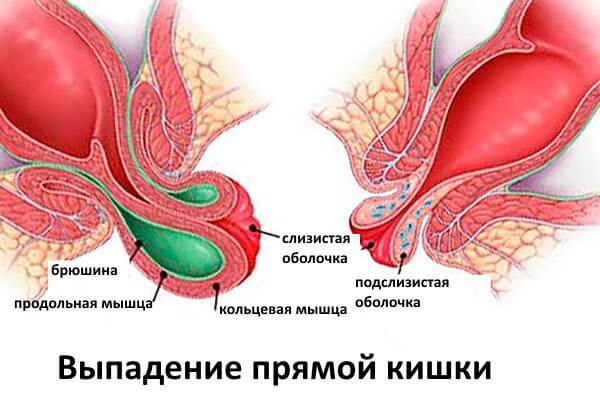
Prolapse of the rectum is an extremely unpleasant pathology, which is accompanied by a displacement of the distal parts of the rectum and its exit beyond the sphincter of the anus. A similar problem is most often encountered by people of young and mature age. The disease is not uncommon in pediatric practice.
Of course, many people are looking for any information about the disease. What is the danger of rectal prolapse? Symptoms, causes, treatment, possible complications - this is important information that should not be overlooked. So, when is it worth going to a proctologist?
Rectal prolapse: ICD-10, general information
Many people are looking for information about this disease. Prolapse of the rectum (ICD - 10 assigned code K62 to this pathology) is a pathology that is accompanied by a displacement of the distal (lower) part of the colon, as a result of which a small fragment of the intestine comes out through the anal sphincter. The length of the segment that falls out can vary from 2 to 20 centimeters, depending on the stage of development of the disease.
Quite often, rectal prolapse is diagnosed in children aged 3-4 years, which is associated with the anatomical features of the growing organism. Risk group - young and mature people under the age of 50 years. By the way, according to statistics, 70% of patients with a similar diagnosis are men.
The main causes of the disease
The causes of rectal prolapse can be varied and a list of them is worth a look.
- There is a hereditary predisposition.
- Constant tension of the abdominal wall and pelvis during bowel movements. Similar is observed during bowel movements.
- Potentially dangerous are salmonellosis, dysbiosis, enterocolitis, dysentery and other diseases that are accompanied by prolonged dierea.
- Prolapse of the rectum in women is often the result of birth injuries, rupture of the perineum, complications during pregnancy.
- Some pathologies of the rectum, in particular, hemorrhoids, can lead to a similar result.
- Prolapse often develops in people with congenital anatomical features (for example, an elongated sigmoid colon is considered a risk factor).
- The development of such a pathology can result in heavy lifting, intense physical activity (professional athletes often face this problem).
- Various neuralgic disorders, injuries and brain tumors, impaired innervation of the muscles of the pelvis and sphincter, inflammation of the nerve structures are potentially dangerous.
Risk factors
There are factors whose influence increases the likelihood of rectal prolapse (if there are prerequisites, of course). Their list is quite impressive:
- diseases of the digestive tract, in particular, the formation and growth of polyps, chronic diarrhea, etc .;
- pathology of the organs of the genitourinary system, for example, urolithiasis, inflammation of the prostate in men;
- decreased sphincter tone, weakening and sprain (such changes are a natural part of the aging process);
- disorders of the pelvic organs, blood stasis;
- excessive passion for non-traditional types of sexual contacts (anal sex is always associated with the risk of damage to the rectum);
- neurological diseases that affect the spinal cord;
- a similar pathology in infants sometimes develops against a background of diseases accompanied by severe cough (pertussis, bronchitis, pneumonia are risk factors).
What symptoms appear on the background of the disease?
Symptoms of prolapse of the rectum can be different, since the features of the clinical picture directly depend on the degree and stage of development of the pathology.
- Often, patients complain of pain in the lower abdomen, the appearance of which is associated with a tension in the mesentery. Soreness increases during walking, running, physical exertion. If you adjust the intestine, then the patient's well-being improves, but only temporarily.
- Sometimes during tension of the abdominal wall, only a small area of the mucous membrane falls out. But in more serious situations, a fragment of 8-10, and sometimes 20 cm, falls outside the sphincter - the process is accompanied by very unpleasant sensations that simply cannot be overlooked.
- A person is constantly tormented by the sensation of a foreign body in the anus, which is associated with a displacement of the mucous membrane and other tissues.
