With a disease such as angina, many are familiar. This ailment is quite common among patients of all ages. However, most often a similar pathology occurs in people under 25-30 years old. Almost 60% of all patients are children. In them, as in adults, the disease, which is an infectious process that develops in the tonsils, can take dangerous forms and can sometimes be reflected in serious complications. In this regard, the paramount task in the event of symptoms of the disease, also known in medicine under the name "acute tonsillitis", is its correct diagnosis, as well as effective treatment.
Definition and ways of infection
The word "sore throat" came to us from the Latin language, where it means "squeezing", "squeezing". However, such a name cannot be considered accurate. The fact is that the symptoms of angina are not always accompanied by such phenomena. Another thing is a medical term. The name "acute tonsillitis" comes from the word tonsilae, which means tonsils. All this is more suitable for angina, which is an acute infectious disease characterized by inflammatory processes, usually palatine, and in some cases - nasopharyngeal and lingual tonsils.
The causative agents of acute tonsillitis are microbes. Most often they are represented by streptococci, less often staphylococci or pneumococci.
Often, microbes are in the throat or in the oral cavity before the onset of the disease. However, until a certain time they are passive. Pathogenic microorganisms are activated under the influence of some external factors, among which there may be hypothermia or a sharp temperature drop. For some people, in order to get a sore throat, it is enough to eat ice cream, soak their feet or swim in a pond.
The infection, which is the cause of the development of symptoms of angina, can be introduced into the body and from the outside. Sometimes its sources are teeth affected by caries. Various irritating substances that systematically enter the throat can also contribute to the development of the ailment. It can be dust, including household dust, smoke, alcohol and so on. Sometimes the development of symptoms of angina occurs due to the presence of adenoids or other ailments of the nasopharynx, the result of which is a violation of nasal breathing. It provokes pathology and malnutrition, as well as violations in the diet. Most often people with sore throat who live in areas with an unfavorable environmental situation. The cause of the development of the disease is a strong overwork and a decrease in the reactivity and sensitization of the body.
How does pathogenic microflora enter the oral cavity or nasopharynx? The following ways of its penetration are distinguished:
- Airborne. As a rule, bacteria with angina enter the body in this way.
- Hematogenous. Sometimes microorganisms penetrate the pharynx with a blood stream from infectious foci already in the patient's body.
- Enteral. In this case, pathogenic bacteria enter the human body along with food, usually dairy.
- Endogenous. Often, angina affects people suffering from carious lesions of the teeth, purulent sinusitis, gastroenteritis and other pathologies.
- Artificial. Sometimes acute tonsillitis infection occurs during surgical interventions on the nasopharynx and in the nasal cavity. In such cases, tonsillitis is called traumatic.
Main symptoms
The signs of a sore throat may be different. As a rule, they are determined by the type of pathogenic microorganism - the causative agent of the disease, as well as the degree of damage that is characteristic of the tonsils affected by the pathology. Doctors divide the symptoms of angina into general and local. As a rule, a sore throat indicates the onset of the development of the disease. This is a local symptom that is common to all forms of this infectious disease. Such pain is very sharp and severe. When swallowing, it intensifies. In addition, sore throat is often accompanied by inflammation of the upper cervical lymph nodes, which is also called regional lymphadenitis.
Common symptoms of tonsillitis (see photo below) are related to the fact that toxic waste products of microbes, as well as biologically active substances begin to accumulate in large quantities in the focus of inflammation and negatively affect the body. A person rises in temperature.
It reaches a value of 38-40 degrees and is accompanied by chills. Against this background, overall health worsens. Headache begins to bother. There is great weakness. Sometimes pain symptoms appear in the joints, muscles and in the region of the heart.
Angina is accompanied by acute pharyngitis. This pathology is manifested by sore and dry throat, as well as pain when swallowing (especially saliva). In this case, a feeling of discomfort often gives to ears.
The classic symptoms of angina in adults and in children, which is caused by streptococcus, are characterized by a sudden onset of intoxication, a rapid increase in temperature, accompanied by chills. In this case, intense pain occurs in the throat and an increase in lymph nodes in the neck with the appearance of purulent formations or white plaque on them. Angina in children (symptoms and photos - below) may begin with several other symptoms. Young patients suffer from vomiting, nausea, and abdominal pain.
The above, as well as many other signs of the disease are characteristic of its other species.
It should be borne in mind that the symptoms of angina and treatment (a photo of a doctor’s examination are presented below) are moments that are necessarily discussed with a professional. The fact is that it is precisely by the signs of pathology that the specialist, as a rule, determines the characteristics of therapy. The first of them begin to show themselves after passing the incubation period, which lasts from 10 hours to 3 days.
