Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a natural result of HIV infection. However, with the early detection and administration of appropriate medications, years pass before the onset of this moment. Control and monitoring of blood leukocyte concentration in HIV infection is an important component of therapeutic treatment. Thus, the progression of HIV can be prevented, and, accordingly, and increase the life of the patient by several decades. White blood elements help the immune system in the fight against microorganisms, viruses, malignant neoplasms. Protect the body of the individual from the penetration of allergens, protozoa and fungi.
What are the most affected white blood cells in HIV?
The immunodeficiency virus, affecting the immune cells, interferes with their work, and over time they cease to perform their functions. As a result of these processes, the body cannot fight infections and slowly dies. HIV infects those protective cells on the surface of which there are CD-4 protein receptors. A large number of them are contained in the membrane of T-helper lymphocytes. Due to the activation of other lymphocyte cells, they significantly increase the response to the penetration of infectious agents into the body. In addition, CD-4 contain macrophages, monocytes, Langerhans cells and others.
Initially, the presence of the immunodeficiency virus can be suspected by deciphering the results of a UAC (general blood test). In the early stages of HIV, white blood cells are elevated. With progression, neutropenia (a decrease in neutrophils) and lymphopenia (a decrease in lymphocytes) and, as a result, a weakening of immunity are observed. Of course, a complete blood count is not specific. At different stages of the disease, white blood cells can be both above and below acceptable values.
Blood test for viral load with suspected HIV
This is a proven and informative type of diagnosis. Some leukocytes contain a protein receptor CD-4, and since these cells are the first to be affected by human immunodeficiency virus , the calculation of CD-4 is important in the diagnosis of HIV. If an individual has the wrong diet or shortly before the delivery of biomaterial, he suffered a severe nervous shock, then the results of the analyzes will be inaccurate. In addition, the final result is also influenced by the time period, i.e., in which half of the day the blood was donated. A reliable, almost one hundred percent result can only be obtained by delivering biomaterial in the morning. Acceptable indicators of CD-4 (measured in units) depend on the state of the individual:
- HIV-infected up to 3.5;
- with a viral or infectious disease 3.5–5;
- almost healthy 5–12.
Thus, the higher the value of this indicator, the less likely the patient to have HIV. To confirm the diagnosis, KLA is needed to be sure of a low white blood cell concentration. An analysis of the viral load reveals in the blood the components of RNA-HIV that are not detected in a healthy individual. Analyzing this indicator, the doctor predicts the further development of the disease.
With HIV, are white blood cells increased or decreased?
Depending on the stage of the disease, the concentration of leukocytes increases or decreases. First of all, HIV has a damaging effect on the protective cells of the body, including the composition of the blood. Therefore, the aggravation of the disease can be prevented and thereby prolong the individual's life. One of the most famous studies that reflect the composition of blood cells is OAC. The biomaterial for the study is taken from the finger. When decoding the results, special attention is paid to leukocytes. With HIV infection, this is especially significant. Blood cells are divided into several groups that perform different tasks:
- Lymphocytes As soon as the infection enters the bloodstream, these cells are activated to fight it and their number increases. Nevertheless, such resistance does not bring effect, and HIV continues to develop. In the absence of therapy at the initial stage, the number of lymphocytes decreases, which is an alarming bell.
- Neutrophils are the body’s defenders from immunodeficiency states and viruses. Their concentration decreases when the pathogen enters the bloodstream, and this condition is characterized as neutropenia.
- Platelets - affect blood coagulation. In HIV-infected individuals, this indicator is low, which contributes to the formation of sudden bleeding, which is quite difficult to stop, and sometimes impossible.
