Pathogenic microorganisms surround us everywhere, but with strong immunity, the body quickly copes with them. When the immune system is weakened, pyogenic bacteria on the surface of the skin are rapidly activated and lead to the development of a disease such as staphylococcal pyoderma. You can get rid of the pathology, but only using an integrated approach to therapy.
Features of the disease
The most common causative agent of the disease is staphylococcus. These bacteria are quite stable, so they can be found in the air, on household items, on human skin. With weakened immunity, the pathogenic microorganism quickly leads to the development of the disease.
Several provoking factors of staphylococcal pyoderma can be distinguished:
- Regular personal hygiene.
- Permanent injuries, abrasions and cuts.
- Impaired metabolism.
- Diseases of the internal systems of organs.
Almost 30% of people are carriers of Staphylococcus aureus. The pathogen can be picked up anywhere, perhaps even self-infection, when the bacterium from a healthy area of the skin enters the wound.
Staphylococcal pyoderma is often found in children and it proceeds much harder, given that in children the immunity is not yet fully formed.
Regardless of the form, the disease is considered contagious, and therefore requires urgent treatment.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Streptococcal infection enters the body through wounds and abrasions on the skin, causing the development of an inflammatory process. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the sebaceous and sweat glands, affect the hair follicles.
The activity of reproduction of the pathogen and the depth of infection depends on the strength of the immune system.
To provoke the development of staphylococcal pyoderma can:
- Dental problems.
- Lymphadenitis
- Purulent lesions of internal organs.
If immunity is weakened, then microorganisms multiply rapidly and quickly spread throughout the body. In the course of their life, they produce toxic substances, which provoke the development of characteristic symptoms of intoxication.
It is important to start therapy when the first symptoms appear, in order to reduce the likelihood of complications.
Varieties of pathology
There are several types of staphylococcal pyoderma. The types of disease doctors distinguish the following:
- Osteofolliculitis. The pathology is localized in the area of the face, it can affect the scalp. Superficial pyoderma often passes in a short period of time without leaving marks on the skin. If the inflammatory process is complicated, then other forms of pathology may develop.
- Staphylococcal folliculitis. With this type of disease, the hair root is inflamed. Of the symptoms, redness around the follicle, the spread of infection to neighboring tissues, can be noted. With complications, an abscess develops, which requires an autopsy. A pustule is formed the size of a pea with a hair in the center. After a few days, the inflammation subsides, the wound dries up, and the resulting crust soon falls off.
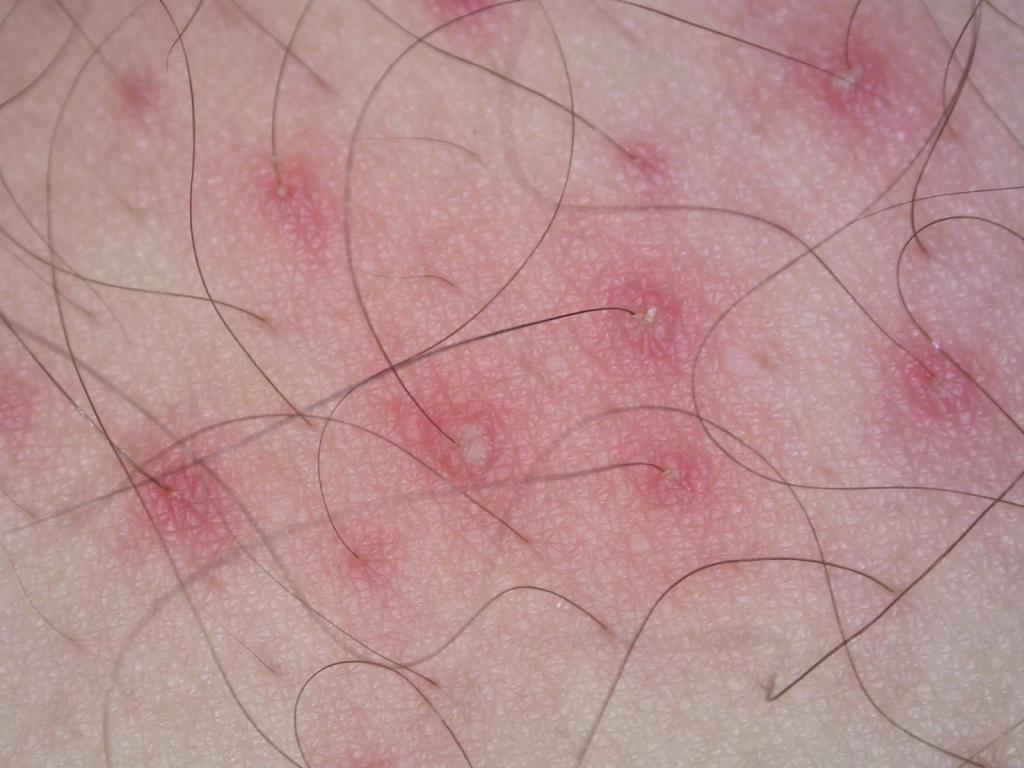
- Sycosis is another superficial form of pathology. It often develops against the background of ostiofolliculitis. Multiple foci of inflammation appear more often on the face, but can also affect the armpits.