Knowing the symptoms of the disease (sore throat), even at its first manifestations it is necessary to consult a specialist - therapist, infectious disease specialist or otolaryngologist. The doctor, after listening to the patient’s complaints and conducting an initial examination, will send him to take urine and blood tests. Laboratory studies are performed to confirm or refute the diagnosis of acute tonsillitis.
It is worth noting that if the symptoms of angina in an adult (photos are presented in the article) in the form of a sore throat do not bother him, this does not mean that the person is completely healthy. Acute tonsillitis can affect not only the tonsils, but also the tissues of the larynx. Severe or acute tonsillitis lasts, as a rule, about a week. A complete clinical picture can only be obtained after additional analyzes, for example, pharyngoscopy. Their results will verify the correctness of the chosen course of therapy.
Types of sore throat
When conducting a diagnosis of the type of acute tonsillitis, one of the important points is the determination of the pathogen that caused the disease. The course of treatment will depend on whether an infectious pathology is caused by a bacterium or a virus. There are a number of signs indicating the bacterial nature of tonsillitis. Among them:
- light plaque on the tonsils;
- soreness and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- lack of cough;
- body temperature over 38 degrees.
Such symptoms (signs and treatment of tonsillitis see in the article) most often occur not in adults, but in adolescents.
If during the development of the disease three of its manifestations coincide, then the probability of the bacterial nature of the disease is 50%. In the presence of one or two points of symptoms, the inflammatory process is most likely caused by non-bacterial microorganisms.
Angina has its own classification, delimiting pathology in intensity and its nature. So, there are four of its varieties: catarrhal and lacunar, follicular and necrotic. Let's consider them in more detail.
Catarrhal sore throat
This type of infectious tonsillitis is its mildest form. It is a primary inflammatory process that is associated with a lesion of the lymphoid ring located in the pharynx. If the disease proceeds in a favorable direction, then the patient will recover after 5-7 days. With reduced protective forces of the body and untimely treatment with antibiotics, a person begins to develop purulent inflammation, accompanied by damage to the gaps and follicles.
Doctors distinguish between primary angina, which is manifested by catarrhal changes, as well as secondary, which occurs in the case of acute infections (herpes, measles, scarlet fever, mononucleosis, etc.). Outbreaks of acute tonsillitis of this type are observed, as a rule, in the autumn and winter. Moreover, children and people under the age of 30-40 years are most often patients.
Causes of catarrhal sore throat
The main factor causing the occurrence of those pathological changes that develop in the tonsils is a viral or bacterial infection. The first of these is represented by enteroviruses and adenoviruses, which infect children under 5 years of age in the epidemic period. Adolescents and adults with the disease overtake in connection with the penetration of influenza viruses, parainfluenza and herpes.
Beta hemolytic group A streptococci often become bacterial pathogens. Adolescents and adults suffer from catarrhal sore throat due to the penetration of other types of staphylococci and streptococci into their body. Less commonly, the causative agents of such an infectious disease are pneumococci, meningococci, influenza bacillus, and moraxella catarralis.
The main route of infection is airborne. But at the same time, sometimes the transmission of infection occurs when using objects on which pathogens have settled. The development of acute tonsillitis, as a rule, occurs against a background of decreased immunity, hypothermia, as well as chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx.
Signs of catarrhal sore throat
What development is typical for this type of disease? The first symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis are expressed by the predominance of local manifestations. An acute form is characteristic of the onset of pathology. At the same time, a tickle appears in the throat, and when swallowing a person feels obvious discomfort. What are the symptoms of angina in children and adults? With a temperature rising to 37-38 degrees, with a feeling of lethargy and weakness, as well as a slight chill, this type of ailment is associated. Examining the pharynx, one can observe isolated foci of redness of the tonsils. Purulent contents in them are absent. Another symptom of catarrhal sore throat is swollen lymph nodes. At the same time, their soreness is noted.