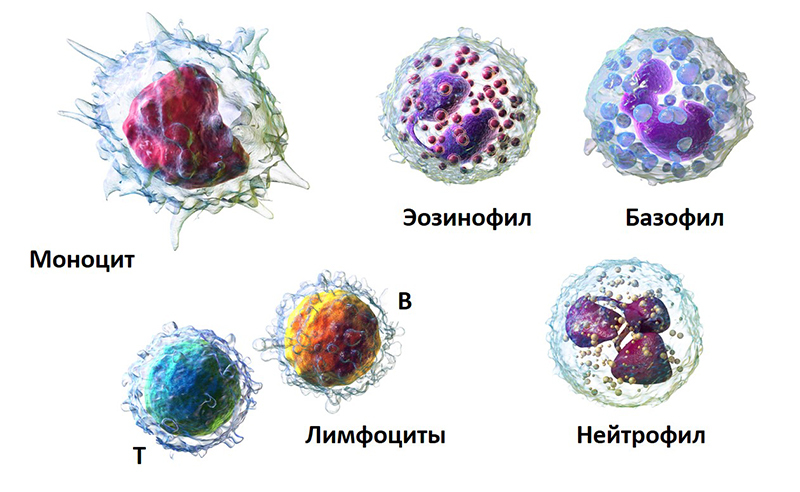
Regardless of the functions performed, all leukocytes jointly organize strong protection of the individual's body, identifying and destroying harmful elements. In addition, the patient has a low hemoglobin due to the deterioration of the red blood cells, which are responsible for the delivery of oxygen to tissues and organs. As a result, the body's resistance to infections is almost completely absent. If HIV is detected, one should regularly visit the attending physician and take the biomaterial to the KLA. When studying the results of the study, the doctor first of all studies in the results how many leukocytes. With HIV, it is these cells that first suffer. Monitoring indicators in dynamics makes it possible to track the development of the disease, prescribe the necessary treatment and extend the life of the infected person. Lack of therapy is fraught with death approximately two years after the initial infection of the blood.
General blood test for white blood cells
An interesting fact is that when examining leukocytes under a microscope, they are pinkish-purple in color, and they call them white blood cells. The biomaterial for the study is taken from the finger. HIV-infected people pass it on a quarterly basis. Special preparation before passing the analysis is not required. Doctors recommend adhering to certain conditions, namely, to take them in one clinical laboratory in the morning and on an empty stomach in order to obtain reliable results, since the number of leukocytes depends on the time of day and diet. Acceptable indicators of white cells in children and adults are different, and gender does not matter. In a practically healthy individual, the leukocyte formula (as a percentage of the total number of immune cells) is as follows:
- neutrophils - 55;
- lymphocytes - 35;
- basophils - 0.5–1.0 - help other white blood cells recognize foreign agents.
- eosinophils attack allergens - 2.5;
- monocytes - 5 - absorb foreign elements that have penetrated into the blood.
For diagnosis, it is important not only a deviation from the norm, but an increase and decrease in the total number of leukocytes. With HIV infection, first of all, attention is paid to the level of lymphocytes. The initial stage is characterized by increased concentration, and the further spread of infection and, as a consequence, a weakening of immunity reduces this indicator. It is important to remember that the KLA does not aim at making an accurate diagnosis, it only shows changes in the blood composition, on the basis of which the doctor decides on further actions.
When is a Jab for HIV needed?
The following are situations in which this analysis is required. You can do it in any healthcare institution and for free:
- When registering for pregnancy.
- A sharp decrease in body weight (in the absence of a cause).
- The use of narcotic drugs for non-medical purposes.
- Unprotected sex and frequent changes of partners.
- Sex with HIV.
- Persistent health problems. When the virus is affected by immunodeficiency, a decrease in immunity occurs, and the individual becomes vulnerable to various diseases.
- Chronic fatigue and weakness.
- With surgical interventions or blood transfusion.
An analysis will show changes in blood counts in infected individuals, including a violation of the white blood cell count.
Changes in the general analysis of blood
With HIV, the level of leukocytes changes and manifests itself:
- lymphocytosis - a high level of lymphocytes;
- neutropenia - a decrease in the number of granular leukocytes;
- lymphopenia - a low concentration of T-lymphocytes;
- platelet lowering.
In addition, revealed:
- high ESR;
- increased mononuclear cells;
- low hemoglobin.
However, not only with HIV, white blood cells undergo changes. This phenomenon occurs in other pathological conditions. Therefore, based on the results obtained, experts prescribe additional types of research.
