possible. As a result, less oxygen enters the blood, respiratory failure develops.
A sluggish inflammatory process in the bronchi, proceeding with periodic exacerbations, is characterized by a prolonged cough. The development of the disease is associated with prolonged damage to the respiratory system by pathological agents. The integrity and functions of the mucosa, the cleansing function of the bronchi are violated, the inflammatory process goes to the deeper layers of the walls of the bronchi. The patient is diagnosed with chronic bronchitis. The ICD code is J42. The disease is part of the group of chronic diseases of the lower respiratory tract (J40-J47).
Causes of bronchitis and risk factors
Chronic bronchitis (ICD classification code - J42) occurs for various reasons, but all of them consist in the initial pollution of the respiratory tract with toxic gases and harmful fumes, tobacco smoke, by-product dust in enterprises and so on. When an infectious agent is attached, the disease worsens. In the period of exacerbation, chronic bronchitis is difficult to treat, which distinguishes the condition from acute simple bronchitis.
Risk factors for chronic bronchitis in adults can be work in hazardous workplaces, living in populated areas with an unfavorable environmental situation, prolonged exposure to hot or cold air (including work in the north), inhalation of alkalis and acids, tobacco smoking, allergic diseases, and infectious pathogens. Internal risk factors contributing to the occurrence of chronic bronchitis include frequent diseases of the respiratory system, impaired functioning of the immune or nervous system.
In the phases of chronic bronchitis, exacerbation and a period of remission alternate. Physical factors can cause aggravation (sharp temperature changes, house dust or tobacco smoke, cold and moist air), chemical factors (inhalation of alkalis, chlorine vapor, acids, carbon monoxide, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide), stagnant blood circulation processes (cardiac and vascular pathologies), the appearance of foci of infection in the oral cavity and nose, bad habits, heredity (congenital disorders of the bronchopulmonary system or allergic predisposition).
Main symptoms
What is chronic bronchitis? This is one of the most common diseases of the respiratory system, the cause of which is most often an infection of a viral or (less commonly) bacterial origin. The main symptom of chronic bronchitis in adults and children is a prolonged cough. The cough lasts more than four weeks, accompanied by the constant release of sputum of a different nature (purulent, mucous, watery). At first, attacks are more often observed in the morning, during the day the patient may cough after exercise or when going out in the cold. In the later stages of the disease, shortness of breath appears.

Other symptoms of chronic bronchitis (ICD code 10, which the specialist notes on the patient’s card - J42) are wheezing and extraneous sounds when breathing, fever, cyanosis (cyanosis) of various parts of the body. Cyanosis occurs due to weakened gas exchange in the lungs, lack of oxygen. This can be manifested by periodic dizziness, nausea, insomnia, headaches. In children, chronic bronchitis most often occurs with infection against a background of weak immunity. Therefore, the disease may be accompanied by a clinical picture characteristic of influenza, infection (streptococci, pneumococci, staphylococci, respiratory syncytial infection).
Diagnostics
In history, chronic bronchitis can be noted by a pulmonologist or therapist only after a minimum of two years of observation of the patient. In order not to confuse the disease with brochiectatic disease or bronchial asthma and similar diseases, the doctor can prescribe a chest x-ray, general, immunological and biochemical blood tests, an antibiotic sensitivity test, bronchoscopy, a sputum test with bacteriological culture, a study of the function of external respiration. If necessary, additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are indicated.
For early detection of severe complications of chronic bronchitis (bronchial obstruction, for example), bronchoscopy may be required. This is an endoscopic examination, which consists in the introduction of a thin tube with backlight for examining the bronchi from the inside. Bronchoscopy can be carried out together with other diagnostic and therapeutic procedures: biopsy, instrumental suction of sputum from the lower respiratory tract, the introduction of drugs. The study is necessary, including with suspicion of anatomical abnormalities in the development of the respiratory system, tumor changes or the presence of a foreign body in the bronchi.
It is difficult to accurately determine bronchitis from an X-ray image. Indirect signs of the disease include uneven filling of the lungs with air, proliferation of connective tissue, distortion of the vascular pattern of the bronchi or lungs, slight subsidence of lung tissue. Spirographic examination allows you to determine the degree of obstruction and respiratory failure, CT is performed according to indications. Sputum sowing on microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics is carried out not so much to confirm the diagnosis, but in order to choose rational antimicrobial therapy. It makes sense to carry out the procedure only before the start of treatment, because otherwise it is likely to receive a false negative result.
