Reasons, treatment of aneurysm are current topics for modern medicine due to the high danger of this condition. The term is used to denote the processes of stretching of the arterial walls, leading to the protrusion of a separate area. Aneurysms localized in the aorta, heart, brain and peripheral circulatory system are considered as an independent pathology.
general information
Aneurysms formed in the brain are called cerebral, intracranial. Such can cause damage to the cerebral arteries, which will eventually lead to hemorrhage. Aortic aneurysm is a stratification of the tissue forming the vascular wall due to fluid leakage. If all layers of the vessel burst, a large-scale hemorrhage will occur, severe blood loss. High probability of death.
Aneurysm, localized in the peripheral vascular system, can affect any limb. Sometimes a lesion of the visceral artery or carotid is established. Cardiac often appears as a complication against a background of heart attack, carditis, trauma. All cases of heart damage are divided into acute, subacute and chronicles. The division into three groups is accepted: mushroom, bag-shaped, expanding.
Where did the trouble come from?
The main cause of aneurysm is genetic prerequisites. There is a higher likelihood of a pathological condition, if the blood flow system does not work correctly, disturbances in the functioning of connective tissues or renal polycystosis are observed. A significant percentage of cases occur in congenital abnormalities in the state of blood vessels.
Possible causes of symptoms of aneurysm of the vessels of the brain, heart, aorta, and other localization options are trauma, neoplasm or wound. There is a higher probability of encountering pathology in heavy smokers and chronic hypertensive patients. Provoking aspects include infectious diseases, atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques on the vascular walls.
And if more?
Quite often, the cause of aortic aneurysm is hypertension. Damage, trauma, wounds localized in the abdominal cavity and chest can provoke pathology. A congenital defect of this vessel, atherosclerosis, can play its role. There are higher risks of aneurysm formation in patients with syphilis, as well as people who are often forced to face increased loads of various kinds - affecting their physical condition and psyche.
A common cause of heart aneurysm is heart attack. This pathological condition causes the formation of scars on the muscle tissue of the cardiac system. The wall formed by such fibers becomes thinner, and the contractility of the organ decreases. Since there is still blood pressure, the tissue is stretched and the segment protrudes outward. More often this type of disease is observed in the septum between the ventricles or in the left side of their cavities.
The cause of the aneurysm of the vessels of the peripheral circulatory system in most cases is erosive tissue changes and the patient received earlier trauma. Chronic hypertension and congenital disorders, abnormalities in the structure and functioning of the circulatory system can play a role. A dangerous factor is atherosclerosis.
How to suspect?
Regardless of the cause of the aneurysm (brain, aorta, other area of localization), the first manifestation of the pathological condition will be tingling, a feeling of constriction, disturbing exactly where the diseased vascular site is located. Discomfort is explained by pressure on organic structures near the vessel. If the aneurysm ruptures, acute and sharp pain occurs. In certain cases, the symptoms are completely absent. It is not uncommon for a pathology to be revealed by chance on a preventive examination, ultrasound, or when evaluating an x-ray, to which the patient was referred for a different reason.
Case clarification
Particularly attentive are patients who have the potential to cause aneurysm. Symptoms of this condition, as indicated above, may be absent, therefore it is important for people at risk to regularly attend preventive examinations to exclude pathology. If an aortic aneurysm is suspected, an instrumental examination of the patient's body is necessary. An ECG is taken, aortography is done, equipment for ultrasound, X-ray is used, the Wasserman reaction is specified.
Under the assumption of cerebral aneurysm, angiography of the vascular system of the organ is necessary. If there are reasons to suspect a cardiac aneurysm, the patient is shown an ECG, ultrasound, echocardiography. If a peripheral circulatory system is suspected as an area of localization, a person is referred for Doppler ultrasound, CT, angiography.
What to do?
If an aortic aneurysm (cerebral, cardiac, or any other) occurs (regardless of the cause), the patient is shown surgery. Untimely intervention or the absence of such a measure is fraught with the risk of rupture of the area. With the heart, as an area of localization, the patient is shown bed rest. At first, the stability of the state can be maintained with drugs for pressure and arrhythmias. With the progress of the case and insufficiency of the heart, it is important to operate on the patient as quickly as possible.