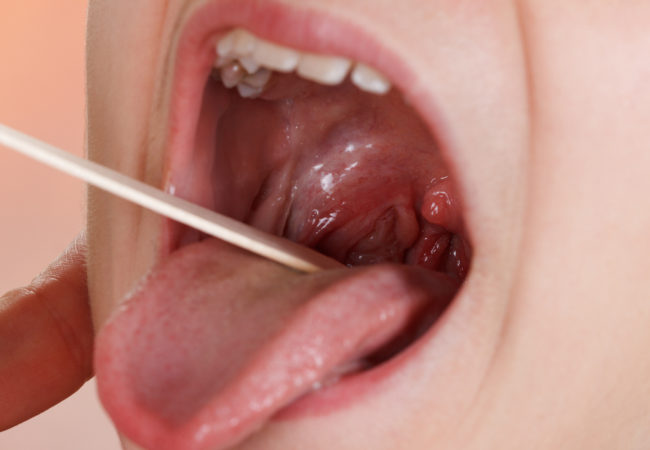
If the symptoms of catarrhal sore throat are detected in a timely manner, its treatment will be started on time. This will allow the patient to conduct etiotropic therapy and prevent the pathology from transitioning to the following, more dangerous clinical forms.
In the case of a favorable course of angina, its symptoms will disappear within a short period. It will be from 3 to 5 days. With a late visit to the doctor, ignoring the symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis, treatment cannot be started in a timely manner. In this case, the development of various complications in the form of the occurrence of chronic tonsillitis is possible. The result of late and ineffective treatment of catarrhal sore throat are endocarditis and myocarditis. Sometimes, as a complication of the disease, glomerulonephritis occurs.
Diagnosis of catarrhal tonsillitis
With this type of tonsillitis, the symptoms in adults and children are similar to a large number of other throat diseases or infectious pathologies. That is why, even when the first signs appear, the pathology needs a thorough diagnosis, which should be carried out by specialist doctors (pediatricians and therapists, otolaryngologists and infectious disease specialists). At the same time held:
- Physical examination. It is carried out using pharyngoscopy, during which the presence of swelling of the tonsils and their increase in size, diffuse hyperemia and the edges of the arches are detected. There is no purulent content in the gaps and on their surface. There are also no accompanying signs of inflammation on the back of the pharynx. In some cases, such an examination reveals hypertrophy of regional lymph nodes, the area of which is characterized by soreness.
- Laboratory research. In order to identify an etiological agent, the doctor prescribes virological or bacteriological tests, for example, a throat swab. How active is the degree of inflammation, it will be possible to determine general clinical blood and urine tests.
Therapy for catarrhal tonsillitis
After detecting symptoms of a sore throat, treatment should be initiated accordingly. It consists in eliminating the existing pathogen of infection, as well as in the speedy elimination of the activity of foci of inflammation and the prevention of possible complications.
In cases where bacterial tonsillitis symptoms are detected, treatment is usually prescribed with penicillin antibiotics. Viral tonsillitis is eliminated by antiviral drugs. In this case, the appointment of medications is anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, as well as general strengthening effect and vitamins.
With such symptoms of a sore throat, local treatment is used. In this case, antiseptics are used, with which the patient must gargle. Means are also prescribed to eliminate or reduce discomfort, such as lozenges and aerosols.
If symptoms of angina are found, treatment in both adults and children with catarrhal diseases is usually carried out at home with bed rest and with maximum restriction of physical activity. On average, the duration of the pathology is from 4 to 6 days. If complications begin to join the disease, then the patient is sent to the otolaryngology department, including glucocorticosteroid homones, as well as drugs to maintain respiratory, heart, central nervous system and kidney function. In the event of symptoms of purulent tonsillitis, when inflammatory processes affect the surrounding tissue, the patient is shown surgery to open a paratonsillar abscess.
Follicular tonsillitis
This type of acute tonsillitis is understood as an infectious disease, an obvious sign of which is inflammation of the tonsils. Such a sore throat occurs due to the penetration of various types of microbes into the body and spreads by airborne droplets, as well as in contact with unwashed foods or dirty dishes.
As a rule, the causative agents of the follicular form of the disease are staphylococci and streptococci. Factors contributing to the development of pathology are weakened immunity and hypothermia. If symptoms of angina are detected, treatment should be started in a timely manner. In addition, it should be borne in mind that the follicular form of the disease is acutely infectious. That is why a patient who is at home will need a separate room, and he should use only personal items.
The considered type of angina is characterized by the presence of inflammatory processes localized in the follicles of the tonsils, where pus formation occurs. Its foci are visible through the mucous membrane in the form of spots of yellow-white color.
Symptoms of purulent sore throat change over time. The foci of inflammation gradually merge with each other. As a result, purulent plaque forms on the tonsils. It is painted yellow-white. Such ulcers are able to melt the tissue, breaking into the throat.
Follicular sore throat has its own symptoms, manifested at the end of the incubation period, which usually lasts no more than one day. Unlike catarrhal tonsillitis, this disease is distinguished by the presence of purulent processes that cause a more serious condition of the patient.
