Elderly people often have to deal with a disease such as intestinal thrombosis. Their further condition directly depends on how quickly they get to the hospital and the doctor prescribes individual treatment. In order not to miss precious time, everyone should know about the primary symptoms of this ailment and subsequently take all necessary measures.
What you should know about the disease?
Blood, as you know, has the property of clotting. In medicine, this process is called coagulation. This is a very important function, without which any person after receiving wounds would lose all the blood and, accordingly, die. On the other hand, coagulation promotes the formation of clots over time, which are otherwise referred to as blood clots. According to experts, they can form in absolutely any part of the body. For example, getting into the intestinal artery, blood clots sequentially clog its lumen, thereby interfering with normal nutrition of a certain part of the organ. As a result, tissue necrosis in the gut is observed. This disease is called intestinal thrombosis (mesenteric). In especially serious cases, it can be fatal.
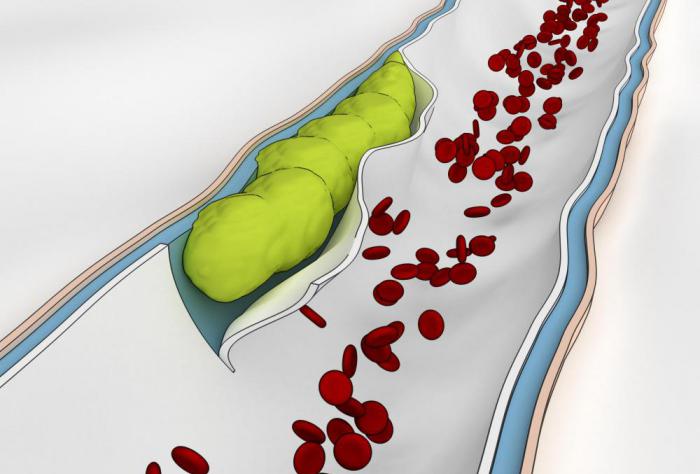
Mesenteric thrombosis of the intestine is a disease that occurs due to impaired patency of the superior, celiac, or inferior mesenteric artery. This pathology often becomes the cause of changes in blood circulation in the digestive tract. According to experts, such an ailment is equally common among women and men, but it is especially common in older people.
Etiology
Unfortunately, today absolutely no one is immune from this disease. However, doctors call a number of predisposing factors, which mainly provoke the development of such a pathology as intestinal thrombosis. The reasons may be as follows:
- Atherosclerosis (a vascular disease characterized by the sequential formation of plaques, upon rupture of which blood clots form).
- Myocardial infarction.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Thrombophlebitis (an inflammatory process localized in the veins on the legs and accompanied by stagnation of blood).
- Endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, contributing to the appearance of blood clots).
- Sepsis (blood poisoning).
- Rheumatism (a disease that affects the connective tissue, as a result of which heart disease develops).
- Postpartum thrombosis.
Often, for example, small bowel thrombosis develops immediately after surgical manipulations on other organs. However, in this case, the patient is more likely to survive, since for some time after the operation he is under close supervision by doctors. In such situations, the specialist immediately makes a decision about the treatment. An anticoagulant or any other drug that dilutes a blood clot is administered.
Primary clinical signs
Experts say that in the initial stages of development it can be very difficult to diagnose intestinal thrombosis. The symptoms listed below always act as an alarm bell and should alert everyone.
- Sudden pain in the abdomen, which occurs immediately after the next meal.
- Blanching of the skin, dry mouth, perspiration.
- Nausea and vomiting, impaired stool (constipation or diarrhea).
- Flatulence.
- Low pressure.
- The presence of bleeding in the feces.
If the above symptoms appear, it is recommended to immediately seek medical help. The sooner treatment begins, the higher the chances of a successful recovery. Otherwise, the likelihood of developing complications is very high. After a blood clot blocks the lumen in the intestine, there is a violation of blood circulation in this area. As a result, intestinal infarction (spasm provoking tissue necrosis) is observed. As a result, peritonitis develops or large internal bleeding occurs in the peritoneum. In the absence of timely qualified assistance, the likelihood of death is very high.
The main stages of the disease
Specialists conditionally divide intestinal thrombosis into three stages of development:
- Intestinal ischemia. At this stage of the disease, the affected organ can still be restored. Patients are constantly accompanied by unbearable pain in the abdomen and vomiting with impurities of bile. The stool becomes loose.