- Folliculitis abscessed. Chronic form of purulent-inflammatory process. Most often diagnosed in representatives of the stronger sex. Pathology is accompanied by the appearance of acne, inflammation of the scalp. If pustules with purulent contents are opened, fistulas form. The treatment of staphylococcal pyoderma is complex and lengthy.
According to experts, the most complex forms of pathology are hydradenitis and furunculosis. These varieties of pyoderma are accompanied by the release of a large amount of pus. Neighboring tissues are involved in the pathological process.
If hydradenitis takes place, then increased sweating appears. Most often, this form is diagnosed in women. Furunculosis can develop after severe hypothermia on the background of a weakened immune system.
Manifestations of the disease
Regardless of the form, staphylococcal pyoderma exhibits similar symptoms, which can be observed immediately after the pathogen penetrates the body. Among the main manifestations, the following are noted:
- Redness and pain.
- Itching and burning of the skin.
- In the area of the formation of pustules, tingling is felt.
- A few days after infection, multiple rashes appear.
- Purulent vesicles with red edges form.
- After rupture of pustules, the wounds heal and disappear.
If the pathology affects the deeper layers of the skin, then scars may appear after healing.
The distinctive symptoms of staphylococcal pyoderma include:
- Itching of the skin.
- Multiple rashes.
- Tendency to relapse.
If the disease becomes chronic, then the painful sensations become less pronounced. The skin becomes tuberous, increases the release of sebum and sweat, which provokes the appearance of new formations.
Chronic pyoderma is characterized by the simultaneous presence of healing wounds and formations with purulent contents.
Staphylococcal pyoderma in adult women is often diagnosed with hormonal disorders. Pathology may be accompanied by gynecological problems.
Establishing diagnosis
Only a thorough diagnosis of staphylococcal pyoderma will reveal the nature of the pathogen and prescribe adequate therapy. It includes the following analyzes and studies:
- General analysis of blood and urine.
- Determination of the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibacterial drugs. For this, purulent contents of pustules are taken for examination.
- Screening for syphilis.
- If necessary, consultation with an endocrinologist and a neurologist will be required.
- Hormone testing for diabetes.
To clarify the diagnosis, it is important to conduct a differential diagnosis to distinguish furunculosis from hydradenitis and carbuncle. Folliculitis can be confused with lichen planus or acne.
Chronic pyoderma must be differentiated from bromoderma, and sycosis from trichophytosis, but this pathology manifests itself with more pronounced symptoms.
Pathology in children
Purulent-inflammatory skin lesions often occur in infants of the first months of life, which is associated with low activity of local immunity. The upper layer of skin in babies has an alkaline environment, which is favorable for the development of pathogenic microflora.
The skin of the child has not yet adapted to temperature changes, the functioning of the sweat glands is not established. All these factors provoke the development of pathology, but several more reasons can be distinguished:
- Lack of vitamins in the diet of the mother, if the baby is naturally fed or in mixtures.