- There are problems with the stool. For example, many patients complain of frequent urges that do not end with bowel movement despite all efforts. In addition, a sick person is tormented by constipation, as well as the feeling that the intestines are not completely empty. Some people complain of chronic constipation, which only exacerbate the situation. At later stages of the development of the disease, involuntary bowel movements are possible.
- The displacement of the structures of the large intestine affects the functioning of the genitourinary system. Many patients report frequent urination, and sometimes complain of a feeling of a constantly full bladder. In later stages, urine leakage is possible.
- Prolapse of the rectum in women is often associated with prolapse or prolapse of the uterus.
- Quite often, the ailment is accompanied by the appearance of mucous secretions, sometimes with an unpleasant odor. Minor bleeding is also possible, which is associated with an injury to the intestinal mucosa during bowel movements.
Having noticed such violations, it is very important to consult a doctor. Unfortunately, people prefer to keep silent about such a delicate problem, therefore they turn to a specialist at the later stages of the development of the disease.
Degrees and stages of loss
Diseases of the anal canal and rectum - the group to which this pathology belongs according to ICD-10. Signs of prolapse of the rectum directly depend on the stage of development of the disease. To date, there are four main stages.
- In the first stage, prolapse occurs only during bowel movements. Immediately after emptying, the direct cyst returns to its place on its own.
- The second stage is accompanied by more severe symptoms. Prolapse of the rectal mucosa, as before, occurs during emptying. The gut itself falls into place, but this happens very slowly. At this stage, patients are more likely to suffer from discomfort. May cause minor bleeding.
- In the third stage, prolapse of the rectum already occurs during physical exertion, in particular, lifting weights. Independently, the mucous membrane no longer sets.
- The fourth and last stage is accompanied by an almost constant loss. The rectum moves through the anus during laughter, talking, walking. At this stage, necrosis of the intestinal mucous membranes begins.
There are four degrees of rectal prolapse in humans:
- I degree - only prolapse of the mucous membrane is observed (it slightly turns out during bowel movements).
- II degree - all layers of the anal part of the rectum fall out.
- III degree - there is a complete prolapse of the rectum.
- IV degree - the entire rectum and even the sigmoid region fall out.
Of course, the choice of treatment methods depends on the degree and stage of development of the pathology. If conservative therapy is still possible at the initial stages, then only surgical intervention can help in the later stages.
Possible complications
Prolapse of the rectum is an extremely unpleasant and dangerous disease that should not be ignored. If untreated, the disease can lead to infringement of the intestine. There is a likelihood of developing intestinal obstruction, and in more severe cases, peritonitis.
If we are talking about the last stages of the development of the disease, then the beginning of the necrotic process is possible. If untreated, the pathological process can spread to other parts of the digestive tract. In such cases, the risk of gangrene is high - in the absence of treatment, the ailment can result in the death of the patient.
Of course, constant pain, fecal incontinence, increased gas formation and other symptoms affect the patient’s emotional state. A person feels constrained, sleeps poorly, has difficulty communicating, becomes closed, and sometimes asocial.
Diagnostic measures
Of course, in this case, diagnosis is very important. The doctor needs to determine the degree and stage of the development of the disease, and also, if possible, find out the causes of the pathology.
- First of all, the specialist conducts a survey, collects information for making an anamnesis, is interested in the presence of certain symptoms and the circumstances of their appearance.
- Subsequently, an external examination is carried out. It is very important to differentiate this disease from hemorrhoids. Prolapse of the rectum is characterized by the formation of transverse folds of the mucous membrane. But if during the examination and palpation, the doctor noticed that the folds of the intestinal mucosa are longitudinal, then this may indicate hemorrhoids. During the examination, the doctor assesses not only the relief, but also the tone of the mucosa. Sometimes a patient is asked to strain in order to determine at what exact moment the prolapse occurs.
- An X-ray examination of the intestine is also carried out.
- Be sure to carry out retro-manoscopy and colonoscopy. With the help of special equipment, a specialist can carefully examine the mucous membrane of the colon, detect damage and neoplasms. If necessary, the doctor performs a biopsy during the examination - tissue samples are then sent for laboratory analysis.
- A procedure such as anorectal manometry helps to assess the degree of functioning of the anal sphincter.
- Women with a similar problem are also sent for a gynecological examination.
Conservative therapy
How to treat rectal prolapse? Only a doctor can answer this question. Here a lot depends on the degree and stage of development of the pathology.