- Intestinal infarction. The disease does not stand still in its development. As a result, some changes sequentially occur in the affected organ, as a result of which intoxication of the whole organism is observed. Fluid stool is replaced by constipation, now in the feces you can detect blood impurities. The pain in the abdomen becomes unbearable, the skin turns pale, and after that they become bluish.
- Peritonitis. At this stage, poisoning of the body with toxins is pronounced, disturbances in the circulatory system occur. The pain may temporarily stop, but it is replaced by a fairly strong vomiting, the chair becomes literally unpredictable. Inflammation over time only intensifies. Paralysis occurs very soon, resulting in stool retention. Hypotension and a slight increase in body temperature are noted.
Classification
Depending on whether there is a systematic restoration of blood flow after its blockage, doctors divide the further course of the disease into three types:
- Compensated (blood circulation in the intestine systematically returns to normal).
- Subcompensated (only partial recovery is observed).
- Decompensated (it is impossible to normalize blood circulation, as a result, intestinal infarction is observed).
How to independently diagnose intestinal thrombosis?
It is very important to constantly monitor the state of your body. If there is pain in the abdomen and feces with impurities of blood, you should immediately seek help from a doctor, since there is a likelihood of a disease such as intestinal thrombosis. Symptoms in each individual patient may vary. So, for some, the skin turns pale, the temperature rises to 38 degrees, hypertension appears, and then there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure. All of these clinical signs should alert. In this kind of situation, it is recommended to call an ambulance. It is important to remember that any delay can literally cost a life. If a person does not go to the hospital with these symptoms, it can be confidently stated that the ailment will result in death.
The main diagnostic methods in a medical institution
Upon admission to the hospital with suspected intestinal thrombosis, the patient is usually subjected to a detailed diagnostic examination. It implies the following procedures:
- Anamnesis and visual inspection.
- A blood test for the level of ESR and the number of leukocytes (in case of thrombosis, these indicators are too high).
- Roentgenography.
- Computed tomography (allows the most detailed study of the state of internal organs).
- Diagnostic laparoscopy (the doctor makes a puncture on the skin, after which a tube with a camera at the end will be inserted through it, the image from which is already displayed directly on the computer screen).
- Diagnostic laparotomy (performed when it is not possible to carry out laparoscopy).
- Angiography of blood vessels using a contrast medium (using this test you can check the degree of blockage of blood vessels).
- Colonoscopy
- Endoscopy
Conservative therapy
When a patient is admitted to the hospital, the doctor first evaluates at what stage of development intestinal thrombosis is. Treatment with conservative methods is usually used if the disease has not begun to progress. Here are used:
- Parenteral administration of anticoagulants, the main purpose of which is to thin the blood. The most commonly used drug is Heparin and some of its analogues.
- Injections of thrombolytics and antiplatelet agents (medicines Trental, Reopoliglyukin, Gemodez).
Despite the rather high mortality from this disease, in case of timely treatment there is a lot of chance for the patient to recover completely.
Surgical intervention
If mesenteric intestinal thrombosis is progressing, or if it was not possible to overcome the ailment with a medication, then the doctor prescribes an operation, and drug therapy acts as an additional treatment.
In the case of intestinal ischemia, the disease rarely goes away on its own, however, antibiotics are recommended as a prophylaxis to remove toxins from the body.
The operation involves the removal of damaged segments of the organ and the subsequent stitching of healthy tissues together. In some cases, shunting is additionally required. During this procedure, the specialist creates a "round" around the clogged vessel so that the blood can move on.
If intestinal vascular thrombosis occurs in an acute form, surgery is also prescribed. The doctor independently determines what exactly needs to be done (remove a blood clot, perform angioplasty, bypass surgery, etc.). These manipulations help stop the development of the disease, subsequently tissue necrosis does not appear.
Rehabilitation
After all surgical procedures, the patient, as a rule, spends some more time in the hospital. Over the next two weeks, any physical activity is contraindicated to him. Otherwise, the occurrence of a hernia can be provoked.
Doctors during rehabilitation recommend observing bed rest, if necessary, do a massage of the abdomen, gently stroking it clockwise.
It is very important to follow all recommendations from doctors. After all, only in this way can you forget about such a problem as intestinal thrombosis.
After the operation, it is equally important to adhere to a milk and vegetable diet. The diet should consist of rice porridge, fruits, low-fat boiled meat / fish, dairy products. All canned and smoked meats, alcoholic beverages, garlic and onions are prohibited. It is not recommended to drink whole milk in the first month after the operation, so as not to provoke digestive upset.
In conclusion, it should be noted that timely treatment of this disease almost always ends in complete recovery. Do not hesitate to visit a doctor and subsequent therapy.