Tactics for the treatment of chronic bronchitis
What is chronic bronchitis? This is a disease that requires an integrated approach to treatment. In the case of bronzitis with a severe concomitant form of acute respiratory viral disease, the patient is shown to be in the pulmonology department, with uncomplicated bronchitis, outpatient treatment is possible. In the process of therapy, it is important to restore the patency of the bronchi, eliminate harmful provoking factors, overcome the infection. In the early days of the disease, if we are talking about acute bronchitis, or during exacerbation, bed rest is necessary, plentiful drinking and a milk-vegetable diet are indicated. Be sure to quit smoking and exclude the effects of harmful factors.
Symptoms of chronic bronchitis in adults and children are relieved by antiviral drugs, mucolytic and expectorant drugs. With a dry cough, the doctor may prescribe medications that suppress the cough reflex. Physiotherapeutic procedures are useful. Antibiotics, as a rule, are not used, except in cases of bacterial infection, with a pronounced inflammatory reaction according to the diagnostic results, with a protracted course of acute bronchitis or with purulent sputum. Sometimes it is necessary to rinse the bronchi with medicinal solutions (bronchoscopy).
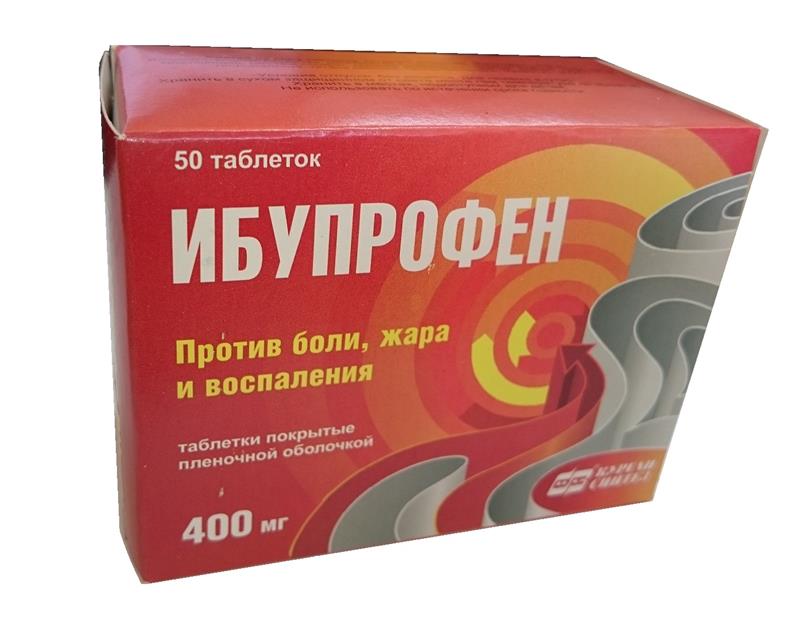

In the treatment of chronic bronchitis, the use of antipyretic drugs may be required. As a rule, inflammation is accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature, so there is no need to drink medicine. But if the indicators increase to 38 degrees or more, then it is advisable to take paracetamol or ibuprofen. With the allergic nature of the disease, antihistamines are prescribed. In the case of concomitant diseases, therapy can be supplemented by other means as prescribed by the doctor.
Antibacterial therapy for the disease
The issue of using antibiotics for chronic bronchitis (ICD code 10 & mdash; J42) is controversial and is decided exclusively individually. Antibacterial therapy is advisable for complicated viral bronchitis or concomitant diseases, bacterial bronchitis. Macrolides, penicillins, cephalosporins are used. The choice of a particular drug depends on the characteristics of the course of the disease and sensitivity. But still, in most cases, antibacterial drugs do not have the necessary effect, and they can also cause a brooch-obstructive syndrome - obstruction of the bronchi caused by swelling of the mucosa.