- Digestive tract diseases.
- Diaper rash on the skin.
- Abrasions, wounds on the baby's body.
- Poor hygiene.
- Allergy.
- Metabolic disorder.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Diabetes.
Many parents do not pay attention to the symptoms of staphylococcal pyoderma. They send the baby to a nursery or garden, without thinking that this infection is very contagious.
Classic treatment
Staphylococcal pyoderma is necessarily treated with antibacterial drugs. Most often, they have to be applied externally to the skin, but with a complicated course of the disease, the doctor prescribes antibiotics inside.
If the disease proceeds in an acute form, then the drugs are taken for a week. With the transition of the pathology to the chronic form, antibiotic therapy lasts at least 15 days. Specialists prefer to use in the treatment of drugs with a wide spectrum of action.
Among the most popular and effective drugs are the following:
- Amoxicillin 500 tablets, the instructions for use contain information on the effectiveness of the drug against coccal infections.
- Ampioks. The medicine fights infection well due to the destruction of the bacterial cell wall.
- "Cefotaxin", "Cefazolin" will help to cope with a mixed type of infection.
- To combat the disease, tetracycline drugs are also prescribed. Among them are Doxycycline tablets. Instructions for use contain complete information about the mechanism of action of the drug. The active substance blocks the synthesis of protein molecules in a bacterial cell, causing its death.
- Macrolides are similar: Clarithromycin.
- Aminoglycosides: Gentamicin, Amikacin can help in the fight against infection.
Treatment of staphylococcal pyoderma with drugs should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
External treatment of the disease
Along with the internal use of antibiotics, each patient is prescribed external use of drugs. Effective are:
- To suppress the reproduction of gram-positive microorganisms, it is possible to treat the skin areas with "Diamond green".
- Salicylic ointment with antibacterial effect. After application, the upper layer of the epidermis softens, and the inflammatory process decreases.
- A solution of potassium permanganate is able to neutralize the effects of certain toxic substances that cause pathogenic bacteria.
- A gel or chlorhexidine solution perfectly inhibits the activity of pyogenic bacteria, which actively multiply with staphylococcal pyoderma. The drug does not lose its activity in human blood and in purulent wounds.
- Cream for external use "Triamcinolone". It reduces the intensity of the inflammatory process and has an anti-allergic effect.
- "Fukortsin." With this tool, you can treat the affected areas of the skin to reduce the intensity of the infectious process and block the activity of fungi.
The duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician. If after applying the external remedy the symptomatology does not decrease, but signs of an allergic reaction appear, it is necessary to inform the doctor and choose another medicine.
Immune Therapy & Combination Therapy
To increase the effectiveness of therapy, doctors often prefer to prescribe combination medications to patients, which simultaneously remove the inflammatory process and destroy bacteria. On the good side, the following drugs have proven themselves:
- Lorinden C This cream is used externally. The course of therapy allows to suppress the growth of staphylococci, removing inflammation and exerting anti-allergic effect. The product must be applied to the affected area of the skin, and cover with a bandage on top. It is necessary to change 3-4 times a day.
- Fucicort cream has a decongestant and antibacterial effect. Apply to the skin twice a day. Such therapy lasts at least 2 weeks.
- To reduce allergic manifestations, eliminate skin itching and suppress coccal infection, ointment "Gyoksizon" is perfect.
To accelerate recovery, immunostimulating therapy is indicated. To do this, the doctor introduces a special vaccine to the patient, which stimulates the formation of immune cells to fight the infection.
Immunostimulating therapy is indicated in cases where the disease often recurs. Of the drugs with such an action, appoint:
- "Lycopid."
- "Timoptin."
- Taktivin.
Classical treatment can be enhanced by the appointment of helium-neon radiation. The procedure is prescribed daily for two weeks.
Surgery
If the pathological process proceeds with a complication and there are symptoms of tissue necrosis, then surgical intervention is indispensable. The essence of the operation is as follows:
- The surgeon opens the abscess.
- Cleans contents.
- Carries out treatment with antiseptic agents.
- Installs drainage.
After surgical treatment, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. These can be Amoxicillin 500 tablets; instructions for use will be given by the attending physician.