With an aortic aneurysm, it is indicated to take medications to stabilize the pressure. In a difficult case, an endovascular intervention or open surgery is performed. Aneurysm in the brain can only be treated surgically. During the intervention, doctors localize the affected area, exclude it from the system of communicating blood vessels.
Brain aneurysm: case features
This form can be suspected if the pain in the area of the eyes, forehead bothers, the pupils increase, vision becomes worse, and doubles in the eyes. Most cases do not attract the attention of patients, as the condition worsens gradually. Pathology can be suspected by numbness of the face, in severe cases - paralysis. Eyelids go down.
Acute sudden pain, blurred vision, stiffness of cervical muscle tissue, nausea, and vomiting indicate a gap in the area. Perhaps a convulsive or unconscious state, photophobia. Some impaired ability to speak coherently and articulate.
Even if, it would seem, there were no causes of the aneurysm of the brain, with a sudden and sharp pain, accompanied by double vision, you need to see a doctor. If a person nearby fell unpredictably, convulsive movements are noticeable, urgent need to call qualified help.
Possible factors: nuances of localization in the brain
Perhaps the most relevant and significant cause of cerebral aneurysm is genetic prerequisites. An abnormal structure, improper bends of system elements, as well as violations of the integrity and functionality of connective tissue can play a role. The likelihood of aneurysm as a complication is increased if a person suffers from Ehlers-Danlo pathology. It is possible to suspect aneurysm for headache if a head injury was previously suffered, a person has had an infectious disease, suffered a fungal infection or syphilis. The causes of cerebral vascular aneurysm include cancerous tumors in this localization area, as well as atherosclerosis.
The risk group for the described pathology includes overweight and smokers, as well as those who regularly use hormonal medications. The risk is higher if an abnormally high cholesterol level is detected in the circulatory system. One of the causes of cerebrovascular aneurysm is considered to be high blood pressure. More at risk are people damaged by stress factors. Certain risks are associated with ionizing radiation, renal hypoplasia.
Minimize risks: is it possible?
Knowing the causes of brain aneurysm, you can adjust your lifestyle so that the dangers are minimal. In particular, it will be necessary to take control of nutrition, reduce the intake of cholesterol with food, introduce adequate physical activity into everyday life and lose weight. In addition, all bad habits, and especially smoking addiction, should remain in the past.
Analyzing the causes of cerebral aneurysms, it is clear that risks can be minimized by controlling pressure, eating properly, and diluting the diet with fruits and vegetables. You will have to limit the use of hormones, and all medications taken are important to coordinate with the doctor. To reduce the dangers, one should revise the lifestyle and rhythm of life to minimize stress, and for any health problems, poor health, visit a doctor to determine the exact cause.
Clarification and treatment
If there are reasons to suspect aneurysm, it is necessary to come to the reception. First, the doctor will examine the patient, collect complaints and send them for analysis to clarify indicators of the functioning of the body. Basic information is obtained by examining cerebrospinal fluid. To confirm the diagnosis or its exclusion, CT of the brain, MRI, angiography are prescribed.
Aneurysm is a reason to worry, so treatment should be started immediately, as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed. With small dimensions of the pathology, you will have to reconsider the lifestyle, control the pressure and minimize the intake of cholesterol, with the given regularity come for examinations. If surgery is necessary, an open surgery can be performed by making cranial trepanation. Using bypass technology, doctors will strengthen the vascular walls. The endovascular method involves the introduction through the femoral artery of microscopic spirals that block the affected area.
Localization - Aorta
This pathology is quite common, in the age group over 65 years of age occurs with a frequency of one case per twenty people. If the problem area is torn, a high probability of death. The therapeutic approach is the removal of diseased tissues and their replacement with artificial ones.
Before considering the causes of aneurysm, attention should be paid to human anatomy. The aorta, among other arteries in the human body, is the largest. Through it, the heart is supplied with blood, from where the fluid through the branches of the arteries enters various tissues and organs. The aorta from the heart goes up in the form of an arc, descends through the chest, abdominal cavity.