The main symptom that indicates the need for antibiotics is purulent sputum. With this symptom, an additional examination is prescribed, according to the results of which a suitable medicine is selected. In no case, with chronic bronchitis, you can not choose an antibiotic yourself. The possible harm from using the wrong medication can significantly exceed the expected effect. Acute inflammation is almost always successfully treated with topical drugs, while antibiotics are not a key therapy.
The use of antiviral drugs
Chronic lung bronchitis, as a rule, is provoked by a viral infection, so the use of antiviral drugs is advisable. But many doctors are sure that drugs of this group with sufficient efficiency simply do not exist, and to successfully fight the virus you just need to create optimal conditions for the body. Other doctors are sure that without antiviral drugs to cope with the disease will not work. As a part of therapy, usually medicines of oseltamivir or interferon are used. You can take such drugs only as directed by your doctor. Some (especially strong drugs) are prescribed only in a hospital setting for continuous monitoring of the patient's condition.
Expectorants for bronchitis
To eliminate the cough, medications are needed to stimulate expectoration and sputum thinning medications. The action of secretory agents is aimed at irritating the mucous membrane, due to which the work of the cough and vomit centers of the brain is enhanced, the production of liquid secretion is increased, and the cough reflex is enhanced. The main drugs of this group are ammonium chloride, thermopsis herb, some essential oils. The drugs have a short-term effect, and an overdose threatens with tearing, nausea and vomiting, nasal congestion.
Mucolytics (drugs that dilute sputum, but do not lead to an increase in its amount) are usually prescribed as follows: Bromexin, Trypsin, Ambroxol, Alteyka, Doctor MOM, Ambrobene. "Trypsin" has an anti-inflammatory effect, it is contraindicated only with individual intolerance to the components. "Ambroxol" is a classic mucolytic, significantly facilitating expectoration of sputum. A variety of forms of release allows the use of the drug even for the treatment of newborns, and Ambroxol has almost no side effects.

"Bromhexine" has no contraindications (except for the first trimester of pregnancy), has no toxic effects on the body and is quite effective. "Doctor IOM" expands the lumen of the bronchi, additionally has an anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect. The medicine can cause allergies, so it can only be used as directed by a doctor. "Marshmallow" - a plant-based drug (marshmallow root). You can not use "Alteyka" with a dry cough, because the composition stimulates the cough, vomit and respiratory centers (cough may increase).
Actively used alternative treatment of chronic bronchitis. A good expectorant is milk with onions. To prepare the medicine, you need to chop half the onion, pour a glass of milk and cook over low heat for ten minutes. Milk should be beige and yellowish. After boiled onions need to be removed. Take the medicine before bedtime in a warm or hot form. You can cook another remedy (folk) for chronic bronchitis: chop the onion head, mix with honey in equal proportions, take a teaspoon after each meal. The mixture must be stored in the refrigerator.
Lifestyle and patient regimen for bronchitis
In chronic bronchitis, doctor's recommendations include changes in regimen and lifestyle. It is necessary to provide the most comfortable environment for the natural restoration of the respiratory system. It is shown abundant drinking (water, juices, herbal teas, fruit drinks of a comfortable temperature), the use of humidifiers, bed rest (especially in the early days of the disease) and the lack of physical activity. Short walks are permissible only after the patient has been relieved. It is important to completely stop smoking, because inhalation of tobacco smoke can not only slow down recovery, but also cause complications.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
In chronic bronchitis, physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended, namely massage, gymnastics for the respiratory system and inhalation. Inhalations are effective with essential oils of mint, pine, rosemary, eucalyptus tree, saline and soda solutions, and medicines (Ambrobene, Lazolvan). It is impossible to carry out inhalation in patients with heart palpitations (tachycardia) and at high temperature. Breathing exercises can increase the functional reserves of the respiratory system, but exercises need to be done in the fresh air. Massage for bronchitis is prescribed already at the stage of recovery, when there are no complications and high temperature, and the cough became wet.
Prevention of chronic bronchitis
Preventive measures include the elimination of provoking factors. It is necessary to stop smoking and minimize the effect on the respiratory system of harmful factors (dust, fumes, polluted air). After all, what is chronic bronchitis? This is a disease that appears with constant irritation of the respiratory system and infection. Therefore, any acute or chronic infections must be treated in a timely manner, prevent allergic manifestations, strengthen immunity and, in general, try to lead a healthy lifestyle.