Low white blood cell count
When identifying such a result, a thorough examination is necessary. Protecting the body from the effects of pathogens is considered the main function of white blood cells. At their low level:
- colds are a frequent companion;
- infectious conditions are observed for a long period and give complications;
- fungi affect the dermis and mucous membranes;
- high risk of contracting tuberculosis.
The level of leukocytes is influenced by the time of day, diet, age. If the number of cells is less than 4 g / l, then this condition is called leukopenia. White blood cells are quite sensitive to various internal and external factors. Low leukocytes are observed with:
- HIV infection
- exposure to radiation;
- bone marrow underdevelopment;
- transformations in the bone marrow associated with age-related changes;
- autoimmune disorders in which antibodies to leukocytes and other blood elements are synthesized;
- leukopenia, the cause of which is a hereditary predisposition;
- immunodeficiency conditions;
- endocrine diseases;
- the destructive effects of leukemia and bone marrow metastases;
- acute viral conditions;
- renal, hepatic and cardiac failure.
Basically, a deviation from acceptable values occurs as a result of insufficient production of cells or their premature destruction, and since there are several types of leukocytes, the deviations of the leukocyte formula are different. Conditions in which both lymphocytes and leukocytes are lowered are:
- HIV
- damage to the immune system;
- hereditary mutations or pathologies;
- autoimmune disorders;
- infectious bone marrow lesions.
Thus, when the level of cells changes, an additional examination is required. Excess and lack of them negatively affects health.
Causes of a decrease in blood lymphocytes
Lymphocytes, which belong to the group of leukocytes, in HIV and other conditions of the body are responsible for cellular immunity, distinguishing between their own and foreign proteins. A low level of lymphocytes, the norm of which depends on age, indicates lymphopenia. In the leukocyte formula, they must correspond to a certain amount. Permissible percentage of deviations from the total number of all elements:
- 20 - in adolescents and adults;
- 50 - in children from five to seven years;
- 30 - in babies.
A slight decrease in lymphocytes occurs with infections. In this case, the focus is rapidly attacked by immune cells, and lymphopenia is temporary. For a correct diagnosis, it is important to find out as quickly as possible the reason why these cells decreased. Low leukocyte counts are detected in HIV, as well as in:
- miliary tuberculosis;
- severe infections;
- aplastic anemia;
- chronic liver disease;
- chemotherapy
- lupus erythematosus;
- destruction of lymphocytes;
- corticosteroid intoxication;
- lymphosarcoma;
- and etc.
The detection of lymphopenia requires immediate treatment of the pathologies that provoked it.
Causes affecting white blood cell count in immunodeficiency virus
The provocateurs of elevated white blood cells in HIV or, conversely, low, are various processes that occur in the body:
- intoxication caused by poisoning with toxic substances;
- malignant neoplasms;
- purulent-inflammatory processes;
- myocardial infarction;
- burn;
- acute stroke;
- leukemia;
- autoimmune conditions;
- hypersplenism syndrome;
- immunodeficiency conditions other than HIV;
- hypoxia;
- conditions that have a negative effect on immunity;
- parasitic and bacterial infections;
- failure in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- and others.
In addition to HIV, an increase in white blood cells is observed in nervous breakdowns. Reduced or increased content of these cells may be from overheating or hypothermia. Therefore, it is impossible to diagnose an immunodeficiency in an individual by only one increased indicator. In order to correctly evaluate the results of studies, it is necessary to find out the anamnesis.
Conclusion
Timely detection of the immunodeficiency virus and the use of antiretroviral therapy prevents the activation of the infectious process, and, accordingly, AIDS. Successfully copes with the tasks of early diagnosis, a conventional blood test. With the immunodeficiency virus, first of all, the indicators of leukocyte cells responsible for the immune system change. It is no coincidence that leukocytes in the blood with HIV are called a mirror, which reflects the course of the pathology. The determination of their number is important both for predicting the infectious process and for the prevention of severe complications.

In addition, the individual has a rather low level of hemoglobin, as a result, the body's resistance is limited and anemia occurs. Detection of HIV cells requires a person to visit the attending doctor at least four times a year, take tests and undergo the necessary examinations. It is important to remember that regular monitoring of the development of the disease and the timely correction of drug treatment prolongs life.