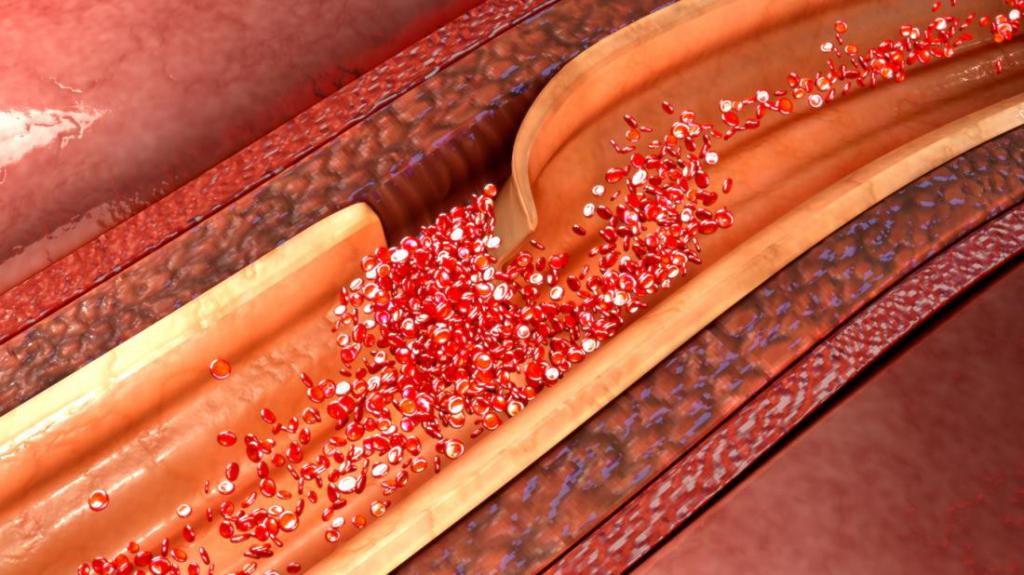
Aortic aneurysm is formed if a separate section of this vessel expands, protrudes. The predominant percentage of cases occur in the localization of the region in the abdominal cavity, the thoracic part is less likely to suffer. The aortic wall weakens, and blood pressure poses a serious threat to it. The probability of a gap largely depends on the size of the aneurysm. With sizes over 5 cm, every fourth patient, the gap occurs in the next nine years. With large dimensions, the danger is higher. If the aneurysm is small, the operation may not be prescribed, but you will have to visit the clinic every six months to monitor progress.
Symptoms and development of pathology
With an aneurysm localized in the abdominal cavity on the aortic wall, a person is disturbed by a pulsation, dull soreness. Your back may hurt. As a rule, before the first expressed manifestations, several years pass from the moment the aneurysm appears.
If a rupture occurs, an acute severe pain appears in the abdomen, extending to the back. The gap is the cause of severe bleeding. If you do not have an emergency operation, a high probability of death.
Causes and consequences
The most common cause of abdominal aortic aneurysm is atherosclerotic plaques. With the disease, cholesterol accumulates on the vascular walls, calcium deposits and fibrin are localized here. All this provokes protrusion and weakens the wall. The higher the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis, and, consequently, aneurysms, if a person smokes, suffers from high blood pressure and excess weight. There are more dangers if there is no physical exertion. A hereditary predisposition, gender (the danger is greater for men) plays a role. Aneurysm is more often fixed in people over 55 years old.
Sometimes an aortic aneurysm is formed against a background of trauma (more often due to an experienced accident), infection (syphilis), and congenital pathologies. The latter is the rarest case. For example, Marfan syndrome is one of the factors that increase the likelihood of thoracic aortic aneurysm.
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, you must consult a doctor. The doctor will examine the patient, prescribe a CT scan, ultrasound, X-ray with a contrast agent. When confirming the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed, based on the symptoms of the case, the size of the affected area. At break urgent operation is necessary. The event is associated with a high risk, the risk of death is quite significant.
About the breaks
Currently, it is not possible to accurately determine the causes of rupture of the aneurysm. It is only known that this can happen quite suddenly, without any prerequisites. According to statistics, with a break, up to 60% of victims die immediately, about a quarter get disability, and only about 15% of people can return to normal life, work activity.
Aneurysm has three stages: prehemorrhagic, hemorrhagic, posthemorrhagic. Before the break, often there are practically no symptoms. An atypical gap with an erased picture, the formation of a small volume is possible. In this case, a rupture of a cerebral aneurysm is similar to inflammatory processes in the meninges, a hypertensive crisis.