- The rectum can be set, but this is only a temporary measure. In the future, doctors recommend excluding contact with risk factors. It is important, for example, to avoid certain types of physical activity. Doctors prescribe laxatives to patients to help prevent constipation. It is worth abandoning non-traditional sexual contacts.
- The muscles of the perineum nevertheless need to be strengthened, so patients are recommended special therapeutic exercises. The exercises are very simple, but you need to remember that repeating them is worth daily. Physiotherapists recommend alternately straining the muscles of the anal sphincter and perineum. Raising the pelvis while lying on the floor is also an effective exercise.
- Various physiotherapy procedures are also recommended for patients. For example, the pelvic floor muscles are stimulated by electric current, which improves their tone. A properly performed rectal massage improves blood circulation, strengthens the muscles and has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the intestines.
It is worth saying right away that such treatment is possible only in the initial stages and only if the patient suffers from a mild degree of prolapse no longer than three years. Otherwise, all of the above methods will not give the desired result.
Rectal prolapse: surgical treatment
Immediately it is worth saying that surgery is by far the only truly effective method of therapy. To date, there are many procedures that help eliminate a rectal defect.
For example, resection of the prolapsed portion of the rectum, plastic of the anal sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, “suspension” of the distal part of the intestine, etc. is possible. In most cases, combined operations are performed during which the affected part of the organ is removed, after which plastic correction is performed to preserve the main functions of the intestine. Surgery is generally well tolerated by patients. Massive resection is required only with gangrene.
Operations can be performed laparoscopically, as well as through an incision in the abdominal wall or perineum - it all depends on the degree of complexity of the procedure, the presence of certain complications.
What can alternative medicine offer?
Many patients are interested in questions about whether treatment of rectal prolapse is possible at home. Of course, folk healers offer a lot of recipes. But it is worthwhile to understand that all homemade products are intended only to eliminate the main symptoms and prevent complications. Decoctions and infusions of plant herbs will not help to eliminate the existing loss.
- Effective are herbal, sedentary baths. To prepare a decoction, you will need to mix 50 g of sage, meadowsweet and knotweed. Mix all the ingredients and pour a liter of boiling water. After the infusion has cooled, it can be filtered and added to the bath water. The procedure is preferably carried out daily. The medicine helps relieve swelling and inflammation of the mucous membrane, get rid of itching and discomfort.
- Fresh quince juice has healing properties. In it, you need to moisten a clean napkin and apply it for 10-15 minutes to the anus. It is believed that this procedure helps to cope with pain.
- Anti-inflammatory properties also have calamus root. A tablespoon (incomplete) of crushed, dried roots should be poured with a glass of cold water. The tool is insisted for 12 hours, after which it is heated (without bringing to a boil) and filtered. It is recommended to drink 2-3 tablespoons of the medicine after eating.
- Chamomile helps to cope with pain and swelling. Her broth is often added to sedentary baths. In addition, pore treatments are also effective. Hot broth should be poured into a wide container and squatting over it. It should be noted that the medicine should not be too hot (steam can burn the skin) or too cold (steam should rise from the liquid).
- For sedentary baths, decoctions of their oak bark are also used.
- The tincture of their shepherd’s bag is effective (it can be prepared at home or you can buy a finished product at the pharmacy). It is necessary to periodically treat the area of the anus with liquid - this helps to get rid of discomfort, relieve inflammation and prevent secondary infection.
Of course, before starting therapy at home, you need to consult a doctor. The use of herbal medicines is not at all a reason for refusing full-fledged conservative therapy and surgical intervention.
Predictions for Patients
It is immediately worth noting that only surgical treatment of rectal prolapse is truly effective. A correctly performed operation allows you to restore the function of the colon by at least 75%. The likelihood of relapse is small, especially if the patient follows medical advice (we are talking about the right diet, timely treatment of constipation and diarrhea, etc.).
Prevention
The development of such a disease can be prevented. Prevention of prolapse of the rectum includes the following measures:
- regular physical therapy exercises, in particular, the implementation of exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the anus and perineum;
- timely treatment of chronic constipation and respiratory system diseases, which are accompanied by severe cough;
- following a proper diet (diet should include foods rich in fiber);
- proper drinking regimen (at least 2 liters of water per day).
When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor. The sooner a problem is detected, the faster adequate treatment begins, the lower the likelihood of complications.