Treatment of pyoderma in children
If the pathology proceeds without complications, then hospitalization of the baby is not required, therapy can be performed on an outpatient basis. The right treatment tactics will help to quickly defeat the pathology. Therapy in children includes the following measures:
- External treatment of affected skin with Chlorhexidine, boric or salicylic alcohol.
- Application to the skin of "Fucorcin" or iodine.
- You can do lotions with potassium permanganate.
- Antimicrobial and corticosteroid drugs are prescribed only by a pediatrician. The choice of drug depends on the severity of the pathology. At the first stages, it is recommended to use ointments based on sulfur, tar.
- If the effectiveness of therapy is weak, then the doctor prescribes treatment with antibacterial agents: Levomycol, Linkomycin.
- In severe cases, it may be necessary to prescribe Prednisolone, Oxycort.
With complications, the doctor prescribes the following drugs to the child:
- Doxycycline tablets Instructions for use of the drug should be studied in detail, therapy is carried out strictly according to the doctor’s scheme and in the recommended dosage.
- Sulfanilamides: Biseptol, Norsulfazole.
- Preparations for stimulating the immune system: Amiksin, Immunal.
- To prevent an allergic reaction, antihistamines must be taken: "Zodak", "Telfast".
For effective treatment, it is important for the child to properly treat the affected areas of the skin. The first procedures are best entrusted to a specialist and carried out in a clinic by a dermatologist. The following can be carried out at home according to the following algorithm:
- Wash hands thoroughly.
- Wear disposable gloves.
- Treat each affected area sequentially separately using a cotton swab.
- Treat healthy skin with an antiseptic.
- After the epidermis has dried, apply the ointment prescribed by the doctor.
- Wear carefully-ironed clothing on both sides of the child.
According to this algorithm, the skin is processed in children of different ages.
Traditional medicine against pyoderma
If the disease proceeds without complications, then you can use the recipes of folk doctors. They will help eliminate skin itching, stop the reproduction of pathogenic microflora. The following recipes have proven effective in therapy:
- Take 20 g of celandine leaves and pour 100 ml of vegetable oil. Insist for several days and use to treat the affected areas three times a day for 3 weeks.
- 2 tablespoons of dill seeds pour boiling water in an amount of 0.5 liters. After insisting, treat the skin up to 5 times a day.
- Squeeze the juice from raw potatoes, soak them in a napkin and apply to inflamed skin for 2 hours.
- It helps to strengthen the body, increase its immunity to infections, decoction of the roots and leaves of dandelion. To prepare it, you need to pour 2 tablespoons of raw materials into a glass of water and boil over low heat for 10 minutes, then leave for several hours to insist. It is recommended to drink the drug before meals in 100 ml.
Disease complications
It is dangerous to let it go by itself or self-medicate pyoderma, since pathology can lead to serious consequences. Among the complications may be the following:
- Sepsis.
- An allergic reaction with Quincke's edema.
- Gangrene.
- Infection of the skeletal system and internal systems of organs.
- Lymphangitis.
- Retinal inflammation.
- Vascular thrombosis in the brain.
- Inflammation of the meninges.
- Purulent mediastinitis.
Disease prevention
Any infectious skin disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Especially if there is a tendency to pyoderma. Prevention measures include the following:
- Strictly follow the rules of personal hygiene.
- Clothing should be made of natural fabrics and not tight, so as not to irritate the skin.
- Any abrasions, cuts must be thoroughly disinfected.
- Use products with antibacterial effect for skin care.
- Monitor the level of perspiration.
- Wash tops regularly and change underwear daily.
- Strengthen the immune system.
- Carry out hardening procedures.
- Eliminate any foci of inflammation in a timely manner.
- To treat the pathology in a chronic form: tonsillitis, pyelonephritis, cholecystitis. Prevention measures include the following: Strictly follow the rules of personal hygiene.
- If the skin is prone to inflammatory reactions, then any abrasions, minor burns should be treated with alcohol, and then washed with hydrogen peroxide. After treatment, apply a sterile dressing.
, . , .