Brain aneurysm: course and rupture
Perhaps the development of a giant aneurysm. Before the break, this is similar in manifestations to a brain tumor. The patient is disturbed by pain in the head, it is difficult to coordinate movements, vision is deteriorating, the head is spinning. At the time of rupture, the manifestations are similar to a subarachnoid hemorrhage of a non-traumatic nature. A person complains of a headache, sensations are comparable to a strong blow, it becomes impossible to navigate in space. The symptomatology resembles meningitis: the muscles on the back of the head are stiff, the light scares, the patient feels sick and vomits. Gradually, signs of a stroke may appear: sensitivity decreases, the pupils do not respond to light, the muscles of the face are asymmetric, the smile is spastic, twisted.
If the case is severe, symptoms of impaired functioning of the nervous system of the brain are gradually observed. Nystagmus appears, on one side of the face the eyelid drops, dries in the mouth, the ability to recognize odors disappears. The meninges are irritated by blood and its metabolites. One of the possible consequences is a vasospasm. Such a complication usually develops a few days after blood loss, due to the toxic effect on the vasomotor centers. In some cases, vasospasm persists until the crescent. It cannot be cured, and the consequence is an ischemic stroke. The nuances of symptoms depend on the area of localization.
Manifestations and clarification of the state
A rupture of the aneurysm is indicated by a deterioration in the patient's perception of speech. Disturbances in motor reactions, difficulty in coordination of movements are visible from the side. Noises in the ears, uncontrolled urinary acts are possible. After a primary hemorrhage, relapse is particularly high over the next month.
To clarify the condition, the patient is shown cerebral angiography by CT. In the framework of the study, the places of protrusion and the area where the vascular lumens are greatly dilated are determined. According to the results of CT scan, bleeding is localized, the volume of affected areas is assessed, the presence and level of hydrocephalus is determined. At the pre-hemorrhagic step, the maximum of useful information can be obtained through MRI. Among invasive ones, the most useful diagnostic method is cerebral angiography.
The patient can take urine and blood for examination. Both general analyzes and biochemistry studies do not show specific abnormalities.
Consequences and future
Rupture of cerebral aneurysm causes a stroke, vasospasm, hemorrhage. This condition can lead to severe dropsy. Perhaps a violation of the structures of the nervous system - they are irreversible. Aneurysm rupture can cause loss of vision, impaired ability to speak. Possible consequences - paresis, paralysis, inability to move, coordinate actions. It is known that in some cases, rupture of the aneurysm became the cause of the tendency to epileptic seizures.
With the clinical picture of non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage, it is urgent to hospitalize a person in a hospital. Regardless of the location of the gap and its dimensions, an urgent operation is required. Vascular spasm significantly worsens the picture and prognosis, reduces the likelihood of a full recovery. Assessing the effectiveness of the selected treatment, it is necessary to analyze the progress of the weakening of symptoms and the rate of return to normal of the main affected functions.
Treatment features
Before surgery, conservative therapy is indicated. The main task pursued by doctors is to stabilize the patient's condition and prevent relapse, as well as vasospasm. If one has developed, medications are chosen so as to alleviate the condition. With manifestations of ischemia, therapy is aimed at stopping them. To reduce the likelihood of complications in the postoperative period, to simplify the intervention itself, lumbar drainage should be done. It is shown to remove about 20 ml of cerebrospinal fluid. To reduce the risk of dropsy, resort to external drainage. Vascular spasm is prevented by the elimination of blood clots, the elimination of a hematoma, after which the aneurysm is excluded from the blood circulation system.
In some cases, the operation is impossible - for example, the patient's condition can be very serious, it is not possible to stabilize him. In such a situation, external decompression and removal of the hematoma without aneurysm are indicated. The patient is given drainage. With small dimensions of the pathological region, the wide neck of the aneurysm, with a giant bulging area that cannot be operated on, occlusion inside the vessels is indicated. Use a stand or balloon remodeling.
If residual bleeding persists after surgery performed by the endovascular method, the operation should be repeated using open technology. After clipping, a puncture or an autopsy is indicated, designed to exclude the diseased area from the system of communicating vessels.