What are the symptoms of follicular tonsillitis? Among them are the following:
- temperature rising to 39-40 degrees;
- chills;
- aches in the joints and lower back;
- weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- swollen and tender lymph nodes;
- inflammation and redness of the tonsils, as well as the areas around them;
- sharp and severe sore throat, which makes it difficult to swallow;
- sometimes a severe runny nose, which does not allow breathing freely through the nose and mouth.
In children, follicular tonsillitis, as a rule, begins with severe malaise. First of all, the child complains of a sore throat. The most common symptoms of viral tonsillitis (treatment in this case should be prescribed accordingly) are aching joints and headache, nausea up to vomiting, and inability to swallow food. Similar symptoms occur against the background of chills and profuse fever, lasting about two hours. After this, the child has a state of improvement. .
. . , , , , .
. , , . , . . , .
. , .
Most often with follicular tonsillitis, protected penicillins are used. With intolerance to such antibiotics, they are replaced with 2nd generation cephalosporins. The dosage is individually prescribed by the doctor, based on the age of the patient and the severity of the disease. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory sprays will help reduce irritation. They relieve pain, making swallowing easier. Various resorption tablets may also be used. Also, a person should spend more time alone. The patient is recommended frequent and plentiful warm drink and gargle.
Lacunar angina
What is the difference between this form of tonsillitis? A similar clinical form got its name due to the fact that the inflammatory process is localized in the gaps of the tonsils of the palate. This is the main difference between this pathology and follicular. In this case, only some follicles begin to become inflamed, which look like small pustules that are located on the surface of the lymph nodes.
Lacunar angina begins to manifest its symptoms after an incubation period of 1 to 2 days. In the future, its symptoms develop so rapidly that they sometimes begin to disturb a person in just a couple of hours. Symptoms of angina in adults with a temperature of up to 38.5-40 degrees are manifested and include in your list:
- general manifestations of the infectious process in the form of a headache, fatigue, malaise and weakness;
- periodic chills (most often they are observed in children);
- severe sore throat;
- an increase in lymph submandibular nodes;
- joint pain.
The inflammatory process can be observed on one or two tonsils. The duration of the disease is 5-9 days. In children, the course of lacunar angina is more severe. Young patients suffer from asthma attacks, abdominal pain, vomiting and nausea, as well as diarrhea.
With the further spread of infection, the patient's condition worsens. Sometimes bronchitis or pneumonia joins a sore throat. With incorrect treatment, a chronic form of tonsillitis appears. In addition, bacteria spread throughout the body, settling in the bones, lungs and heart. The consequences of this disease are very dangerous and threaten kidney inflammation, arthritis, rheumatism, myocarditis, sepsis, lymph nodes and meningitis.
In the treatment of this type of sore throat, antibiotics are also used. If symptoms of a sore throat occur without fever, then such funds are enough. Otherwise, it is recommended to take antipyretic drugs. It is very important for the patient to gargle with antiseptic solutions. Such a procedure is especially relevant in the first two days of illness. To eliminate dehydration, attention should also be paid to heavy drinking.
Necrotic tonsillitis
This form of pathology is extremely rare and is also characterized by inflammatory processes on the tonsils. The key difference between necrotic tonsillitis from other types is the destruction of the diseased surface. As a rule, in this case, the child and the adult have symptoms of tonsillitis without fever. The patient's condition remains almost the same, in addition to the formation of a white coating of dense consistency.
Symptoms of a sore throat without fever should be recognized as early as possible. This will allow timely treatment of the disease, which is considered very contagious.
Necrotic tonsillitis is practically not found in children. This is due to the lack of teeth in babies, which are a common cause of throat infection. However, as a child grows up, the risk of such an ailment increases significantly. If a pathology occurs, the baby feels a sore throat with a violation of the swallowing reflex. In rare cases, body temperature may rise. Tonsils of the baby are covered with a dense white coating.
Symptoms of angina in an adult without fever are accompanied by such signs:
- sharp pain in the throat;
- the formation on the tonsils of a gray-yellow plaque;
- discomfort while swallowing.
There are secondary signs of pathology. These include:
- serious intoxication;
- increased salivation;
- bad breath from the oral cavity;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- redness of the tonsils.
In case of timely detection of the disease and effective therapy, necrotic tonsillitis passes without any complications. Tonsils after recovery fully restore their functions.
The treatment tactics are selected by the doctor. As a rule, it consists in performing several times a day procedures involving the lubrication of the tonsils with a solution of furatsilina, hydrogen peroxide or potassium permanganate. In addition, necrotic tonsillitis requires the use of antibiotics. In especially difficult cases, they must be injected.